Rate constant and activation energy of potassium permanganate and oxalic acid reaction
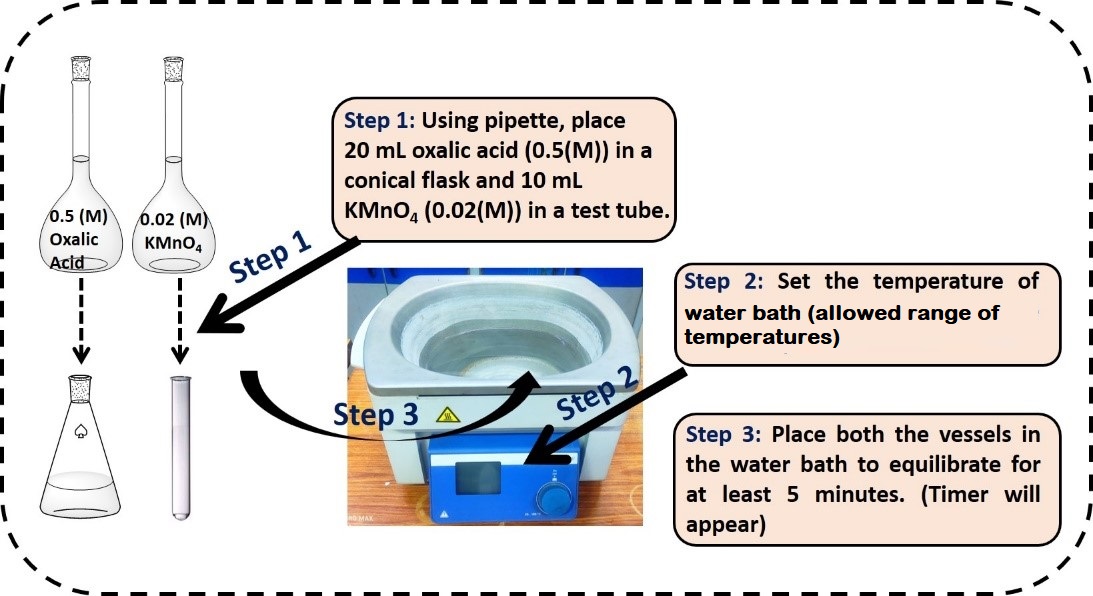
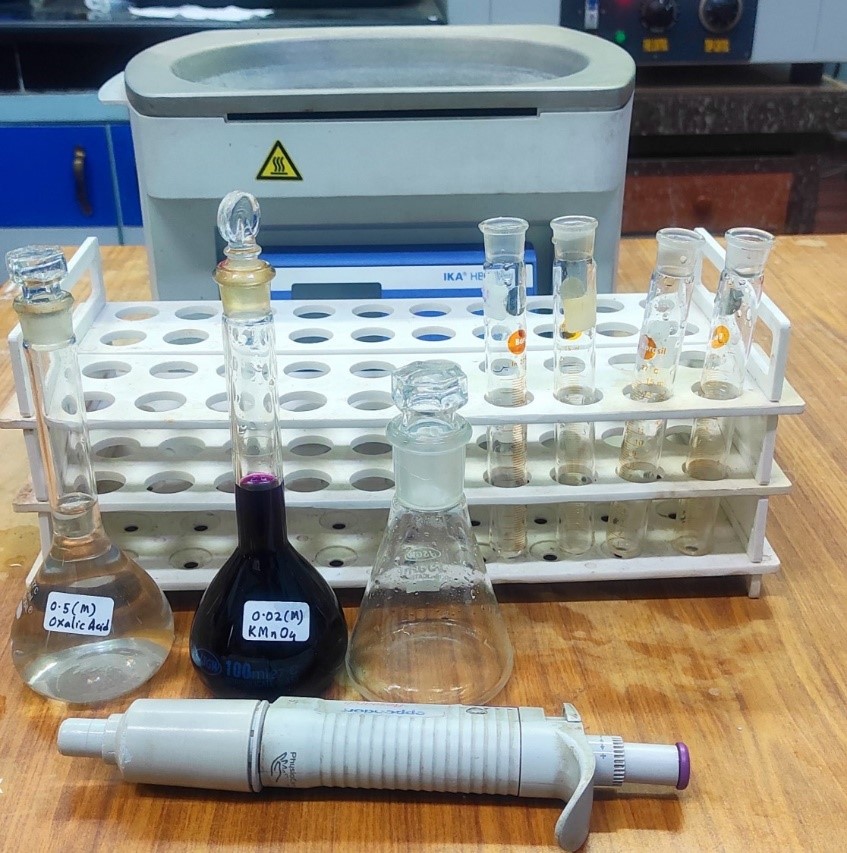
- Prepare 0.5 M oxalic acid and 0.02 M KMnO4 in a cleaned suitable volumetric flask. Pipette out 20 mL of oxalic acid and 10 ml of KMnO4 in a conical flask and a test tube respectively.
- Set the temperature of water bath up to the allowed range and place both the vessels into the water bath. Allow a 5 min equilibrium time for both of them.
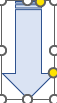
- Add the oxalic acid into the conical flask and start the stop watch to record time.
- Swirl the reaction mixture regularly keeping it to the water bath.
- Pause and record the time of the stop watch when the reaction mixture turned to purple from yellow/brown (completion of reaction).
- Repeat the same procedure for 4 other temperatures and determine the activation energy of the reaction.
Materials & Reagents Required:
- Temperature controlled water bath.
- Volumetric flask (250 ml)
- Conical flask (250 ml)
- Test tubes
- Micropipette (5 ml)
Procedure in laboratory (diagram)
Procedure in laboratory

Data and the analysis:
After mixing 20 mL, 0.5(M) oxalic acid with 0.02(M) KMnO4,
The Concentration of KMnO4 becomes = 0.0067 (M)
The Concentration of Oxalic acid becomes = 0.33 (M)
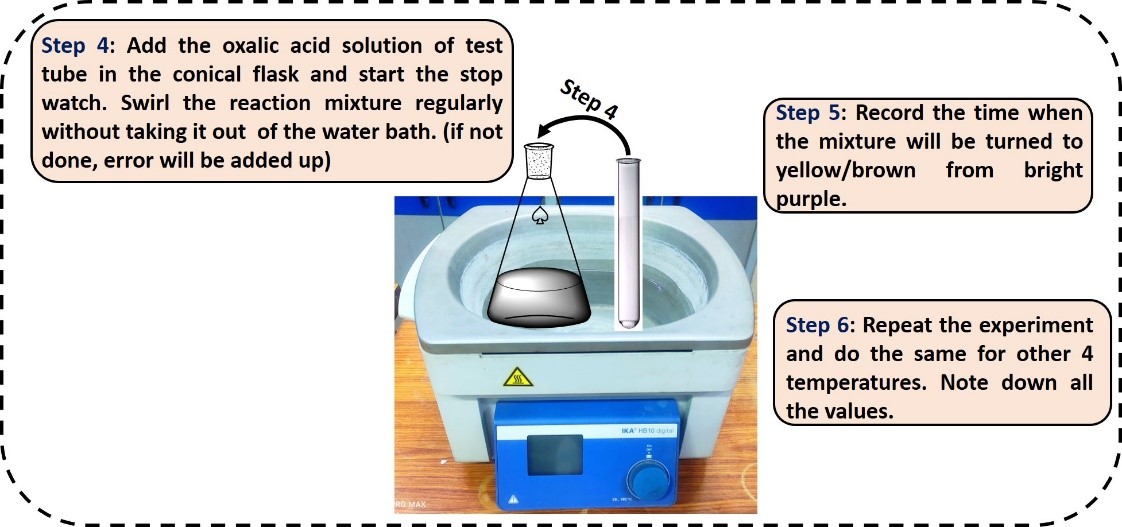
We have calculated the rate by using following equation
Rate= [KMnO4]/time
Next, we have measured rate constant (k) by using following equation
k = rate / [KMnO4] [Oxalic Acid]
.png)
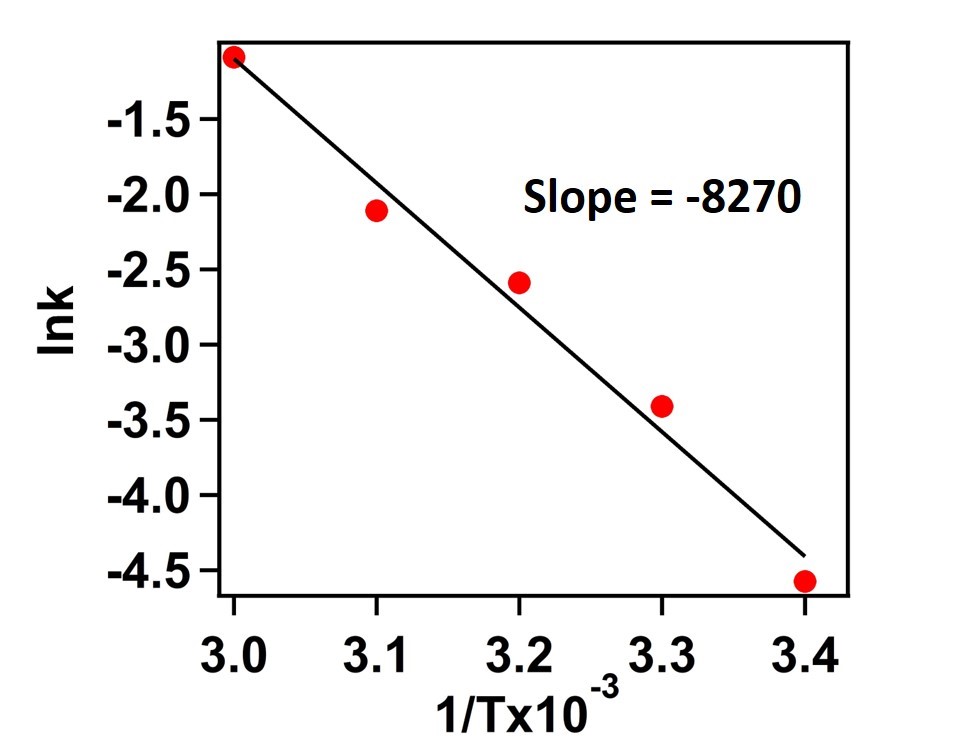
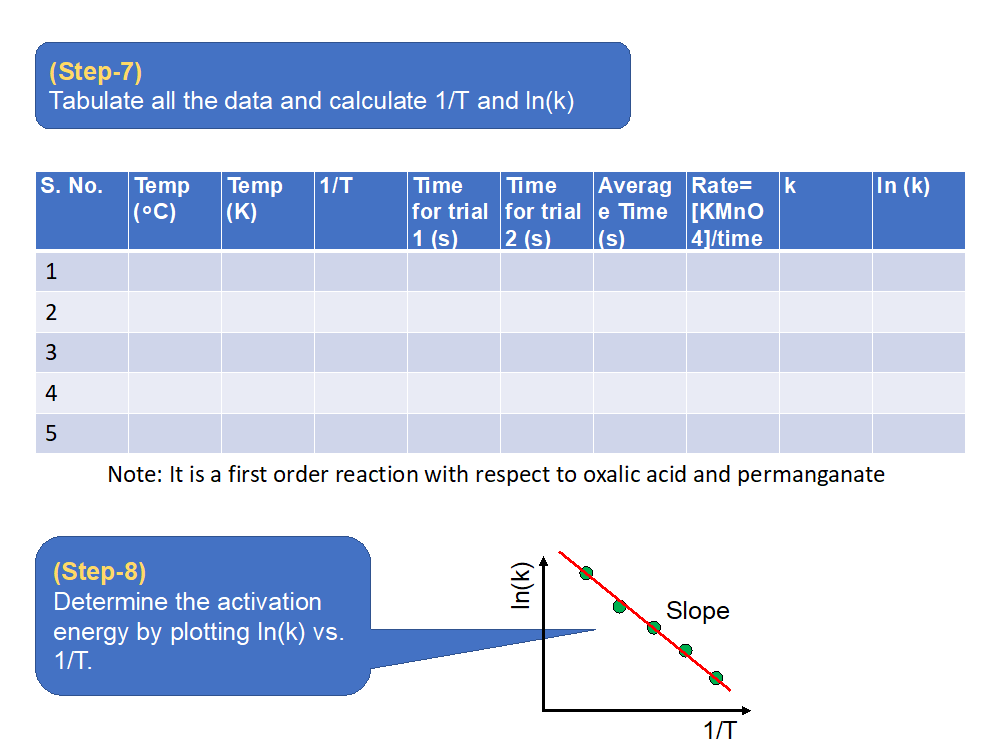
Therefore,
Slope = -Ea/R = - 8270 K
Then Ea E(a )=(8270 K ×R)
=(8270 K×8.314 J 〖mol〗-1 K-1 )
= 68.75 kJ 〖mol〗-1
Activation Energy for this chemical reaction = 68.75 kJ mol-1
Analysis
Therefore,
Slope = -Ea/R = - 8270 K
Then Ea Ea =(8270 K ×R)
=(8270 K×8.314 J 〖mol〗-1 K-1 )
= 68.75 KJ 〖mol〗^(-1)
