Topological Sort
Trees and Graphs
- Tree is an abstract data structure that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root and subtrees of children with a parent node, represented as a set of linked nodes.
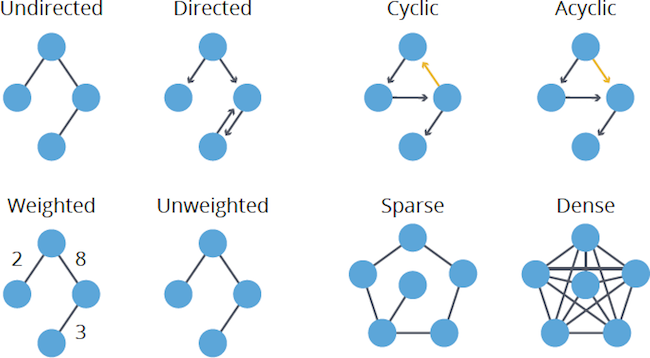
- A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links that connect the vertices are called edges.
- Graph with all vertices connectes is a connected graph and a tree that covers all vertices in called spanning tree.
- Graphs with edges that have weights are called weighted graphs. Graphs with directions is known as a directed graph.
Types of graphs
Depth First Search (DFS)
A Depth First Search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing a finite graph. DFS visits the child vertices before visiting the sibling vertices; that is, it traverses the depth of any particular path before exploring its breadth. A stack (often the program's call stack via recursion) is generally used when implementing the algorithm.
What is a DAG?
A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a graph that is directed and without cycles connecting the other edges. This means that it is impossible to traverse the entire graph starting at one edge. The edges of the directed graph only go one way.
Time and Space Complexity
Time complexity of an algorithm gives the measure of time taken by it to run as a function of the length of the input. Similarly, space complexity of an algorithm quantifies the amount of space or memory taken by an algorithm to run as a function of the length of the input.
