Norton's theorem
Procedure
Apparatus:
Resistors, Battery, connection wire etc..
Procedure:
- Make an electric network using specific resistors and voltage sources.
- Determine the current through the load resistance in the original circuit using an ammeter.
- Determine the equivalent Norton current INO and Norton resistance RNO.
Steps to find Norton equivalent resistance RNO and current INO:
- Calculate the output current for zero load resistance. This gives INO.
- Calculate the output voltage V for infinite load resistance (i.e., under open circuit condition).
- RNO equals V divided by INO.
An example for Norton equivalent circuit
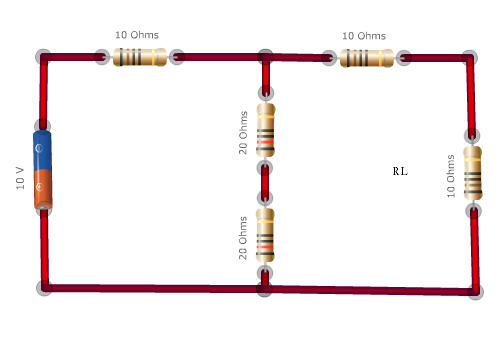
Step 1: Original circuit.
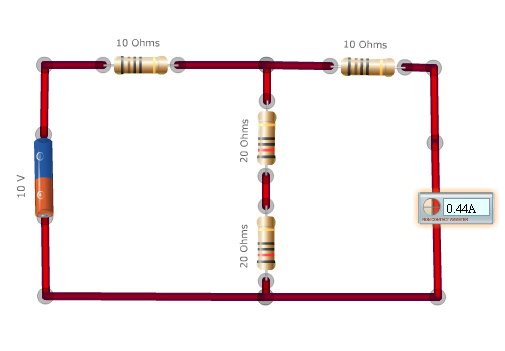
Step 2: Calculating Norton equivalent current.
Step 3: Calculating the Norton equivalent resistance.
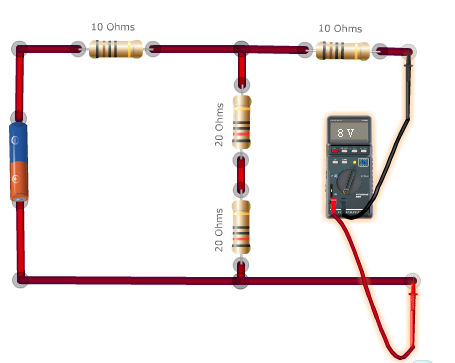
RNO = V / INO = 8 / 0.44 = 18.18 Ω
Now the Norton equivalent circuit is given by.
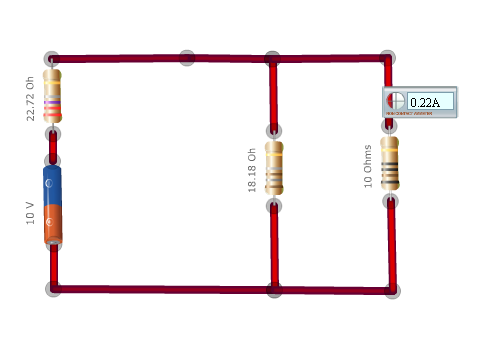
- To make a current source, connect a suitable resistance in series with a voltage source as shown in the last picture.
- Construct the Norton equivalent circuit and hence find the load current.
- Show that in both cases the load currents are equal, hence verify that Norton's theorem is correct.
Components:
- Resistor: A resistor is a two-terminal electronic component that produces a voltage across its terminals that is proportional to the electric current through it in accordance with Ohm's law.
- Lamp: A lamp is a replaceable component such as an incandescent light bulb, which is designed to produce light from electricity. These components usually have a base of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which makes an electrical connection in the socket of a light fixture.
- Wire: A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, elongated string of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate.
- Switch: In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
- Battery: A battery or voltaic cell is a combination of many electrochemical Galvanic cells of identical type to store chemical energy and to deliver higher voltage or higher current than with single cells.
- Voltmeter: A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring the electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to digital converter.
- Ammeter: An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name.
- Non-contact ammeter: A type of ammeter that need not be a part of the circuit.
