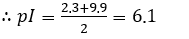Determine the pI of a glycine using potentiometric method
Glassware required :
- Burette and Pipette
- Conical flask (150 ml)
- Measuring cylinder
- pH meter
Chemicals required :
- NaOH solution (0.1 M)
- HCl (0.25 N)
- KCl solution (1 M)
- Glycine (0.1 M)
- Distilled water.
Laboratory procedure :
- Take 50 mL of NaOH solution (0.1 M) in a 50 mL burette and adjust zero reading.
- Pipette out 25 mL of the given solution of glycine in a 250 mL beaker and add 25 mL of distilled water to the amino acid solution using pipette.
- Insert the cleaned pH electrode into the beaker solution and record the initial pH of the solution.
- Do not remove the electrode from the beaker till the end of the experiment.
- Add NaOH in 0.5mL increment from the burette. Stir the solution and mix it well.
- Record the corresponding pH values until the pH starts increasing drastically. At this time, add 0.1 mL increments of NaOH till the pH stabilizes around 8.
- After reaching pH 8, continue adding 0.5 mL increments of NaOH till you reach pH 11.
- Plot the graph of pH vs volume of NaOH solution.
- The two almost horizontal parts of the graph give the values of pKa1 and pKa2 for glycine. Use mid-points of these regions to get the values.
- The average of these values (pKa1 and pKa2) gives the pI of glycine.
Precautions :
- Handle the burette carefully.
- Take the reading of 0.5 ml interval continuously.
- pH-meter calibration must be done carefully.
- Allow the pH meter reading to stabilize before recording each value to minimize errors in the titration curve.
Laboratory procedure (diagram) :
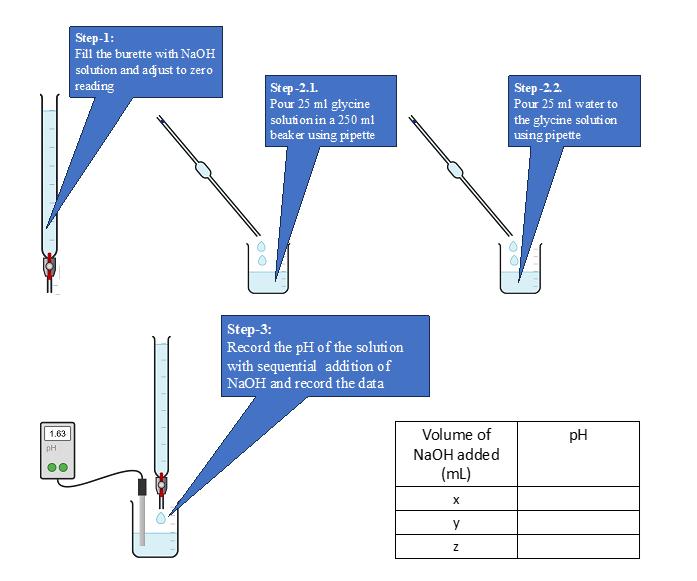
Procedure in laboratory :

Data & Analysis :
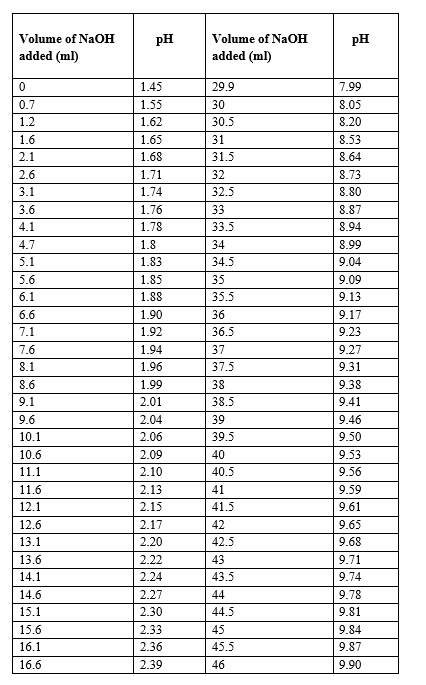
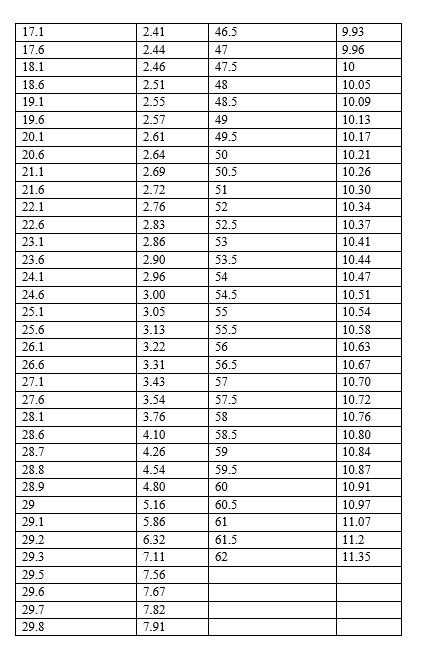
Graph :
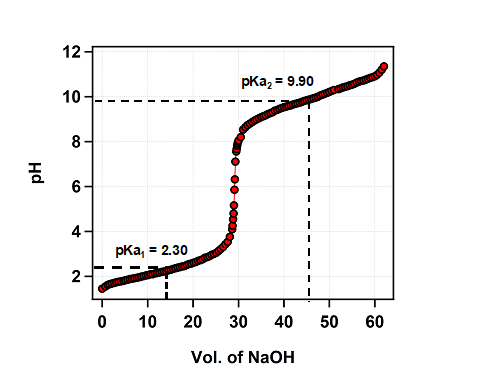
Result :
From the graph, the pKa1 is estimated to be 2.3
From the graph, the pKa2 is estimated to be 9.9