Heat Exchangers
INTRODUCTION
User Objectives and Goals:
- To determine the Log mean temperature difference.
- To determine the overall heat transfer coefficient for the inside area.
- To determine the effectiveness of the heat exchanger.
Theory
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between two fluids, one hot and one cold as shown in Fig. 1.
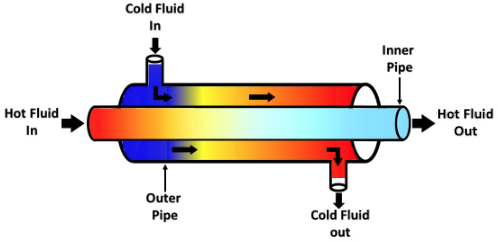
Fig 1. Schematic representation of a heat exchanger
Heat transfer from one fluid to another fluid is given by the expression,
Q=A×U×(∆T)m
Where,
(∆T)m is the mean temperature difference
U is the overall heat transfer coefficient for the inside area
A is the inside area of the heat exchanger
Temperature Profiles for Parallel and Counter Flow Heat Exchangers
For which,
(∆T)m=log(θi/θo)θi−θo
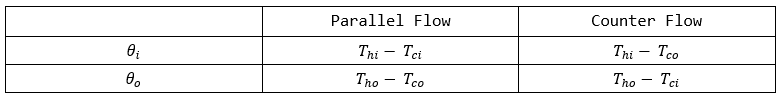
This expression for the mean temperature difference is known as the Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD).
U=(∆T)m×AQabsorbed
In order to make comparisons between various types of heat exchangers, the term Heat Exchanger Effectiveness is used, which is defined as:
∈=Maximum possible heat transferActual heat transfer
Actual heat transfer may be computed by calculating the energy lost by the hot fluid or the energy gained by the cold fluid as
Q=Ch(Thi−Tho) or Q=Cc(Tco−Tci)
Both for parallel and counter flow heat exchanger where
Ch=WhCph and Cc=WcCpc
Wh = mass of hot fluid flowing per unit time
Wc = mass of cold fluid flowing per unit time
Cph and Cpc are the specific heats of the hot and cold fluid respectively
Maximum possible heat transfer is given by
Qmax=Cmin(Thi−Tci)
Where Cmin is either Cph or Cpc, whichever is lesser.
Hence, effectiveness
∈=Cmin(Thi−Tci)Ch(Thi−Tho)
∈=Cmin(Thi−Tci)Cc(Tco−Tci)
Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD).
(ΔT)m=log(θi/θo)θi−θo U=(ΔT)m×AQabsorbed
Effectiveness (ϵ)
∈=Cmin(Thi−Tci)Ch(Thi−Tho)
∈=Cmin(Thi−Tci)Cc(Tco−Tci)


