Cyclic codes
1. Choose the correct option for a cyclic code of length , dimension , and generator polynomial
2. Consider two polynomial and in . What will be ?
3. Consider two polynomial and in . What will be the quotient () and remainder () when divided by ?
4. Consider the shift register based encoder for a cyclic code given in Figure 7. What will be the contents of the shift registers at the next time instant? 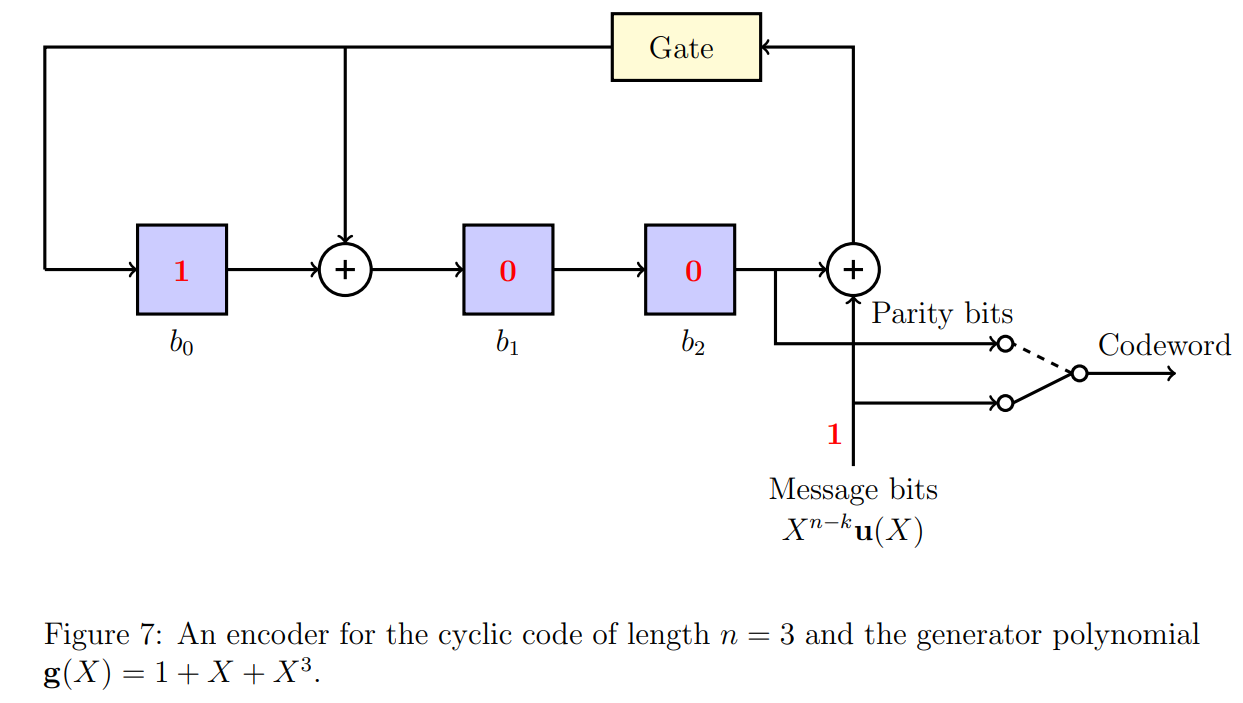

5. Consider cyclic code generated by . Suppose the syndrome of a received vector . Then, the syndrome of the vector is
6. Consider the Meggitt decoder of cyclic code generated by . If the error location is , then after how many shifts the error bit is corrected once the syndrome is formed in the syndrome register?
