Basic Algorithms in Bioinformatics
Introduction
The concept of an algorithm becomes more relevant with the precise use of variables in mathematics. It has been noted that due to the huge size of biological data, the problems in bioinformatics require a wide range of computational power to solve the problems in bioinformatics. Algorithms function as a key to open the various problems in a bioinformatics approach and applications. It is important to evaluate how the basic algorithm in bioinformatics defines the problems in biology, such as in molecular biology, and to understand the methodology approaches in designing the algorithms and to fix the weakness for a better outcome. In biology, with the advances in X-ray structure analysis, a large amount of data and structural features regarding biological sequences have been identified for further analysis. Bioinformatics applications such as algorithms aid in studying sequence and structure alignments, predicting protein structure, classifying protein function, and modelling homologous proteins for progressive applications in life science research.
Theory
An algorithm is defined as a set of sequential instructions that one must perform for solving a well-formulated problem. Considering a Protein or a nucleotide sequence, it is important to find the similarity matches for predicting the functional role, features and structural aspects. Sequence alignment generally describes the comparison of sequence with several methods for sequence analysis in a better way. The accuracy of sequence alignment determines the subsequent analyses for phylogeny prediction, genomics studies and structure and function prediction and for identifying conserved regions. In biological research, sequence analysis helps in drug discovery process, pathogen detection and identification of common genes. The basic algorithm in bioinformatics employs techniques for efficiently finding optimal alignments.
Algorithms for Pairwise Sequence Alignment
In Pairwise Sequence Alignment the similarity regions are identified for mapping functions, structure and evolutionary relationships between two biological sequences of interest. There are different algorithms associated with pairwise sequence alignment like the Brute Force algorithm, Dotplot, Needlemann Wunsch algorithm, Smith Watermann algorithm etc..
Brute Force Comparison
Brute Force Comparison refers to the simplest string comparison algorithm. It is applicable to check whether two equal-length sequences are identical or not. In Brute force comparison, alignments are done without gaps and produce N^2 complexity. N represents the length of the sequence. In biological sequence alignment, brute force comparison involves all possible alignment of the given sequence for computing a similarity score and identifies the alignment having the highest score. The scoring system has specific scores or penalties for matching pairs, mismatches, and gaps (insertions or deletions). The alignment scores evaluate the similarity or dissimilarity between two biological sequences. The highest score indicates the given sequence has higher similarity. Brute force algorithm is the straightforward approach for solving a problem that included direct computation and problem statement based on concepts. Brute force approach can also be called as exhaustive search for solving small size instance of problem. It is important for both educational and theoretical purposes. The implementation of Brute force algorithm is the simplest approach, and it can be only applied to problems with smaller input size.
Dot-plot
A dot plot is a simple alignment using graphical methods for visualizing sequence similarities and alignments between two biological sequences. In dot-plot, visual comparisons between the sequences were done to find out the regions of close similarities. Here, the two sequences were arranged along the axes of a simple graph. While comparison, a dot is placed at the point where two sequences are identical. A diagonal stretch of dots in the graph indicates regions of two similar sequences. The dot plot does not provide precise alignment between two sequences, and it is considered semi-quantitative. Dot plot represents a graphical method for comparing two biological sequences for identifying regions of close similarity between them. It is a simple method for comparing two sequences, either DNA or protein, and is probably the oldest way of comparing biological sequences. Dot plot creates two-dimensional graph for showing comparison of two sequences.
Needleman-Wunsch Algorithm
The Needleman-Wunsch algorithm is a dynamic programming method that breaks down the alignments into smaller units as sub-sequences for optimal alignment. In this algorithm, a matrix is constructed that aligns specific scores (for matches, mismatches, and gap penalty) for all possible alignments by backtracking through the matrix. Overall, the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm has two matrices: score matrix and traceback matrix.
Steps in the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm
- Initialization
The initial matrix is created with m+1 columns and n+1 rows (where m and n correspond to the length of the sequences). Extra rows and columns are given to align with a gap at the start of the matrix. For more details see https://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=274&sim=1431&cnt=1
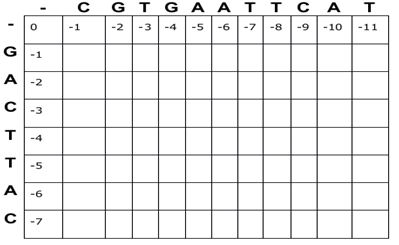
Fig.1. Initialization of matrix in Needleman-Wunsch algorithm
- Matrix filling (score calculation) The first row and first column of the matrix represents gap penalties. From the second row, calculate the score for each cell in the matrix. The score is determined by match, mismatch, insertion, and deletion in the given sequence. Gap penalties are represented by negative values that represents a score deduction for introducing a gap. A score for each cell depends on scores of the neighboring cells and provides substitution score of the corresponding sequences.
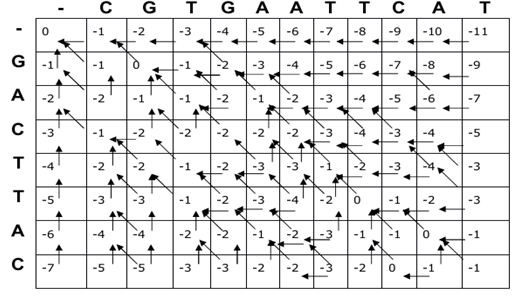
Fig.2. Matrix filling in Needleman-Wunsch algorithm.
- Traceback After filling the entire matrix, the optimal alignment can be obtained by backtracking from the bottom-right cell (corresponding to the end of both sequences) to the top-left cell (corresponding to the beginning of both sequences).
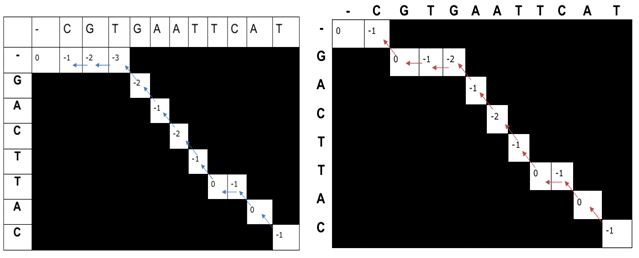
Fig.3. Traceback in Needleman-Wunsch algorithm The best alignment can be identified by using the maximum alignment score which may be user defined.
Algorithms for Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) represents the alignment of three or more biological sequences of similar length. It is useful in molecular biology to study evolutionary relationships and there exists many algorithms for studying the sequence alignment. Scoring scheme in algorithm represent a set of rules that assigns the alignment score to any given alignment of two sequences. A gap in the matrix corresponds to an insertion or a deletion of a biological residue. Progressive alignment is one of the algorithms that is used for most of the tools For e.g. CLUSTALW
Algorithms for Pylogenetic tree construction
Phylogentic tree helps us to study the evolutionary relationships and there exists many algorithms and tools for constructing trees. Algorithms like Margoliasch-Fitch algorithm, Neighbor joining, UPGMA can be used. These algorithms are used in tools like Phylip, ggTree, Figtree etc..
