Break Down a 3D Framed Structure into 2D Frames
Theory
In manual structural anlysis of real life structures, the first step is to break down the 3D frame into 2D frames for easy visualization and manual computations.
This experiment aims to simulate the application of decomposition of a 3D frame into 2D frames. It also displays the principle of transfer of loads from one member of the frame to the other in a sequence of arrangement. The loads are transferred from slabs to beams, beams to columns and columns to footings. The load calculations can be manually done by disassembling a 3D structural frame into multiple 2D frame units.
The experimental calculations involve:
Step-1: Calculation of total load intensity of slab involving Dead loads + Floor finish loads.
Step-2:Calculation of superimposed dead load of slab transferred to beams.
Step-3: Calculation of self-weight of beam.
Step-4: Calculation of total imposed load of the frame to footing (superimposed Slab load + self-weight of Beam + self-weight of column).
For imposed(live) load calculations, an intensity of 3kN/m2 is considered for the structure as per IS875 Part-II 1987 (Reaffirmed 2008). Dead load and imposed load calculations are done seperatly.
The user may carry out the summation of loads of all the 2D frames which will lead to the total load can be transferred to the footings. After this, the user may calculate the seismic loads on the building by using the standard base shear formula as per IS 1893 Part-1 (2016).
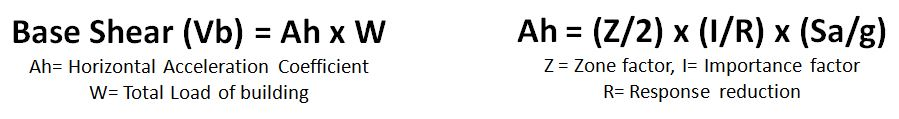
Sa/g = Design acceleration coefficient for different soil types, normalized with peak ground acceleration, corresponding to natural period T of structure (considering soil-structure interaction, if required).
For the analyis of the given structure the user can calculate the amplitude time period(T) and the the SA/g value using the formula given in the simulation.
