Flow through orifice meter
Apparatus required :
CCL4 manometer, Hg manometer.
Procedure :
- Keep the bypass valve completely open and the main valve completely closed. Switch on the pump.
- Connect a CCL4 manometer across the orifice.
- Open the main valve and set a flow rate of water using the Rotameter.
- Note down the Rotameter reading and manometer reading after a steady state is attained.
- Increase the flow rate by opening the main valve and throttling the bypass valve suitably and repeat step 4.
- Use mercury manometer for higher flow rates.
- Take readings withCCL4 manometer as well as with Hg manometer.
- Repeat the experiment with different
.gif) ratios and with different fluids.
ratios and with different fluids.
Data :
Diameter of the pipe = d = cm
Diameter of the orifice = d0= cm
Density of CCl4 =.gif) CCL4 = kg/m3
CCL4 = kg/m3
Density of Hg =.gif) Hg = kg/m3
Hg = kg/m3
Density of fluid =.gif) = kg/m3
= kg/m3
Viscosity of fluid= .gif) = kg/m3 = cp
= kg/m3 = cp
Observations :
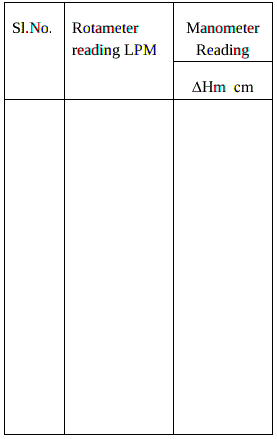 Hg = kg/m3
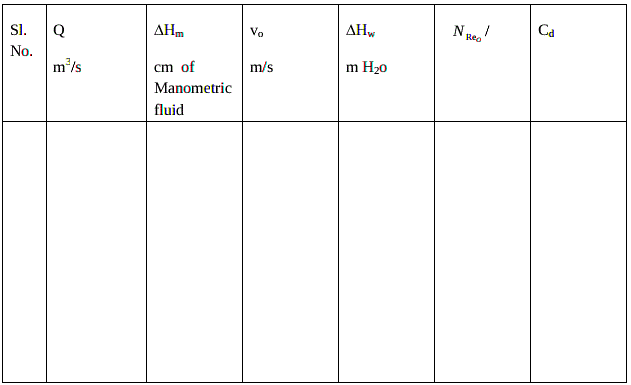
Hg = kg/m3Calculations :
Flow rate:
∆Hm = cm of manometric fluid.
Volumetric flow rate = Q = m3/s
.gif) = m of H2o
= m of H2o
.gif) =density of manometric fluid.
=density of manometric fluid.
Average velocity through the orifice = .gif) = m/s
= m/s
A0 = cross sectional areaof orifice = .gif)
Reynolds Number at the orifice = .gif) =
=
.gif) =
=
Coefficient of discharge = Cd = .gif)
Plot Q vs .gif) and Q vs
and Q vs .gif) on ordinary graph(calibration).
on ordinary graph(calibration).
Plot Cd vs NReo on a semilog graph sheet (with NReoon log scale).
Plot log Q vs log .gif) .Find the slope and the intercept. Find the coefficient and power of
.Find the slope and the intercept. Find the coefficient and power of
.gif) . Comment on the nonlinear flow head relationship. Obtain Cd from the plot.
. Comment on the nonlinear flow head relationship. Obtain Cd from the plot.
Results :
- Report on calibration
- Comment on Cd vs NReo
- Report the Cd
- Comment on flow head relationship
