Measurement of electrical conductance to determine the dissociation constant of acetic acid
Materials & Reagents Required:
A. Volumetric flask (100 mL)
B. Measuring cylinder (100 mL)
C. Burette (25 mL)
D. Conical flask (100 mL)
E. Beaker (250 mL)
F. Conductivity meter
Procedure in laboratory (diagram)



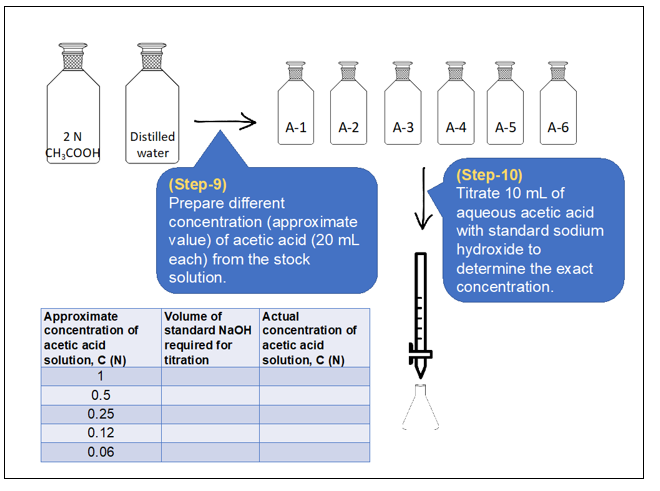
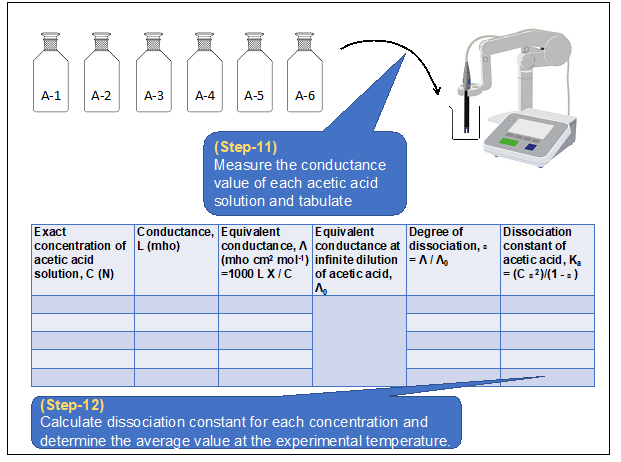
Procedure in laboratory
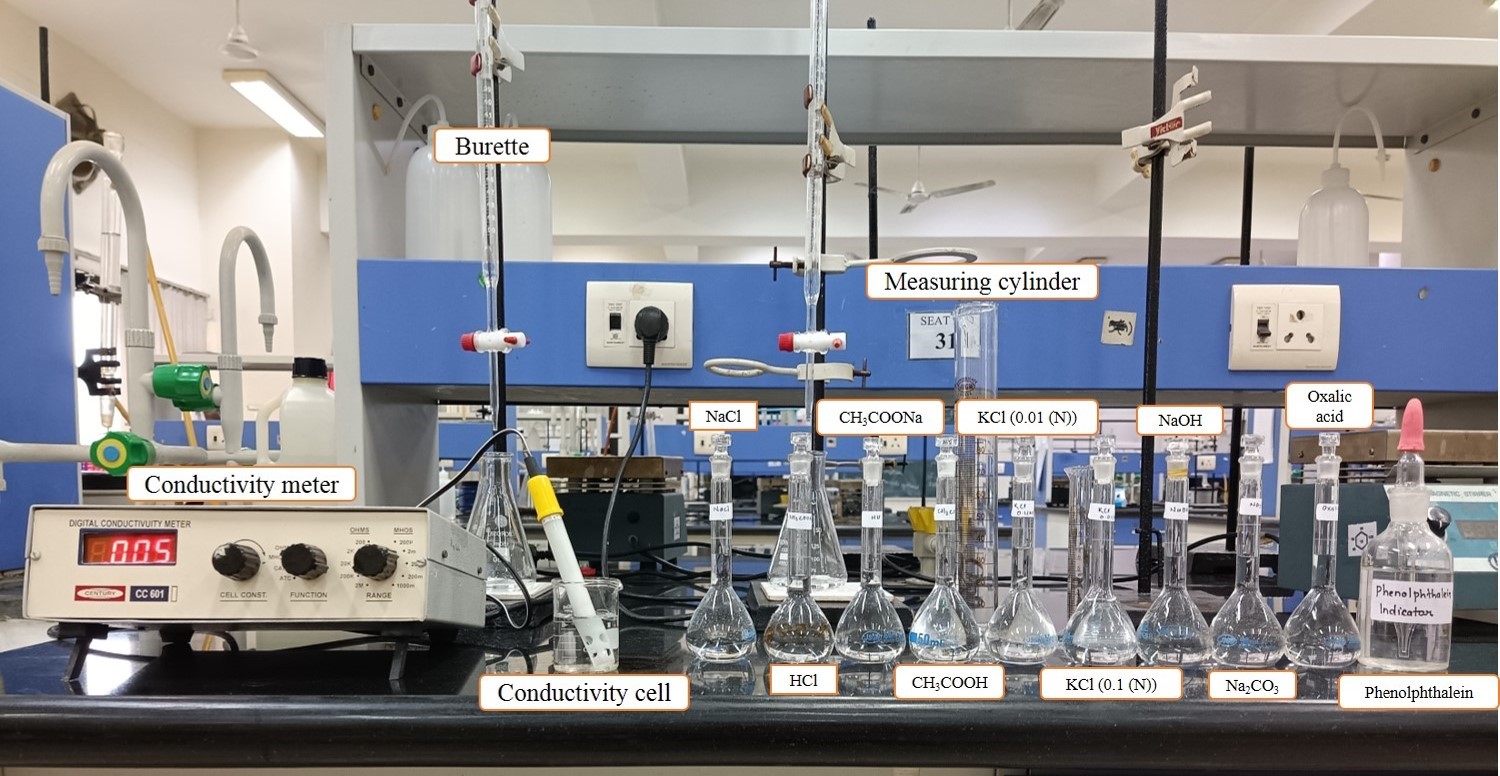

Sample Data and Analysis
The experimental temperature is 26 ⁰C.
Determination of cell constant
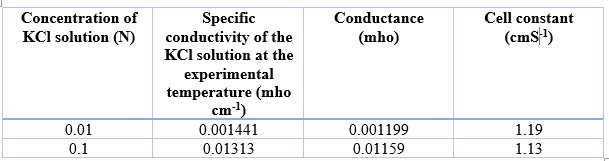
Average cell constant = (1.19+1.13)/2 = 1.16 cm-1
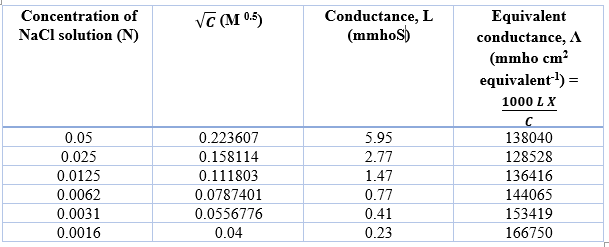
Determination of equivalent conductance of NaCl at different concentrations
Determination of equivalent conductance of HCl at different concentrations
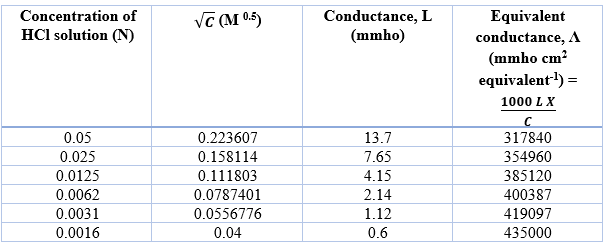
Determination of equivalent conductance of CH3COONa at different concentrations
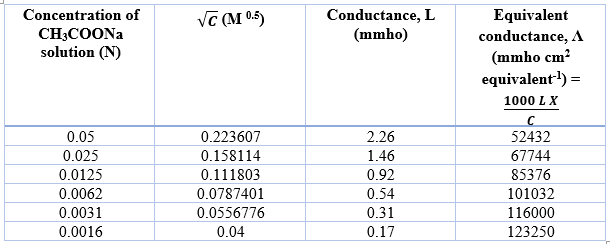
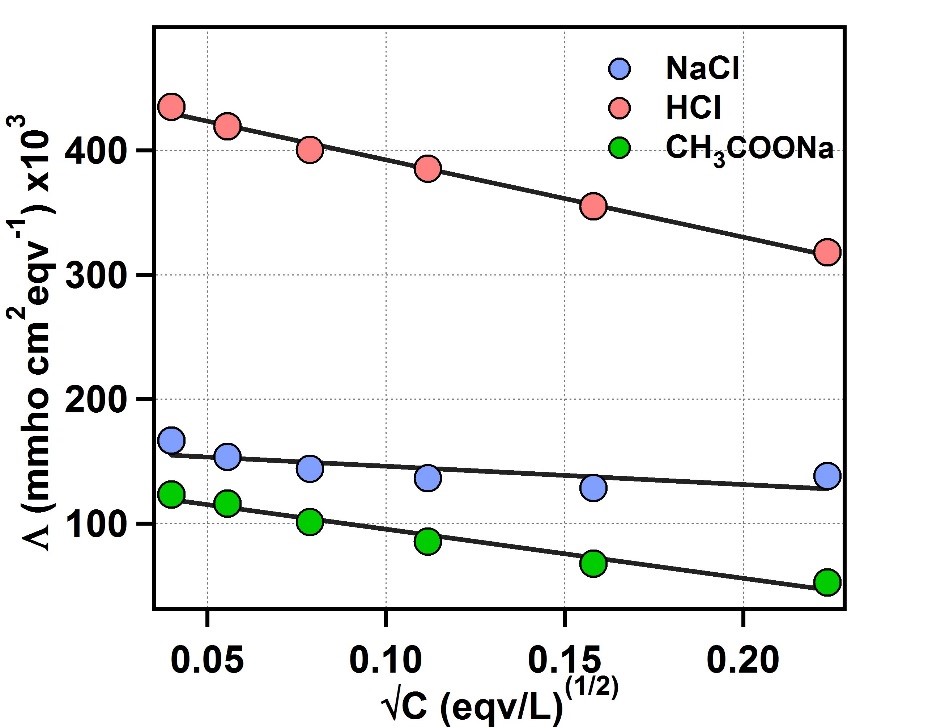
Figure 1: Plot of equivalent conductance vs √C for NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa.
The Y-axis intercept for NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 169960 mmho cm2 eqv-1, 454680 mmho cm2 eqv-1, 135130 mmho cm2 eqv-1, respectively.
The equivalent conductance of acetic acid at infinite dilution (Λ0) is given as,
Λ0 = Λ0CH₃COONa + Λ0HCl - Λ0NaCl
= (135130+454680-169960) mmho cm2 eqv-1
= 419850 mmho cm2 eqv-1
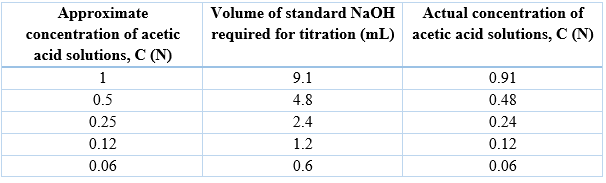
Determination of exact concentration of acetic acid solutions
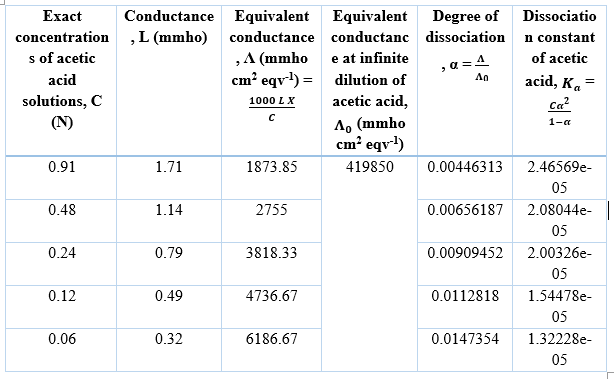
Determination of dissociation constant of acetic acid by conductance measurement
Procedure in simulator of the experiment
7. Analysis
A. Determine the cell constant of the conductivity cell.
B. Determine equivalent conductance at infinite dilution for NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa.
C. Determine the dissociation constant of acetic acid by conductivity measurement.
