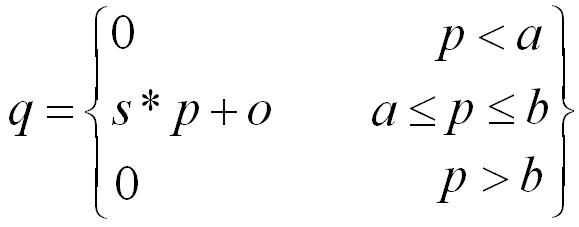Point Operations
Point operations are simple image enhancement techniques. Here, the operations are directly performed on the pixel values. A given image f(x,y) is transformed into an output image g(x,y) using some transformation T. Let f(x,y) = p and g(x,y) = q; p and q are also known as pixel values in the corresponding images at location (x,y). Thus,
q = T(p)
where, T is a transformation that maps p into q. The results of this transformation are mapped into the grey scale range as we are dealing here only with grey scale digital images. So, the results are mapped back into the range [0, 255].
There are four commonly used and basic types of functions (transformation) are described here:
Linear function
Non-linear function
Clipping
Window function
Linear function: The output pixel value is linearly related to the input pixel value. This can be described using a line equation as follows:
q= s * p + o;
where, s is the slope of the line and o is the offset from the origin. This type of transformation is particularly useful for enhancing white of gray details embedded in the dark regions of an image.
Non-linear function: The output pixel value is not linearly related to the input pixel value. Here, we consider example of log-transformation function to explain the process. In this function is:
q= c * log(1+p)
where c is a constant variable. This function converts a narrow range of low gray-level values of p in to a wider range of q values or vice versa. This type of transformation is useful in expanding values of dark pixels while compressing the higher values.
Clipping: The value of output pixel is related to the input pixel value in piece-wise linear fashion. Though such functions are complex and require user input but useful in many practical situations. This function is defined as
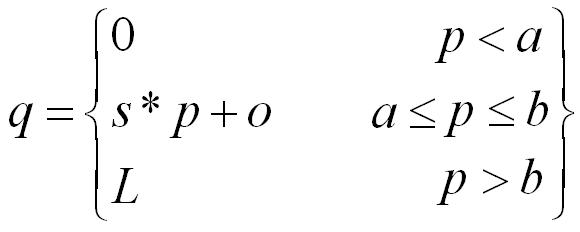
where, a and b are constant variables which define input pixel value range in which linear function with a slope s and offset o is applied. In gray level image, value of L is 255. In our experiment section, we kept value of offset fixed to zero.
Window: This function is similar to the clipper. In this, only a desired range of gray levels is preserved in the output image. It is defined as: