Linked List
Introduction to Doubly Linked List
A doubly linked list is a linear data structure where each node contains a data part and two pointers: one pointing to the next node and another pointing to the previous node. This allows traversal in both directions.
Structure of a Doubly Linked List Node (C Example)
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
Pictorial Representation
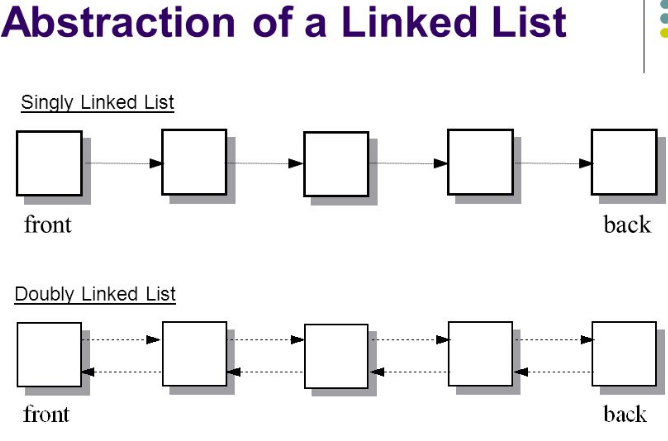
Insertion in Doubly Linked List
There are three main cases for insertion:
1. Insertion at the Beginning
- Create a new node.
- Set its
nextto the current head andprevto NULL. - If the list is not empty, set the current head's
prevto the new node. - Update head to the new node.
void insertAtHead(struct Node** head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = *head;
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
*head = newNode;
}
2. Insertion at the End
- Create a new node.
- Traverse to the last node.
- Set the last node's
nextto the new node and new node'sprevto the last node. - Set new node's
nextto NULL.
3. Insertion After a Given Node
- Create a new node.
- Set its
nextto the next of the given node andprevto the given node. - Update the next node's
prev(if not NULL) to the new node. - Update the given node's
nextto the new node.
Deletion in Doubly Linked List
There are three main cases for deletion:
1. Deletion of the Head Node
- Update head to the next node.
- Set new head's
prevto NULL (if not NULL). - Free the old head node.
2. Deletion of the Last Node
- Traverse to the last node.
- Set the previous node's
nextto NULL. - Free the last node.
3. Deletion of a Middle Node
- Update the
nextof the previous node and theprevof the next node to bypass the node to be deleted. - Free the node.
Advantages of Doubly Linked List
- Can be traversed in both directions.
- Easier to delete a given node if a pointer to the node is given.
Disadvantages
- Requires extra memory for the previous pointer.
- More complex insertion and deletion logic compared to singly linked lists.
Applications
- Navigation systems (forward/backward)
- Undo/Redo functionality in editors
- Implementation of various data structures (e.g., deque, browser history)
