To study and prepare Process Flow Diagram
Preparing process flow diagram is an expert’s job and has to be done very carefully. Here is a detailed process, its pros and cons, effective matrix, and teams involved while preparing a process flow diagram for a process automation project :
Sample assignment Process :
Preparing a Process Flow Diagram for a Process Automation Project
Step 1: Define the Process Boundaries
- Identify the specific process to be automated
- Determine the start and end points of the process
- Define the inputs and outputs of the process
Step 2: Gather Information and Data
- Conduct stakeholder interviews to gather information about the process
- Review existing process documentation and data
- Observe the process in action to identify key steps and activities
Step 3: Identify Process Steps and Activities
- Break down the process into individual steps and activities
- Identify the tasks, decisions, and actions involved in each step
- Determine the sequence of steps and activities
Step 4: Create the Process Flow Diagram
- Use a process mapping tool or software to create the diagram
- Represent each step and activity with a symbol or shape
- Use arrows to show the flow of the process
- Include decision points, loops, and branches as necessary
Step 5: Review and Refine the Diagram
- Review the diagram with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness
- Refine the diagram based on feedback and suggestions
- Ensure the diagram is clear, concise, and easy to understand
Step 6: Finalize the Diagram and Document the Process
- Finalize the process flow diagram and document the process
- Include annotations and notes to explain each step and activity
- Store the diagram and documentation in a shared repository for future reference
Pros:
- Helps to clarify and understand the process
- Identifies inefficiencies and areas for improvement
- Facilitates communication among team members and stakeholders
- Provides a visual representation of the process
- Enables process automation and optimization
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive
- Requires stakeholder buy-in and participation
- May not capture all nuances and complexities of the process
- Can be difficult to maintain and update
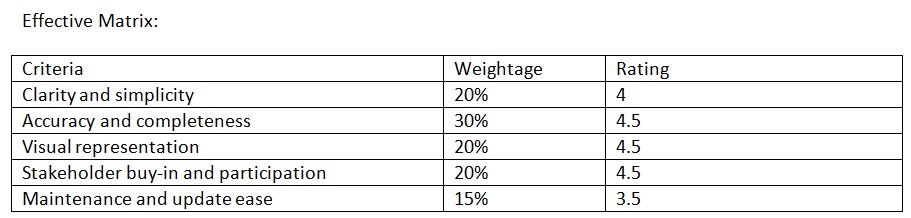
To make process flow diagram flawless the explicit list of care to be taken while preparing a Process Flow Diagram (PFD) for a process automation project is as follws :
I. Understanding the Process
- Familiarize yourself with the process: Before creating a PFD, ensure you have a thorough understanding of the process, including its inputs, outputs, and all the steps involved.
- Gather information from various sources : Collect data from operators, maintenance personnel, engineers, and other stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Review existing documentation: Study existing process descriptions, flowcharts, and P&IDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams) to gain a deeper understanding of the process.
II. PFD Structure and Layout
- Use a standard template or format : Establish a consistent structure and layout for your PFD to ensure clarity and ease of understanding.
- Keep it simple and concise : Avoid clutter and focus on the essential process steps and information.
- Use clear and concise labels : Label each process step, instrument, and equipment clearly and concisely.
III. Process Steps and Activities
- Identify and include all process steps : Ensure that all process steps, including manual and automated activities, are included in the PFD.
- Describe each process step clearly : Provide a brief description of each process step, including any relevant details or conditions.
- Indicate process step relationships : Show the relationships between process steps, including sequencing, parallel activities, and decision points.
IV. Instrumentation and Automation
- Include all instruments and automation components : Identify and include all instruments, sensors, actuators, and automation components in the PFD.
- Specify instrument and automation details : Provide details about each instrument and automation component, including its function, type, and tag number.
- Show instrument and automation connections : Illustrate the connections between instruments, sensors, actuators, and automation components.
V. Material and Energy Flows
- Show material flows : Illustrate the flow of materials, including inputs, outputs, and intermediate products.
- Indicate energy flows : Show the flow of energy, including utilities, such as electricity, steam, and water.
- Highlight potential hazards: Identify and highlight potential hazards, such as toxic substances, high temperatures, or explosive environments.
VI. Control and Monitoring
- Indicate control systems and strategies : Show the control systems and strategies used to regulate the process, including feedback loops and control algorithms.
- Specify monitoring and alarm points : Identify monitoring points and alarm conditions to ensure process safety and efficiency.
VII. Error Prevention and Quality Control
- Identify potential error sources : Highlight potential error sources, such as human error, equipment failure, or process deviations.
- Include quality control checks : Show quality control checks and inspections to ensure process quality and product integrity.
VIII. Review and Validate
- Review the PFD with stakeholders: Review the PFD with operators, maintenance personnel, engineers, and other stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Validate the PFD against actual process data : Validate the PFD against actual process data to ensure it accurately represents the process.
By following these guidelines, you can create a comprehensive and accurate Process Flow Diagram that effectively communicates the process and its requirements to all stakeholders involved in the process automation project.
