Trifiliar Suspension
Procedure
Experimental set up:
A metallic circular disc of suitable radius and uniform thickness is hung from the ceiling using three wires. The points of suspension are equispaced from the centre of the disc so that the wires are vertical and of equal length, and the disc is horizontal. Mass of the disc and its outside radius are measured. Let them be mo kg and r meters respectively. Similarly, the length of wires between the point of suspension from the ceiling to those on the disc and distance of point of suspension on the disc from its centre are measured. Let them be l metre and a metre respectively. Such an arrangement is called a trifiliar suspension. In such an arrangement, if is a small angular displacement is given to the disc in horizontal plane and left, the disc will oscillates about the vertical axis passing through its centre.
Read background for details. The period of angular oscillation of the disc is given by 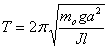 , g is acceleration due to gravity, 9.81 m/s2 and J is mass moment of inertia of the disc about the vertical axis passing through its centre and is given by
, g is acceleration due to gravity, 9.81 m/s2 and J is mass moment of inertia of the disc about the vertical axis passing through its centre and is given by 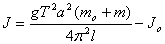
A solid body of irregular shape, whose mass moment of inertia is to be found, is kept on the circular disc. The center of mass of the body is aligned approximately with the centre of the disc by judgment.
Now the set up is ready for performing the experiment by following the procedure given below:
Procedure:
Prepare the trifiliar suspension using the circular disc and tree wires as explained in the experimental set up.
Keep the solid body of irregular shape on the disc. See that the centre of the mass of the body is aligned with the centre of the disc by moving the body on the disc and using your own judgment.
Give a small angular displacement to the disc in its own horizontal plane and about the vertical axis passing through its centre, say about 100, and leave. The disc alongwith the solid body will oscillate about the vertical axis passing through the centre of the disc and centre of mass of the body.
Measure time taken by the disc for known number of oscillations, say 10 oscillations.
Calculate period of oscillation of the disc, i.e. time taken for one oscillation. Let it be T seconds.
Calculate the moment of the inertia of the solid body using the formula (read theory)
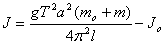
Where,
J = mass moment of inertia of the solid body about its centre of mass that was aligned with the centre of the disc, kg.m2
g = acceleration due to gravity, 9.81 m/s2
T = period of the oscillation of the disc + the solid body, second
a = distance of point of suspension on the disc from its centre, metre
mo = mass of the disc, kg
m = mass of the solid body, kg
l = length of the wire between the points of suspension on the ceiling and the disc, metre.
Jo = mass moment of inertia of the circular disc about vertical axis passing through its centre, kg.m2; it is given by,
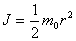
r = outside radius of the circular disc, metre.
