Ion exchange column for removal of hardness of water
3. Theory of the Experiment:
The presence of calcium (Ca2+) and/or magnesium (Mg2+) in water results in water being considered “hard”. Calcium and magnesium ions in water react with soap to produce insoluble components and decrease the effectiveness of the soap for cleaning. Hard water can be softened using an ion exchange softening process. The ion exchange water softening process can remove nearly all calcium and magnesium from water.
During ion exchange treatment, water is passed through a resin containing exchangeable ions. Stronger binding ions displace weaker binding ions in the resin and are removed from the water. There are two types of ion exchange – anion exchange and cation exchange. Anion exchange resins generally exchange chloride for anionic contaminants.
Cationic ion exchange involves removing the calcium and magnesium ions and replacing them with soft ions, typically sodium, supplied by dissolved sodium chloride salt, or brine. The ion exchange column contains a microporous exchange resin, usually sulfonated polystyrene beads that are supersaturated with sodium to cover the bead surfaces. As water passes through this resin bed, calcium and magnesium ions attach to the resin beads and the loosely held sodium is released from the resin into the water.
The softening process is illustrated in Fig. 1. After softening a large quantity of hard water, the column becomes saturated with calcium and magnesium ions. When this occurs, the exchange resin must be regenerated, or recharged. To regenerate, the ion exchange resin is flushed with a brine or sodium hydroxide solution. The sodium ions in the solution are exchanged with the calcium and magnesium ions in the resin and excess calcium and magnesium is flushed out with wastewater.
img src (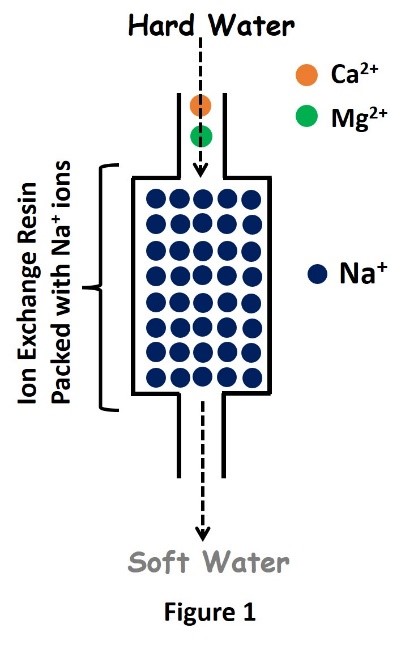 )
)
The estimation of hardness is based on complexometric titration. Hardness of water is determined by titrating with a standard solution of ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) which is a complexing agent. Since EDTA is insoluble in water, the disodium salt of EDTA is taken for this experiment. EDTA can form four or six coordination bonds with a metal ion.
EDTA (Ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid) forms colourless stable complexes with Ca2+and Mg2+ ions present in water at pH = 9-10. To maintain the pH of the solution at 9-10, a buffer solution (NH4Cl + NH4OH) is used. Eriochrome Black-T (E.B.T) is used as an indicator. The sample of hard water is treated with the buffer solution and EBT indicator and forms an unstable, wine-red colored complex with Ca2+and Mg2+ present in water.
img src (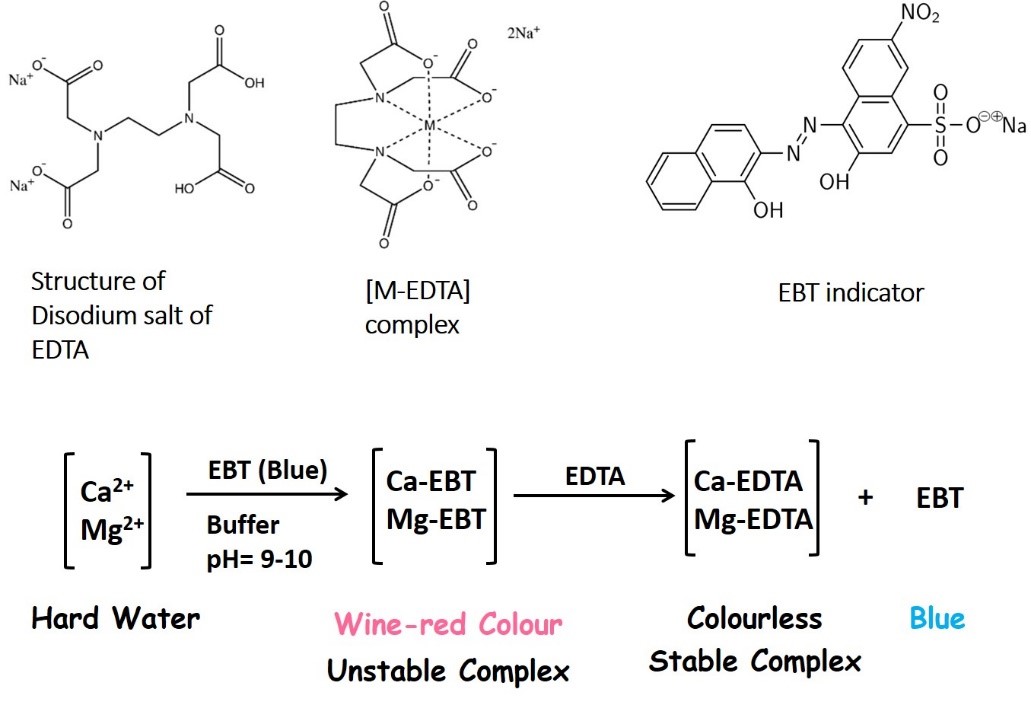 )
)
