Kinetic characterization of protein-ligand binding by surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
Refer to the following sensorgram and answer the questions accordingly:
1. Which curve has the fastest dissociation rate constant (kd) out of the four?
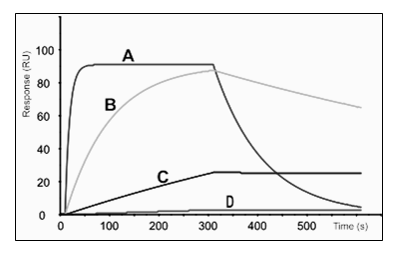
1. Which curve has the fastest dissociation rate constant (kd) out of the four?
2. Which of the curves is saturating the ligand?
3. Which of the curves have fastest association rate constant?
4. A sensorgram exhibits a rapid rise in response units upon injection of the analyte, what does this response suggests?
5. The purpose of a blank injection in an SPR experiment is to:
6. For SPR, analytes should be used in replicates to:
7. The equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) in SPR is calculated as the ratio of the dissociation rate constant (kd) to the association rate constant (ka). Mathematically, it is represented as: KD=kd/ka If ka=2.5 x 104 M-1s-1 and kd=1.0 x 10- 2 M-1, what is the KD value?
8. What functional groups on the ligand or sensor surface are often utilized for bonding in covalent immobilization?
9. In EDC/NHS covalent immobilization, what is the role of EDC (1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride)?
10. If the EDC/NHS activation step is incomplete, what is a likely outcome during ligand immobilization?
