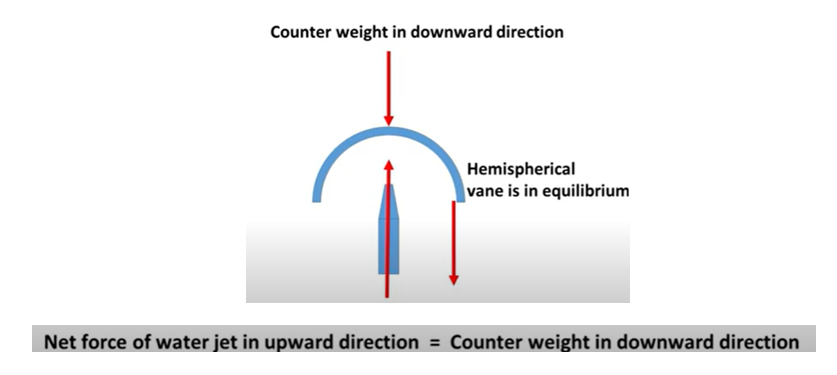
Verification of impulse momentum principle
Many problems cannot be easily solved by consideration of energy principle (Bernoulli's equation) alone due to complicated geometry of flow in some situations. Examples of such flows are in pumps, turbines, vanes, pipe bends & enlargements etc. In such cases impulse momentum principle can be conveniently used. It states that the impulse of the force or product of the force and the time increment during which it acts is equal to the change in the momentum of the body i.e. product of the mass of the body on which the force acts and the velocity of the body.