Determination of Friction Coefficient of pipe of various diameters
The following steps are to be followed to calculate the friction coefficient of pipes:
- Check whether all the joints and the sump are not leaking
- Close all the cocks, pressure feed pipes and manometer to prevent damage and overloading of the manometer. Check the gauge glass and meter scale assembly of the measuring tank and see that it is fixed water height and vertically.
- Check proper electrical connections to the switch, which is internally connected to the motor. First open the inlet gate valve of the apparatus. Adjust the control valve kept at the exit end of the apparatus to a desired flow rate and maintain the flow steadily.
- The actual discharge is measured with the help of the measuring tank. The differential head produced by the flow meter can be found from the manometer for any flowrate.
- Start the motor keeping the delivery valve close. The water is allowed to flow through the selected pipe by selecting the appropriate ball valve.
- By regulating the valve control the flow rate and select the corresponding pressure tappings. Make sure while taking readings, that the manometer is properly primed. Priming is the operation of filling the manometers upper part and the connecting pipes with water by venting the air from the pipes.
- Note down the difference of head “h” from the manometer scale, and time required for the rise of 10 cm (i.e. 0.01m) water in the collecting tank by using stop watch.
- The actual loss of head is determined from the Manometer readings. The frictional loss of head in pipes is given by the Darcy's formula. The friction coefficient indicates ' f '
- Repeat the steps 4 to 8 for different sets of readings by regulating the discharge valve
Formulae –
Calculate Actual Discharge (Qact)
Note down the time required for the rise of 10 cm (i.e 0.1 m) water in the collecting tank by using stop watch. Calculate discharge using below formulae:
Discharge: The time taken collect some ‘R’ cm of water in the collecting tank
Qact=((A×R)/t)
A = area of the collecting tank in m²
R = rise of water level taken in meters (say 0.1 m or 10 cm)
t = time taken for rise of water level to height ‘R’ in secondsCalculate the velocity of the jet by following formula:
V= Discharge/(area of Pipe)= Qact/A
D = pipe diameter
A = Cross sectional area of the pipe = (πD2)/4The head calculated from Darcy's formula should be equal to manometer head. Then, we can calculate the friction factor for the given pipe by
hf= f (4LV2)/2gD
Where,
H= difference of head in meters =(h1-h2 )×((sm)/sw -1)
or H =(h1-h2 )×12.6 or (h)×12.6
sm = Specific gravity of mercury =13.6
sw = specific gravity of water = 1
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m2⁄s)
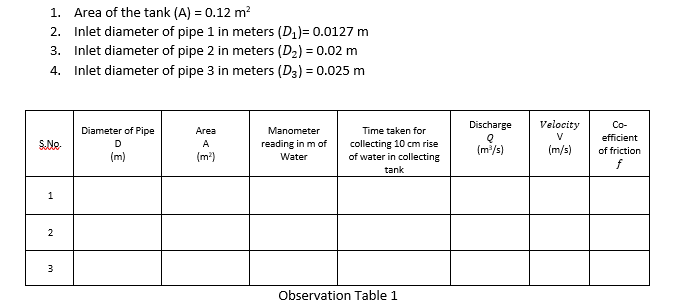
Observations –