Newton’s ring experiment: to determine the wavelength of light
Apparatus
Travelling microscope, sodium vapor lamp, Newton’s ring apparatus.
Formula

Prior Concept
Monochromatic and Coherent source, Principle of superposition, Interference, Path difference, thin film, Interference in thin film, condition for Maxima and Minima for intensity of light etc.
Theory
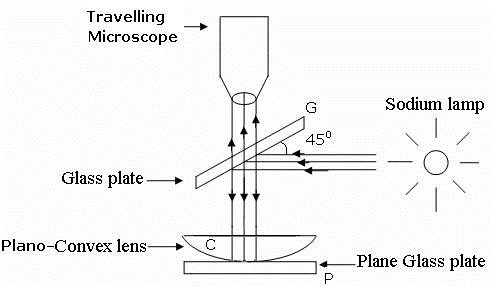
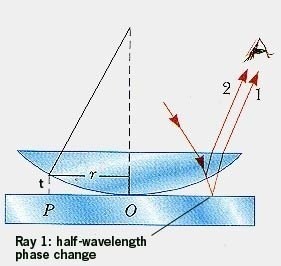
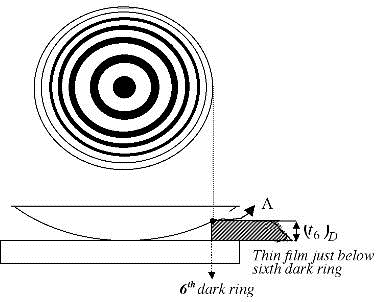
Circular interference fringes produced by enclosing a thin air film of varying thickness between the surface of a convex lens of large radius of curvature & plane glass, plate known as Newton’s ring. The light from a monochromatic source is rendered parallel by convex lens L. It is made to fall on a glass plate G inclined at angle 450 to the incident beam. It is made to fall on a glass plate ‘p’ as in diagram. Light rays reflected from top & bottom surface of the air film superimpose in such way to measure the diameter of the fringes.
The diameters of nth & mth dark fringes are given by,

Subtracting these we get
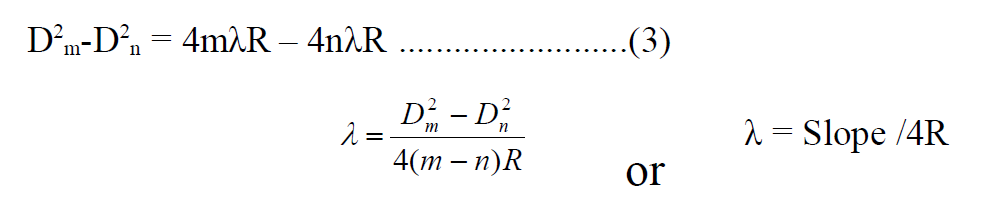
Substituting the values in above equation we can find out the radius of curvature also.
Diagram