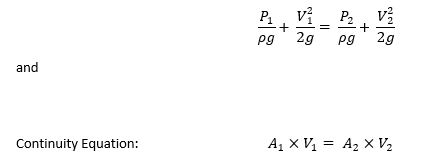Coefficient of discharge of given Venturi meter
Introduction
A venturi meter is a simple device used for measuring the flow rate of liquid flowing through a pipe. A venturi works on a simple principle that by reducing the cross - sectional area of the pipe, a pressure differential is created between the inlet and throat. This pressure differential is measured with the help of differential manometer which enables the determination of the discharge through the pipe. A Venturi meter consists of an inlet section followed by a convergent cone, a cylindrical throat, and gradually divergent cone.
Components of a Venturi meter Test Rig
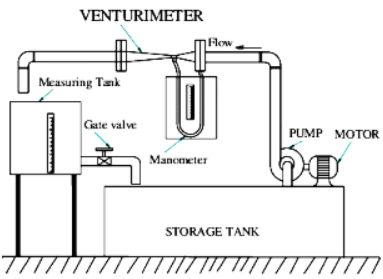
Fig. 2: Components of a Venturi meter test rig
Fig. 2, shows a test rig or bench for a Venturi meter whose each part is explained as follow:
- Flow Meter
The test bench consists of flow meter with of size 25 mm for the experiments. The meter has the adequate cocks also with them.
- Strainer
A strainer acts like a filter which stops the solid particles entering the impeller through suction pipe. Strainer is attached at that end of the suction pipe which is dipped into the sump.
- Piping
Piping in the test bench consist of G.I. pipes of size 25 mm with sufficient lengths on the upstream and downstream, also provided with separate control valves. Individual upstream and downstream pressure feed pipes are provided for the measurement of pressure heads with control valves situated on a common pipe for easy operation.
- Centrifugal pump
A mono block centrifugal pump is provided with the test bench which delivers the water through the test bench pipeline fittings and venturi meter. The pump is rigidly fixed onto sump tank.
- Measuring Tank
Measuring tank with gauge glass and scale arrangement for quick and easy measurement to determine height of water filled in the tank.
- Differential Manometer
A Differential manometer with 1 mm scale grading is provided to measure the differential pressure head produced by the venturi meter.
- Sump
Sump is a water tank which stores adequate amount of water for circulation through the entire unit for experimentation and is arranged on the floor of the test bench.
Working of a Venturi meter
• A venturi meter works on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation, i.e., the pressure decreases as the velocity increases.
• The cross-section of the throat is less than the cross-section of the inlet pipe.
• As the cross-section from the inlet pipe to the throat decreases, the velocity of the fluid increases, and hence the pressure decreases according to Bernoulli’s equation.
• Due to the decrease in pressure, a pressure difference is created between the inlet pipe and the venturi meter’s throat.
• This pressure difference can be measured by applying a differential manometer between the inlet section and throat section or using two gauges on the inlet section and throat.
• The pressure difference through the pipe is calculated after obtaining the flow rate.
Bernoulli’s Equation for horizontally placed venturi and neglecting frictional losses: