Determination Discharge Coefficient for flow through an Orifice
Introduction
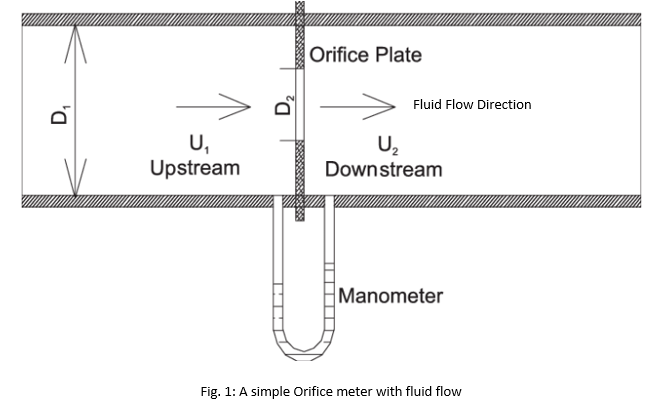
An Orifice meter is a simple device used for measuring the flow rate of liquid flowing through a pipe. It works on a simple principle of pressure differential. This pressure differential is measured with the help of differential manometer which enables the determination of the discharge through the pipe. There is basically an Orifice Plate installed in the orifice meter which provides obstruction to the fluid flow. Here, the streamline contracts because of the area contraction due to orifice which is placed between the pipe by the flange. Differential pressure is developed across the Orifice Plate which is directly proportional to the flow-rate of the liquid or gas.
Components of an Orifice meter Test Rig
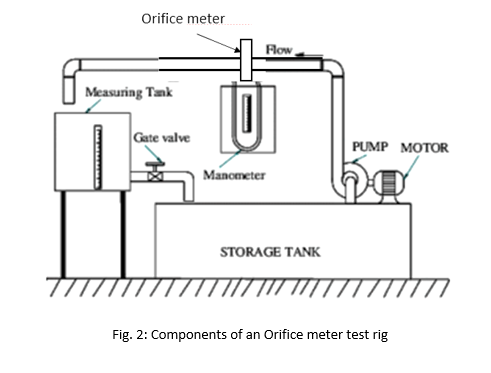
Fig. 2, shows a test rig or bench for Orifice meter whose each part is explained as follow:
1. Flow Meter
- Flow Meter
The test bench consists of flow meter with of size 25 mm for the experiments. The meter is equipped with adequate control cocks.
2. Strainer
A strainer acts like a filter which stops the solid particles entering the impeller through suction pipe. Strainer is attached at that end of the suction pipe which is dipped into the sump.
3. Piping
Piping in the test bench consist of G.I. pipes of size 25 mm with sufficient lengths on the upstream and downstream, also provided with separate control valves. Individual upstream and downstream pressure feed pipes are provided for the measurement of pressure heads with control valves situated on a common pipe for easy operation.
4. Centrifugal pump
A mono block centrifugal pump is provided with the test bench which delivers the water through the test bench pipeline fittings and Orifice meter. The pump is rigidly fixed onto sump tank.
5. Measuring Tank
Measuring tank with gauge glass and scale arrangement for quick and easy measurement to determine height of water filled in the tank
6. Differential Manometer
A Differential manometer with 1 mm scale grading is provided to measure the differential pressure head produced by the Orifice meter.
7. Sump
Sump is a water tank which stores adequate amount of water for circulation through the entire unit for experimentation and is arranged on the floor of the test bench
Working of an Orifice meter
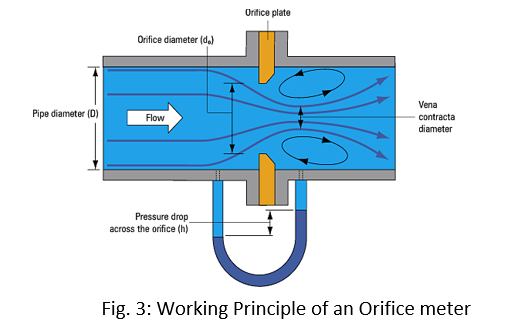
The fluid flowing in the pipe starts to converge when it sees the orifice ahead of it. The amount of convergence of the flow depends on the size and location of orifice. Once the fluid reaches the bore and passes through the orifice, the convergence of fluid does not stop immediately. As the fluid converges more and more, the pressure decreases more and more.
Due to the inertia of flowing fluid, the fluid tends to converge upto some distance downstream the plate and it reaches a point known as vena contracta. At the point of vena contracta, the state of fluid is such that it has a of maximum velocity and minimum pressure. It’s important to properly design orifice plates so that the pressure of the fluid does not fall below its vapor pressure at the given temperature or otherwise if pressure falls below the vapor pressure then the fluid will vaporize in the vena contracta region and the phenomenon of cavitation may take place which can damage the pipe.
