Binomial coefficients and Pascal's triangle
Pascal's Triangle and Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorem
Binomial theorem is the algebraic theorem used to expand the term where n is a non negative integer. More formally
Where the right hand side in the theorem gives us the binomial expansion.
Binomial coefficient
Binomial coefficient is which is the coefficient part of the terms in the binomial expansion. As the binomial coefficient does not depend on the value of and , the value of binomial coefficient remains the same even though the term in binomial expansion for the corresponding and might change.
Pascal's triangle
Pascal's tringle is a figure that constitues of binomial coefficients from the binomial expansion with , starting from , increasing the further we go down and , starting from , increasing the further we go to the right . It is named after the French mathamatecian Blaise Pascal, though its origins predate him.
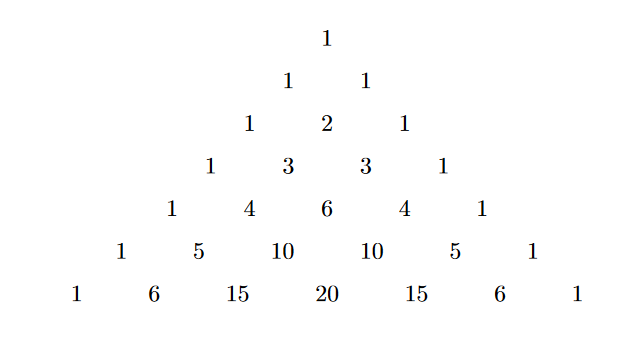
The figure above represents Pascal's triangle which itself exhibits many interesting properties. Some of these include
- Sum of the elements of any row in the triangle equals to 2^n, when n=0 for the first row.
- The first diagonal after the leftmost one represents the set of natural numbers.
- The second diagonal after the leftmost one represents the set of triangular numbers.
- the value of any element in the triangle can written as sum of the two elements above it.
