To draw the characteristics of an n-p-n or p-n-p transistor in common emitter mode. From the characteristics find out (i) the current gain (β) and (ii) the voltage gain of the transistor.
Procedure:
A. Input Characteristics:
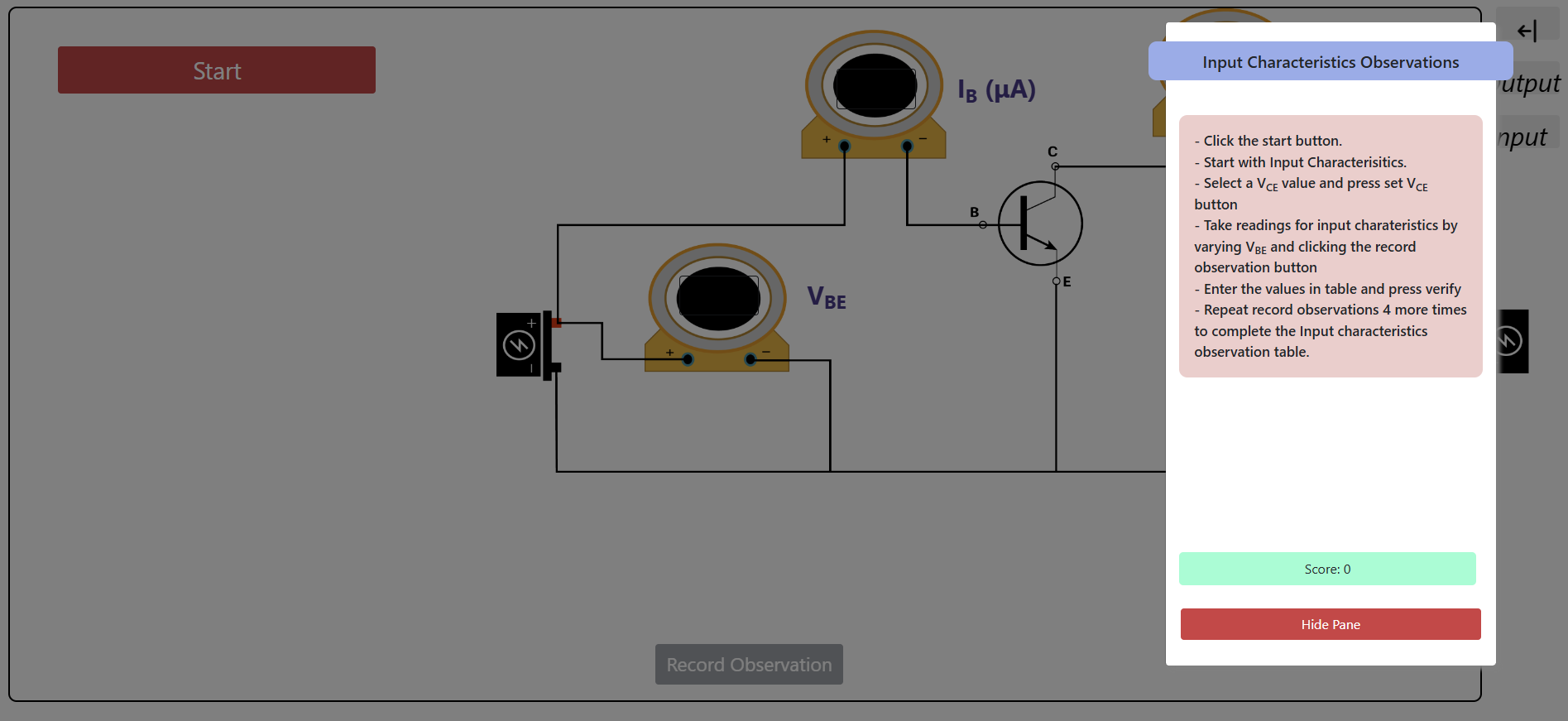
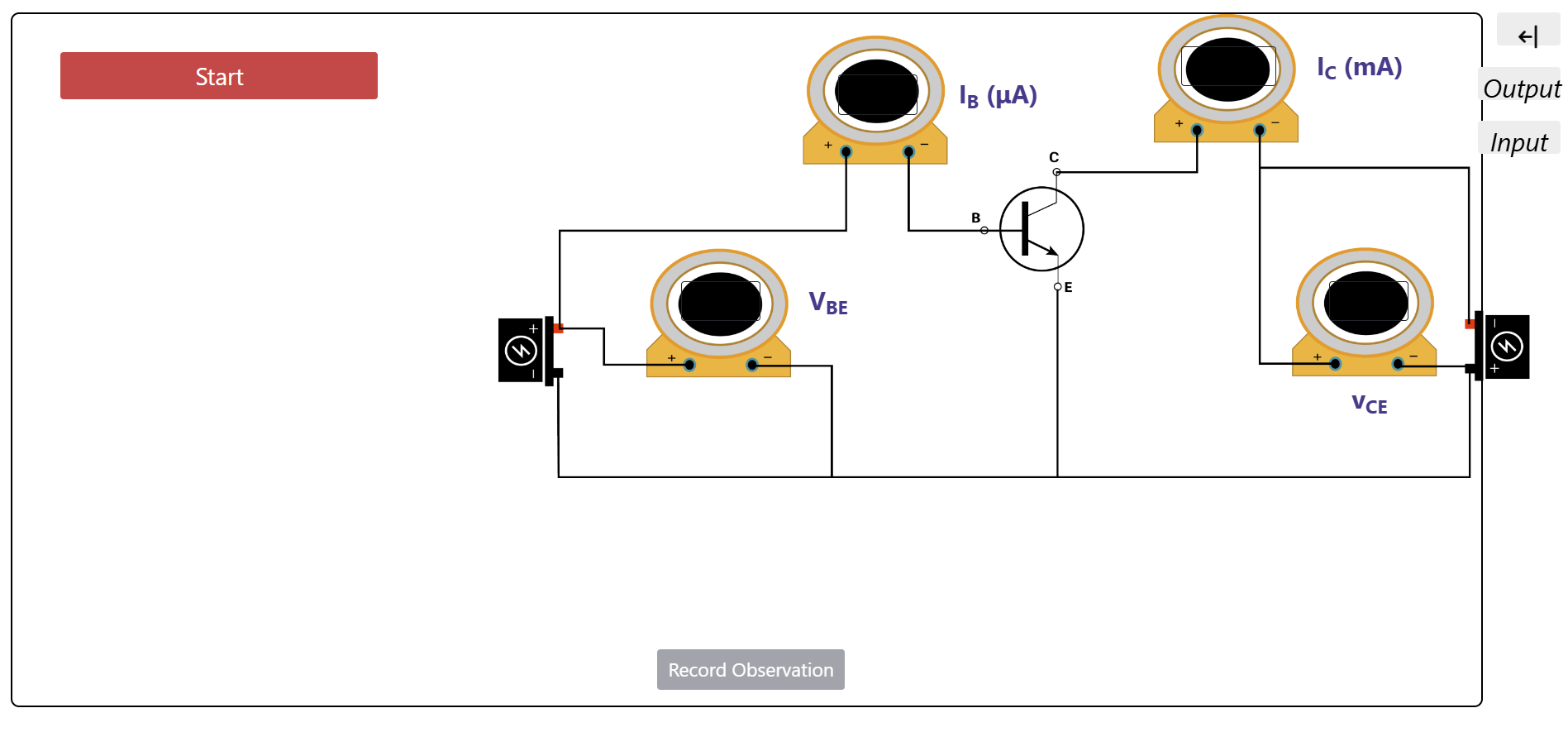
- Make the circuit connection as shown in the circuit diagram.
- Set the voltage VCE = 2 V and vary IB with the help of VBB and measure VBE.
- Set the voltage VCE = 3 V and vary IB with the help of VBB and measure VBE.
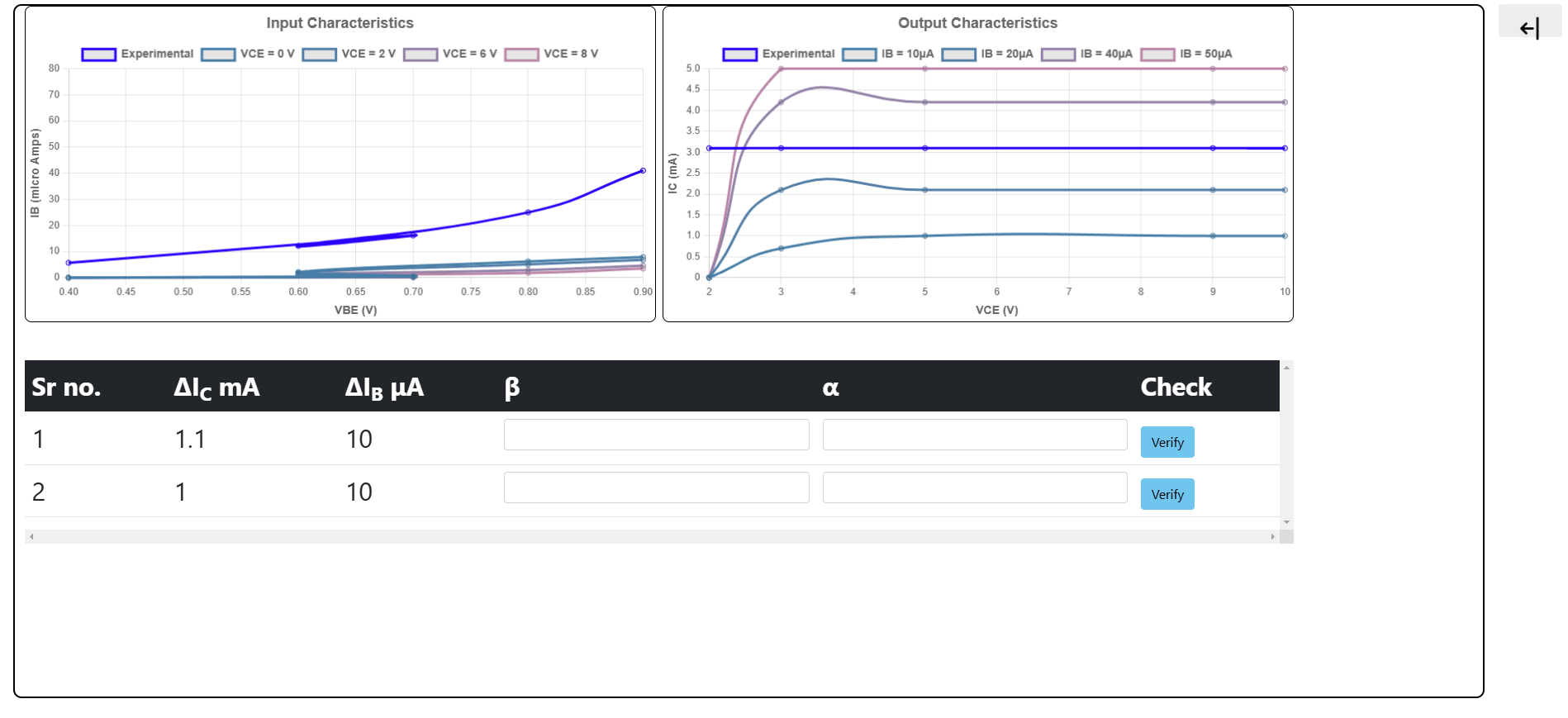
- Plot a graph of IB vs. VBE.
- Evaluate the dynamic input resistance, which is the ratio of change in VBE to the resulting change in base current at constant collector-emitter voltage. It is given by ΔVBE / ΔIB.
- The reciprocal of the slope of the linear part of the characteristic gives the dynamic input resistance of the transistor.
B. Output Characteristics
- Keep IB constant, say 10 μA, vary VCE and note down the collector current IC.
- Now keep IB = 20 μA, vary VCE and note down the collector current IC.
- Plot a graph of IB vs. VCE.
- The change in collector-emitter voltage causes a small change in the collector current for a constant base current, which defines the dynamic output resistance and is given as ΔVCE / ΔIC at constant IB, or the output conductance is given by ΔIC / ΔVCE with IB at a constant current.
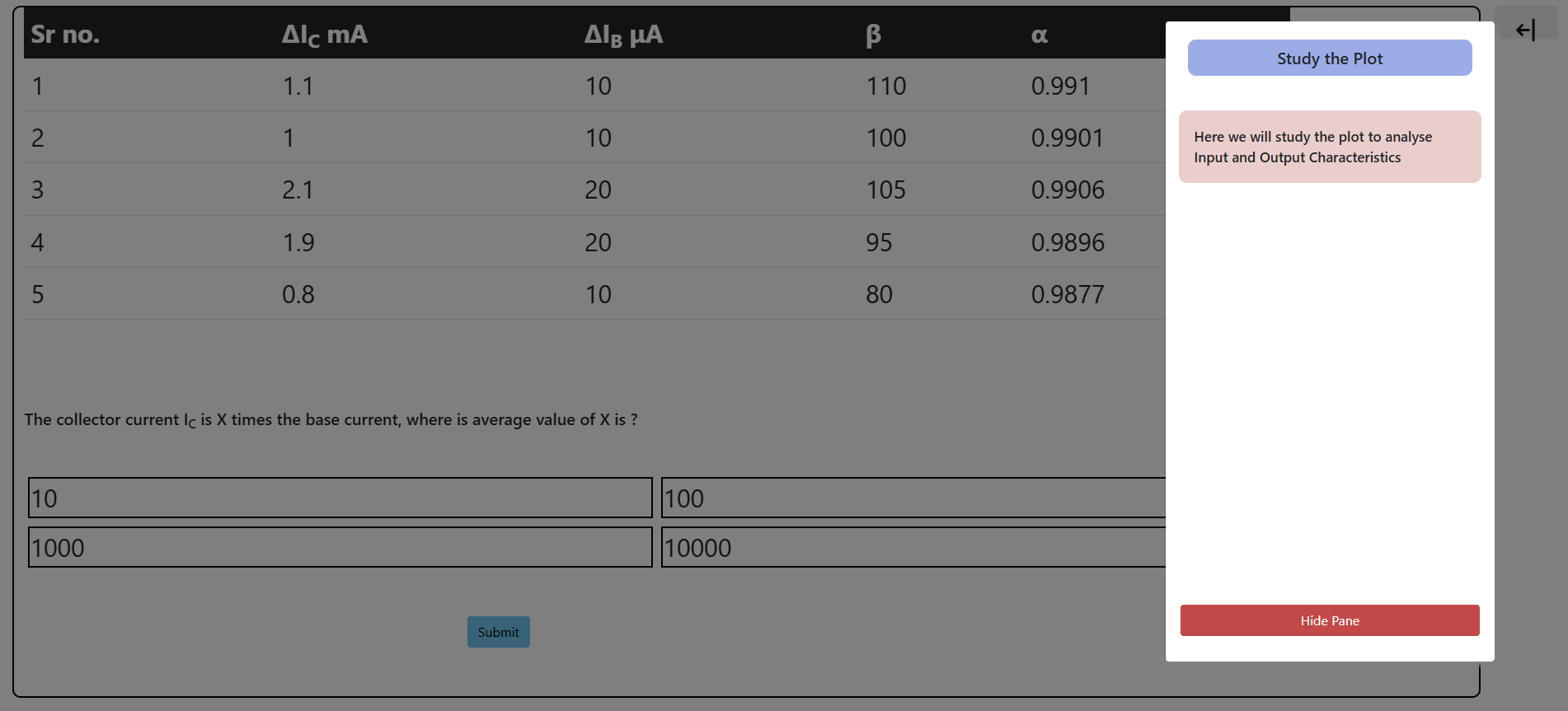
- Find the output conductance from the slope of the linear portion of the characteristic curves and also find the small-signal current gain, which is calculated by β = ΔIC / ΔIB with VCE at a constant voltage.
Calculations:
- Small-Signal Current Gain: β = ΔIC / ΔIB with VCE at a constant voltage.
- Dynamic input resistance: It is given by ΔVBE / ΔIB at constant VCE.
- Dynamic output resistance: It is given as ΔVCE / ΔIC at constant IB.
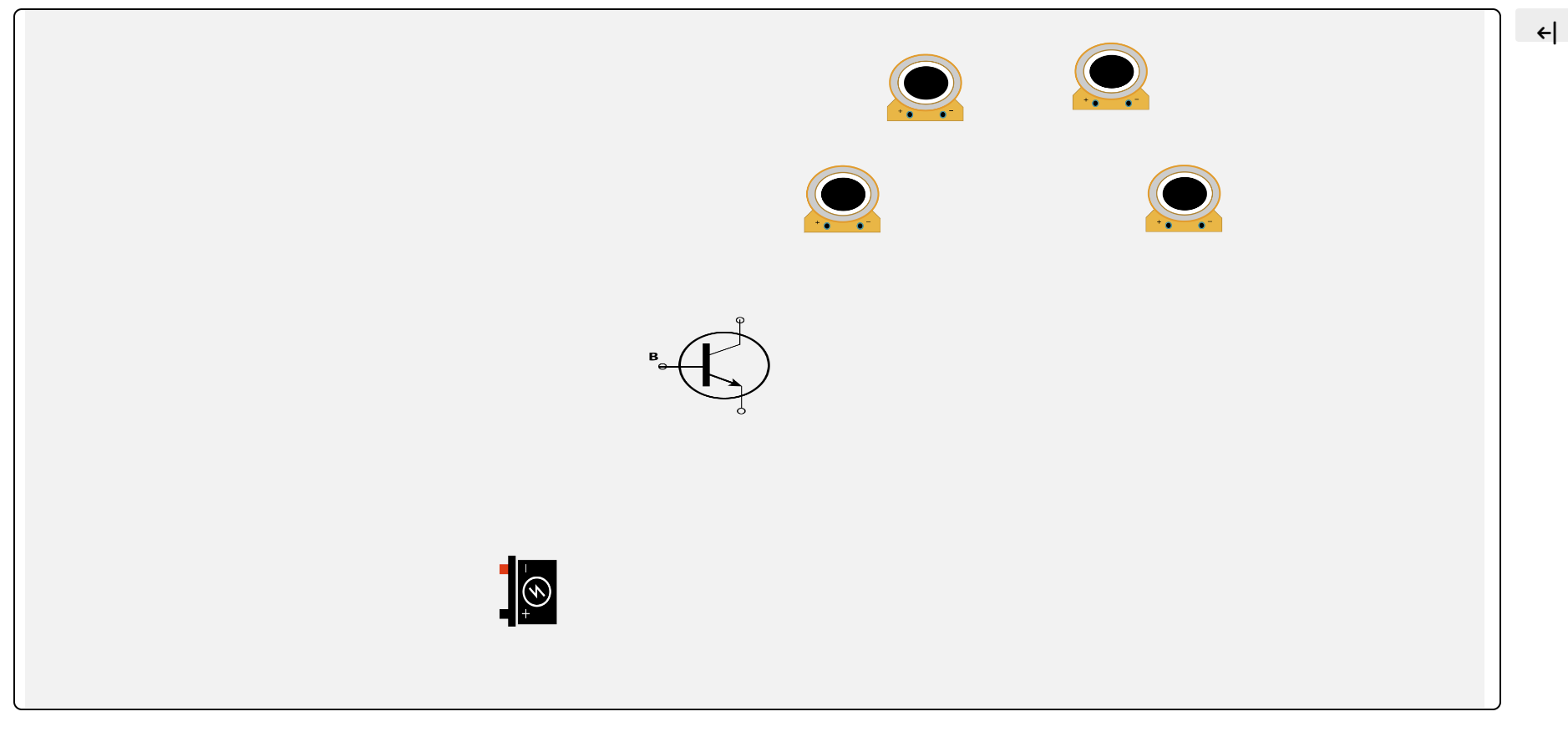
STEP 1:
Follow the instructions and identify the components.
STEP 2:
Follow the instructions and take reading for Input and Output Characteristics.
STEP 3:
Study the plot and verify the values.
STEP 4:
Choose the correct options.