Performance Characteristics of Kaplan Turbine
1. Introduction :
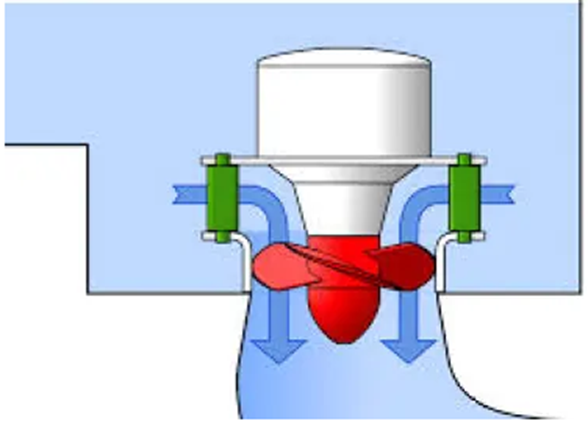
Fig. 1: Front view of Kaplan turbine model
Kaplan turbine also known as Propeller turbine by virtue of its propeller blades used in the setup. Kaplan turbine was invented by an Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan in 1913. Kaplan Turbine working principle is that of axial flow reaction, it is also categorized under reaction turbine since it operates in a closed conduit from head race to tail race. In axial flow turbines, the water flows through the runner along the direction parallel to the axis of rotation of the runner. At inlet, the water possesses both kinetic energy as well as pressure energy for effective rotation the blades. Kaplan turbine can work at low head and high flow rates very efficiently which is impossible with Francis turbine.
2. Parts of a Kaplan Turbine :
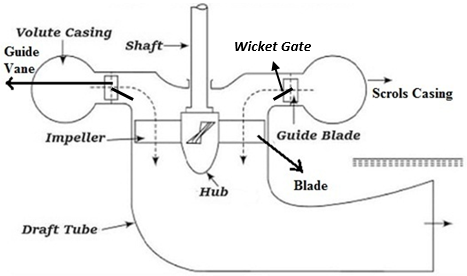
Fig. 2: Parts of Kaplan Turbine
2.1 Penstock
It is a large size conduit which conveys water from the upstream of dam/reservoir to the turbine blade
2.2 Spiral/ Scroll Casing
The complete turbine can be covered with a casing with a gradually decreasing cross sectional area along the flow direction. The maximum area is at the junction where penstock delivers the water into the volute/scroll.
Essentially, the casing of the turbine avoids the critical parts like impeller blades, guide vanes, a runner from damages because of external load.
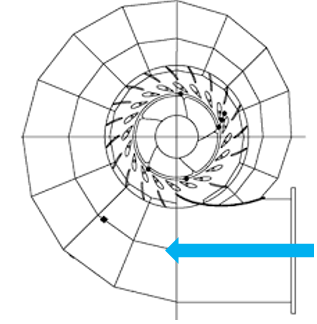
Fig. 3: Scroll Casing of Kaplan turbine
2.3 Guide Blades/ Wicket Gates
It is the only controlling part of the whole turbine, which opens and closes depending upon the demand of power requirement. In case of more power output requirements, it opens wider to allow more water to hit the blades of the rotor and when low power output requires it closes itself to cease the flow of water. If guide vanes are absent then the turbine cannot work efficiently henceforth its efficiency would decrease.
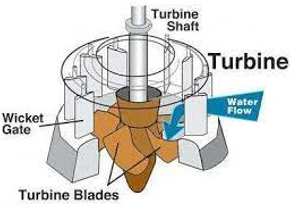
Fig. 4: Wicket Gates of Kaplan turbine
2.4 Governing Mechanism
Governing mechanism is used to change the position of the wicket gates to affect in change in water flow rate, depending on the load conditions requirement.
2.5 Runner and Runner Blade
The heart of a Kaplan turbine is the runner blade, it is the rotating part which help in generating electricity. The runner blade shaft is connected to the shaft of the generator which rotates the generator rotor to produce electricity. The turbine runner consists of a large hub on which its blades are attached which can be adjustable to an optimum angle of attack for maximum power output according to load demand and flow rates. The runner blades have twist along its length in order to have always optimum angle of attack for all cross section of blades to achieve maximum efficiency.
2.6 Draft Tube
The pressure at the exit of the runner of Reaction Turbine is generally less than atmospheric pressure. The water at exit cannot be directly discharged to the tail race. A tube or pipe of gradually increasing area is used for discharging water from the exit of turbine to the tail race. This tube of increasing area is called Draft Tube. One end of the tube is connected to the outlet of runner while the other end is sub-merged below the level of water in the tail-race.
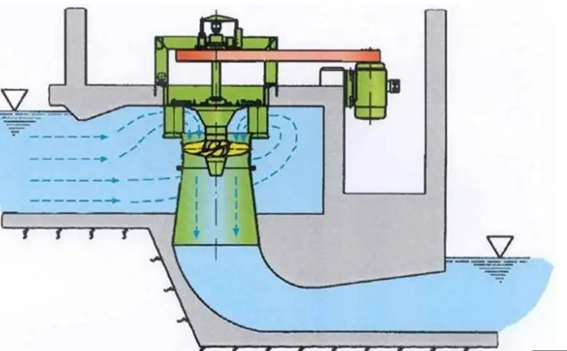
Fig. 5: Draft Tube of Kaplan turbine
3. Working of Kaplan Turbine
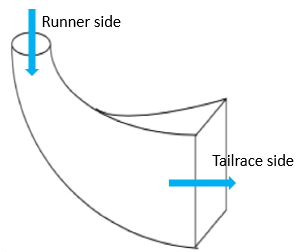
Fig. 6: Schematic working model of Kaplan turbine
The water released from the Penstock enters the scroll casing which has such a shape that the required flow pressure is not lost. Through guide vanes water is directed to the runner blades. Since the vanes can be adjusted through governor mechanism, henceforth vanes adjust itself according to the flow rate. The water takes a 90 degree turn, so the direction of the water is axial to that of runner blades. When the water strikes the runner blades, the turbine starts to rotate due to the reaction force of the water. Twist is provided along the span of the runner blade in order to maintain optimum angle of attack at all cross section of blades in order to achieve higher efficiency. The water enters into the draft tube as it leaves the runner blades where its pressure energy and kinetic energy reduces i.e. Kinetic energy gets converted into pressure energy resulting in increased pressure of the water. Since shaft of the turbine and that of the generator are interconnected, hence rotation of turbine rotates the generator shaft hence producing electricity.
4. Advantages of Kaplan Turbine
The advantages of the Kaplan turbine include the following.
• It works at low head
• It has fewer blades which are adjustable too.
• It occupies less space and has simple construction.
• Very high efficiency as compared to other turbines.
• Applicable for high discharge-based applications.
5. Disadvantages of Kaplan Turbine
The disadvantages of the Kaplan turbine include the following.
• Due to pressure drop within the draft tube, Cavitation can occur.
• Works at only high flow rates.
• Runner blades need constant maintenance due to cavitation.
