Representation of components of Optical microscope and working principle using Virtual Reality
Microscope is the fundamental equipment based on principles of optics to observe the microstructure of a material. As optical wavelengths are utilized to image the polished surface, variations arising due to material processing, heat-treatment, mechanical damage, and service-related aberrations can be captured to quantify the features and compare two material with respect to that of a reference/ideal material. Microscope is a basic tool of observation for metallurgists and materials scientists. Microscope mainly comprises of various part that include:
(i) light source (illuminator) to illuminate and brighten the field of view
(ii) condenser lens to concentrate light from its source on to the object
(iii) objective lens to focus and magnify the features of the sample (and located close to the sample to be observed)
(iv) an eyepiece / ocular (for viewing the image, located close to eye) to enlarge the image formed by the objective lens.
(v) diopter provide adjustment on eyepiece to allow correct the vision on the eyepiece
(vi) stage on which the specimen is kept for viewing
(vii) base on which the microscope is supported
(viii) focus knobs (coarse- and fine-focus knobs) through which the microstructural features are brought to focus for viewing
(ix) diaphragm / iris is a rotating disc that has varied opening sizes permitting to control
(i) aperture diaphragm controls the diameter of light and vary the light intensity as well, and (ii) field diaphragm controls the view of field
(x) camera captures the view/image via arrangement of split mirror
(xi) turret/ revolving nosepiece permits changing the magnification among placed objective lenses
(xii) stage clips permit holding the specimen on the sample stage
(xiii) Arm joins the base of microscope to the body tube
Virtual Reality tool permits observing the exploded view in 3-D rendering to observe how the illuminator source provides the light, and how the mirrors direct the travel of light, and how condenser lens brightens the field of view to either go through the sample (biological) or fall on the optically flat sample (opaque/ metallurgical sample) to be picked up by the objective lens to collect and magnify (say -100×) the features, are focused using focusing knobs (coarse and fine), which eventually are further magnified (say -10×) to achieve overall magnification (-1000 ×). Thus, a microstructural feature can be magnified and perceived by the observer.
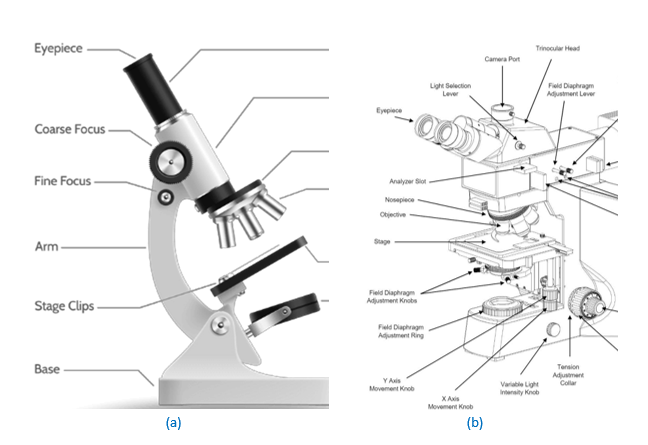
Figure 1: Features of an optical microscope: (a) Biological microscope, where illuminator is below the biological sample to pass through it (Courtesy: www.vedantu.com), and (b) Metallurgical microscope, where the light is reflected from a mirror-polished metallurgical sample (Courtesy: www.greatscopes.com). The specimen is kept on specimen stage, and its features are observed via eyepiece through focusing and magnification achieved by objective lens.
