To study the torque speed characterstics of three phase induction motor.
Introduction
An induction motor has several major advantages over a DC motor such as the absence of brushes and commutator segments, rugged construction, lower cost, reduced maintenance requirements, and smaller size for the same power output. Due to these advantages, induction machines have become more popular in industrial applications. For any motor load application, it is essential to understand the torque-speed characteristic of the motor.
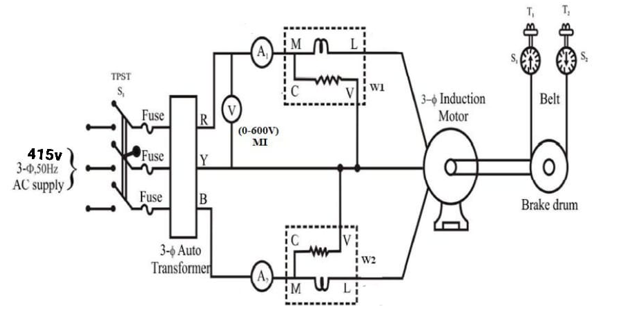
Figure 1: Three-phase Induction motor
Consider a three-phase squirrel cage induction motor whose stator has three windings displaced in space by 120°. When these windings are energised with currents that are displaced in time by 120°, a rotating magnetic field is produced, rotating at a speed called synchronous speed Ns. The synchronous speed Ns is given by
$$N_s = \frac {120f}{P}........(1)$$
where, f is the frequency and P is the number of poles. If the rotor of the induction motor rotates at a speed, Nr, then the slip, s is defined by
$$s = \frac {N_s - N_r} {N_s}........(2)$$
The torque developed by the induction motor is given by
$$\displaystyle T = \frac{3 (I_2)^2 \cdot R_2}{W_s \cdot S}$$
$$T = \frac {3}{W_s} \frac{\left(V_s\right)^2 \frac{R_2}{S}}{\left(R_1 + \frac{R_2}{S}\right)^2 + \left(X_1 + X_2\right)^2} \quad \text{.......(3)}$$
where, Ws is the synchronous speed in rpm, Vs is the voltage applied to the stator, I2, R2, X2 are the rotor current, resistance and reactance referred to stator respectively. R1, X1 are the stator resistance and reactance respectively. If equation (3) is plotted, we get the T-Nr characteristics as shown in Fig. 2. The maximum torque developed, Tm and the slip, Sm at which Tm occurs is given by.
$$T_m = \frac {3}{2 W_s} \frac{\left(V_s\right)^2}{R_1 \pm \sqrt{R_1^2 \pm \left(X_1 + X_2\right)^2}}$$
$$S_m = \frac {R_2}{\sqrt{R_2^2 + (X_1 + X_2)^2}}$$
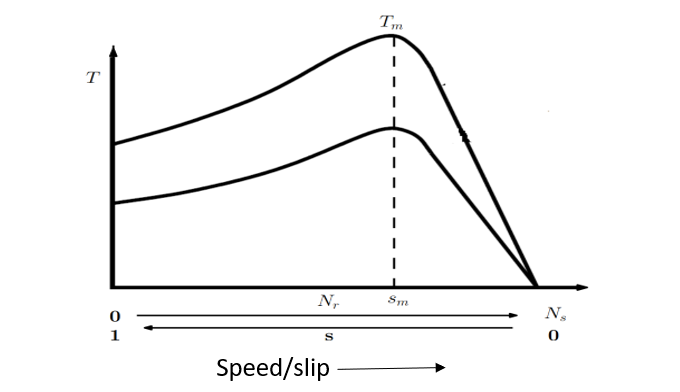
Figure 2: T-Nr characteristics of a three phase induction motor
If the voltage applied to the stator of an induction motor is varied, the developed torque will vary according to the following relation:
$$S_m \propto R_2$$
$$T \propto \left(V_s\right)^2........(4)$$
The maximum torque developed, Tm is proportional to the square of the applied voltage as in eq.(5), but Sm is independent of applied voltage. Therefore, if the T-Nr characteristics are plotted for different voltages, the resulting curves appear as shown in Fig. 3
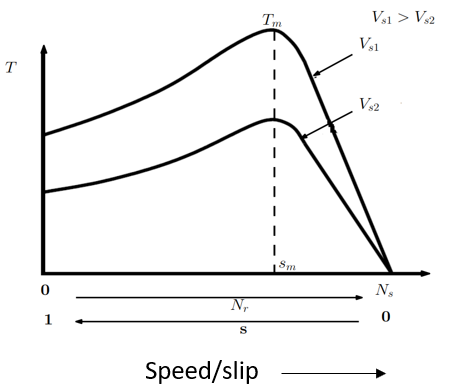
Figure 3: T-Nr characteristics of a three phase induction motor with different voltages
If the weight of the load on the rotating pully in the induction motor is W1 & W2, then the torque of the induction motor is given by
$$T = (W_1 - W_2) \cdot 9.81 \cdot r ..........(5)$$
Advantages of Three phase Induction motor
The absence of brushes eliminates sparking, allowing the motor to operate safely in hazardous environments.
The motor's operation is independent of environmental conditions due to its robust and mechanically strong design.
Induction motors are highly efficient, with full-load efficiency ranging from 85% to 97%.
Disadvantages of Three phase Induction motor
Speed control is difficult because a three-phase induction motor operates at an almost constant speed, with minimal variation over the entire loading range.
High input surge currents, known as magnetizing inrush currents, occur at startup, leading to temporary voltage drops.
