Heat Transfer Co-efficient in Natural Convection
INTRODUCTION
User Objectives and Goals:
- To determine the total thermal resistance of the composite slab
- To determine the total thermal conductivity of the composite slab.
- To plot the temperature vs distance graph
Theory
Natural convection heat transfer takes place by movement of fluid particles on solid surface caused by density difference between the fluid particles on account of difference in temperature. Hence there is no external agency facing fluid over the surface as shown in Fig 1. It has been observed that the fluid adjacent to the surface gets heated, resulting in thermal expansion of the fluid and reduction in its density. Subsequently a buoyancy force acts on the fluid causing it to flow up the surface. Here the flow velocity is developed due to difference in temperature between fluid particles. Fig 2 shows experimental setup which demonstrates heat transfer by natural convection
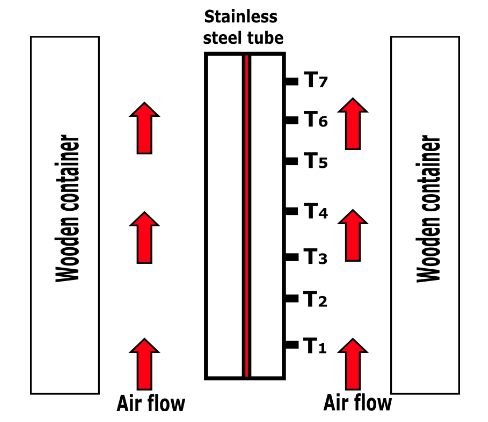
Fig 1. Schematic representation of heat transfer by natural convection

Fig 2. Experimental setup demonstrating heat transfer by natural convection
A vertical Cylinder can be treated as a vertical plate when
Therefore,
(complex but more accurate)
