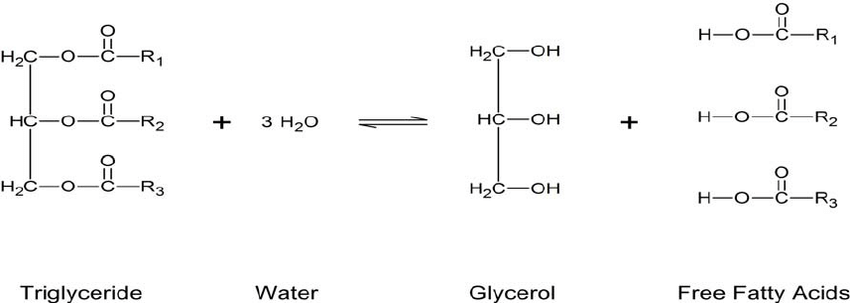
Determination of free fatty acid content in fats and oils
The quality of edible oil is of primary importance to both manufacturers and consumers of deep fried food products. Edible oil is subject to significant chemical changes and formation of degradated hazardous products for human being. Free fatty acids (FFA) are produced by the hydrolysis of oils and fats. The level of FFA depends on time, temperature and moisture content because the oils and fats are exposed to various environments such as storage, processing, heating or frying. Since FFA are less stable than neutral oil, they are more prone to oxidation and lead to various undesirable changes like production of off flavor, decrease of smoke point and acceleration of further hydrolysis. Thus, FFA is a key feature linked with the quality and commercial value of oils and fats. Free fatty acid is the amount of fatty acids hydrolyzed from triacylglycerols and represented as the percentage by weight of a specific fatty acid generally oleic acid.