Potentiometric titration of a strong acid and strong base.
Theory:
Potentiometric titration is a type of voltammetric analysis. It is used to determine the concentration of an analyte (strong acid or base) in a sample and the titration is performed using a titrant of known concentration. After performing the titration, the potential difference between the reference and indicator electrode is measured in conditions where a thermodynamic equilibrium is maintained and the current through the electrodes does not disturb this equilibrium.
Potentiometric determination of endpoint depends on the potential across two electrodes immense into a solution. The potential is measured in millivolts using electrodes. By using the measurements of electric potential, the equivalence point can be determined. The potential of the solution depends on the nature and the concentration of ions present. In this experiment, quinhydrone is used, it is an equilibrium mixture of quinone and hydroquinone. A known volume of the acid to be titrated is kept in a beaker. It consists of 25ml HCl and a pinch of quinhydrone. Along with this, a platinum electrode and saturated calomel electrode are connected to the potentiometer and the electrodes are dipped in the beaker. The prepared standard NaOH solution is filled in a burette and added in a small volume to the beaker. The value displayed on the potentiometer is noted after each addition. A graph is plotted by taking the volume of NaOH added along the x-axis and the corresponding voltage on the y-axis.The following graph represents a steep rise in the curve that indicates the equivalence point.
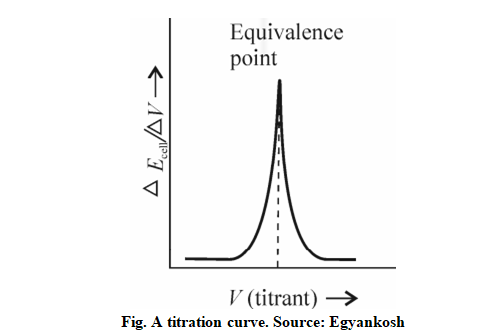
A sudden change in potential in the graph of Δ𝐸/Δ𝑉 against the volume of the titrating solution will reveal the equivalence point of the reaction. Potentiometric titration involves the measurement of Ecell with the addition of titrant. The electromotive force of the cell can be represented as:-
EMF of the cell,Ecell = Ecal - EQuinhydrone
= 0.2422 – (0.699 – 0.0591 pH)
= 0.2422 – 0.699 + 0.0591 pH
Where,
EMF = Electromotive Force
E cell = Cell Potential
E cal = Calomel Electrode Potential
E Quinhydrone = Quinhydrone Electrode Potential
Ecell depends on the concentration of the interested ions with which the indicator electrode is in contact. The overall cell potential, Ecell is calculated at every interval where the titrant is measured and added.
