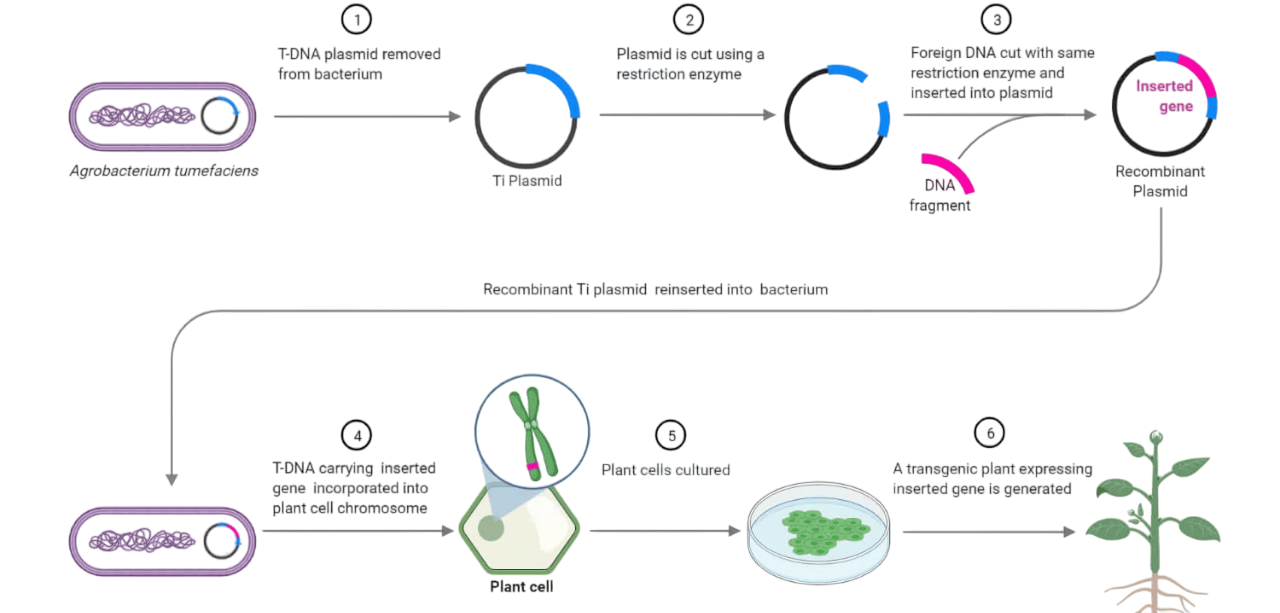
Genetic transformation techniques- Gene gun mediated, Agrobacterium mediated transformation - Overexpression, antisense expression (in model as well as crop plants)
Procedure
Media Preparation for Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer
- LB Medium – For Growing Agrobacterium This medium helps grow the Agrobacterium bacteria.
Ingredients for 1 liter:
- 5 grams yeast extract (for nutrients)
- 10 grams tryptone (a protein source)
- 5 grams sodium chloride (common salt)
- Mix everything in 1 liter of distilled water
Before use (for 50 ml):
- Add 50 µl of rifampicin (100 mg/ml stock)
- Add 50 µl of kanamycin (50 mg/ml stock) These antibiotics help select the right strain of Agrobacterium.
- MS Medium – For Seed Germination This medium is used to grow seeds into small plants.
Ingredients for 1 liter:
- 4.43 grams MS powder (contains nutrients for plant growth)
- 3 grams sucrose (sugar for energy)
- Mix in 1 liter of distilled water
- Add 2.5 grams of gellan gum (to make it gel)
- Sterilize the medium by autoclaving (heating under pressure)
- Pour 25 ml per Petri plate inside a clean laminar flow hood
- Cocultivation Medium – For Infection with Agrobacterium This medium helps plants absorb the gene from Agrobacterium.
Start with MS medium and then add:
- 750 µl of BAP (2 mg/ml) – helps promote cell division
- 500 µl of ABA (2 mg/ml) – helps in stress responses Pour 25 ml per Petri plate under sterile conditions.
- Shooting Medium – For Shoot Formation This medium helps the plant start growing new shoots (small stems/leaves).
Start with cocultivation medium, then add:
- 50 µl of kanamycin (50 mg/ml) – selects transformed cells
- 2.5 ml of carbenicillin (200 mg/ml) – kills leftover Agrobacterium
- Rooting Medium – For Root Development This medium supports root growth in the shoots.
Start with MS medium, then add:
- 50 µl of kanamycin (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of carbenicillin (200 mg/ml)
Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer Procedure
Step 1: Sterilize and Germinate the Seeds
- Clean the seeds by exposing them to chlorine gas for 1–2 hours.
- Soak the seeds in water for 2 hours at room temperature.
- Peel off the seed coat using forceps.
- Dip the seeds quickly (for 30 seconds) in 75% alcohol to kill germs.
- Rinse with a 3% sodium hypochlorite solution to make sure they're fully sterilized.
- Place the clean seeds on a growth medium in Petri dishes.
- Keep them in the dark at 28°C for 2 days so they can sprout.
Step 2: Prepare Agrobacterium (the Gene Carrier)
- Take 2 ml of LB medium (a nutrient-rich liquid) and add antibiotics like rifampicin and kanamycin.
- Add a small amount of Agrobacterium to this medium and grow it in a shaker at 28°C.
- After it's grown, spin the liquid in a centrifuge to collect the bacteria.
- Remove the liquid and wash the bacteria with MS medium (a plant-friendly liquid).
Step 3: Prepare the Explants (Cotyledons)
- Take out the germinated seeds and put them on a clean Petri dish.
- Cut off the root (radicle) and split the seed to get the two cotyledons (seed leaves).
- Clean the cotyledons and place them into a sterile beaker with MS medium.
- Mix these cotyledons gently with the Agrobacterium culture.
- Cover the beaker and place it in a vacuum chamber for a few minutes to help bacteria enter the plant tissue.
- After vacuum treatment, place the infected cotyledons on a filter paper laid over a special cocultivation medium, with the flat side facing up.
- Seal the Petri dishes and keep them in the dark at 28°C for 2 days to let the bacteria transfer the gene.
Step 4: Start Shoot Growth
- Move the cotyledons to a new medium that encourages shoot growth and contains antibiotics (kanamycin to select transformed cells and carbenicillin to kill remaining bacteria).
- Keep them under light at 25°C for 2–3 weeks.
Step 5: Regenerate the Shoots
- Once small shoots appear, gently remove them and place them on clean filter paper.
- Use a sterile scalpel to cut off the shoot tips and remove the embryoid (non-useful) part.
- Transfer the healthy shoot pieces into small glass jars or culture vessels with a rooting medium.
- Keep them under light at 25°C for 1–2 weeks.
- If roots don’t form, trim the leaves and ends of the shoots and put them in a fresh rooting medium.
Step 6: Move to Soil (Acclimation)
- Once roots form, loosen the lid of the culture vessels and keep them at 25°C for 3 more days.
- Take out the plantlets, wash off the gel-like medium under running water.
- Transfer them into pots with moist compost and cover with plastic bags to keep humidity high.
- Keep the pots in a growth chamber with light at 25°C for 1–2 weeks.
- When the plants are strong and healthy, remove the plastic bags and start watering normally.