Structural and Behavioural Patterns
Theory
Structural Pattern: Structural design patterns are concerned with how classes and objects can be composed, to form larger structures. Decorator pattern is a type of Structural pattern.
Decorator Pattern: Decorator pattern allows a user to add new functionality to an existing object without altering its structure. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern acts as a wrapper to existing class.
The shape like Circle and Rectangle can have red, blue or any other color based on the decorator applied.
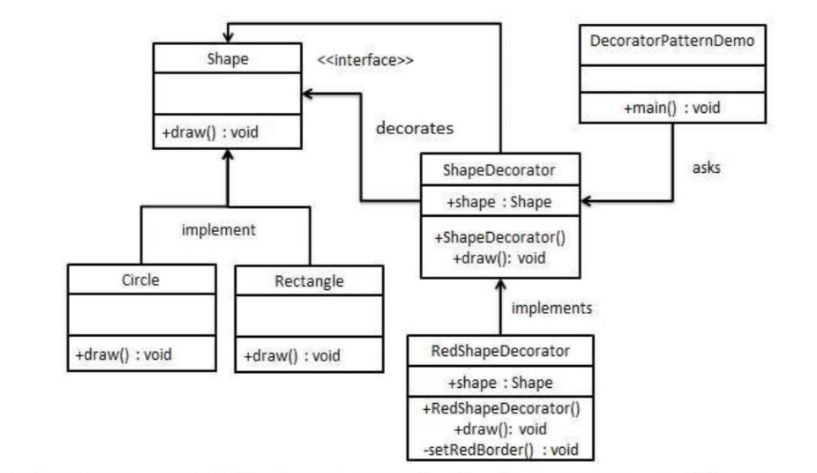
public abstract class ShapeDecorator implements Shape
{
protected Shape decoratedShape;
public ShapeDecorator (Shape decoratedShape){ this.decoratedShape = decoratedShape;
}
public void draw(){
decoratedShape.draw();
}
}
public class RedShapeDecorator extends ShapeDecorator {
public RedShapeDecorator (Shape decoratedShape) {
super(decoratedShape);
}
@Override
public void draw() {
decoratedShape.draw();
setRedBorder (decoratedShape);
}
private void setRedBorder (Shape decoratedShape) {
System.out.println("Border Color: Red");
}
}
public class DecoratorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape circle = new Circle();
Shape redCircle = new RedShapeDecorator (new Circle());
Shape redRectangle new RedShapeDecorator (new Rectangle());
System.out.println("Circle with normal border");
circle.draw();
System.out.println("\nCircle of red border");
redCircle.draw();
System.out.println("\nRectangle of red border");
redRectangle.draw();
}
}
It displays the following output:
Circle with normal border
Shape: Circle
Circle of red border
Shape: Circle
Border Color: Red
Rectangle of red border
Shape: Rectangle
Border Color: Red
Behavioral Pattern: Behavioral patterns deals with the interaction between the objects such that they can easily talk to each other and still should be loosely coupled. Iterator Pattern is a type of behavioural pattern.
Iterator Pattern:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Animal implements Iterable<String>
{
private ArrayList<String> animal = new ArrayList<String>();
public Animal (ArrayList animal) {
this.animal animal;
}
public ArrayList getAnimal() {
return animal;
}
@Override
public Iterator<String> iterator()
{
return new AnimalIterator(this);
}
}
public class AnimalIterator<String> implements Iterator<Object> {
private ArrayList<?> animal;
private int position;
public AnimalIterator (Animal animalBase) { this.animal = animalBase.getAnimal(); }
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (position
animal.size()) {return true;}
else {return false;}
@Override
public Object next() {
Object aniobj = animal.get(position); position++; return aniobj; }
@Override
public void remove() {
animal.remove(position); }
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestIterator
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList<String> animalList = new ArrayList();
animalList.add("Horse");
animalList.add("Lion");
animalList.add("Tiger");
Animal animal = new Animal (animalList);
for (String animalobj:animal){
System.out.println(animalobj);
}
}
}
