pH-titration of amino acids and small peptides, and estimation of isoelectric point (pI)
1. Which of the following amino acids has the lowest isoelectric point?
2. Which of the following amino acids has the highest isoelectric point?
3. Sample A is a mixture of 3 polypeptide chains, polypeptide 1 (MW = 100 kDa), polypeptide 2 (MW = 200 kDa), and polypeptide 3 (MW = 400 kDa). All the peptides have their isoelectric point at pH 6. What would you see if electrophoretic separation is carried out at pH 6 for protein sample A?
4. For lysine, the pKa1 is equal to 2.18, pKa2 is equal to 8.95 and pKR is equal to 10.53. At which pH will it assume an overall neutral charge
5. Calculate the pI of the given amino acid.
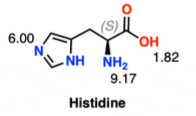
6. Which of the following amino acids cannot participate in intermolecular H-bonding due to the chemical group in its side-chain?
7. Which of the following amino acids are expected to have a net negative charge at pH 7.4?
8. During pH titration, HCl is added to glycine at the beginning of the experiment. What is the role of HCl?
9. During the titration of Gly with NaOH, the change in pH is slow before and after the inflection point. This is because,
10. Calculate the pI of the tripeptide Asp-Gly-Glu.
Hint: Firstly, find out the net charge at pH = 0, 2.5, 4, 5 and 10 respectively. Then use the pKa values corresponding to the pH at which net charge of the tripeptide is zero to calculate the pI.
Hint: Firstly, find out the net charge at pH = 0, 2.5, 4, 5 and 10 respectively. Then use the pKa values corresponding to the pH at which net charge of the tripeptide is zero to calculate the pI.

