Hall-Effect : Determination of carrier concentration
If a metal or a semiconductor carrying a current I is placed in transverse magnetic field B, Potential difference VH is produced in a direction normal to both the magnetic field and current directions. This is known as HALL EFFECT.
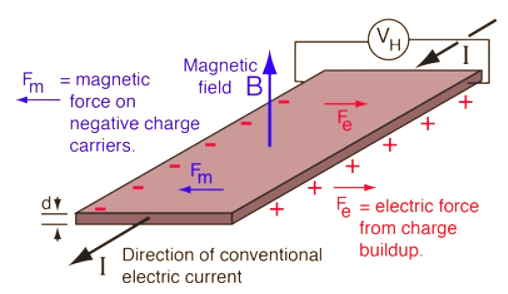
Let a semiconductor sample of thickness t and area of cross section A, carrying a current I be acted upon by a transverse magnetic field B. The magnetic field tends to deflect charge carriers in the sample towards one of its faces leading to an accumulation of charges there. This in turn produces an electric field EH in a direction which opposes the Lorentz force due to the magnetic field. The electric field builts till it exactly compensated for the effect of magnetic field. The potential difference VH arising due to EH is given by
VH = BI/net
Where n- carrier concentration , e- charge of an electron and t- thickness of the sample. The ration 1/ne is known as the Hall Coefficient (RH)
RH= (VHt)/BI
Knowing the Hall coefficient, the concentration of charge carrier in the sample can be determined by
n= BI/VHet
Due to difference in the velocity of the carriers, a correction factor is applied to the formula for the concentration. So, the final formula is
n=(3⫪/8)(BI/etVH)
