Transformations: Translation
Introduction to Translation:
Translation is a fundamental transformation in computer graphics that involves displacing objects from one position to another within a three-dimensional coordinate space. It plays a crucial role in repositioning graphical elements to achieve desired visual effects.
Translation in 3D Space:
In 3D graphics, the translation of a point (x, y, z) involves moving it along the x, y, and z axes by specific amounts represented by the translation vector (vx, vy, vz). The new coordinates (x', y', z') after translation can be expressed mathematically using matrix multiplication.
Matrix Representation of Translation in 3D:
The translation operation in 3D space can be efficiently represented using a 4x4 matrix T as follows:
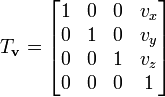
Matrix Multiplication for Translation:
To apply the translation matrix T to a point (x, y, z), the matrix multiplication is performed as follows:
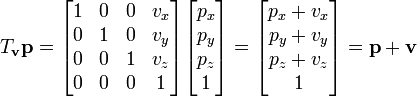
The resulting vector (x', y', z', 1) contains the translated coordinates. The additional fourth element, 1, ensures compatibility with the homogeneous coordinate system.
