Rigidity Modulus -Static Torsion
Theory
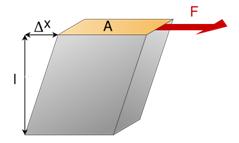
Shear modulus, or rigidity modulus n is defined as the ratio of stress F/A to strain when a shearing force F is applied to a rigid block of height l and area A. is the deformation of the block, and
This is similar to what happens when a torque is applied to a rigid rod of length l and radius r. Looking at the cross-section of the rod, consider a ring of width dr' at radius r' , which will have area , with force applied tangentially. The weighted average force over the cross-sectional area A of the rod is then
If the torque deforms the rod by twisting it through a small angle , the deformation distance (corresponding to ) at the outside edge of the rod is approximately . The definition of the rigidity modulus n becomes
In our apparatus the torque is supplied by hanging a weight of mass M from a string wound round a pulley of radius R, so and our definition of rigidity modulus n becomes
Now suppose we mount a small mirror on the rod at distance l from its fixed end, and look at a centimeter scale in the mirror through an adjacent telescope, both at distance D from the mirror. When the rod deforms and the mirror rotates through a small angle , we look at a point on the scale a distance approximately ¸ from the original point, which was aligned with the telescope. We can measure D and S and substitute in our definition of rigidity modulus n, to get
Application
Engineers consider the value of shear modulus when selecting materials for shafts, which are rods that are subjected to twisting torques.
