Flow through Fluidized Bed
Apparatus required :
CCL4 manometer, Hg manometer, bucket, Stop watch.
Procedure :
- Keep the bypass valve open and the main valve closed. Switch on the pump.
- Connect CCL4 manometer across the bed.
- Allow the fluid through flow through the bed by opening the main valve.
- Ensure for steady flow condition note down the flow rate using the rotameter .
- The corresponding height of the bed and the difference in levels in the manometer limbs to be noted down.
- The procedure is to be repeated for different flowrates, both for static and fluidized bed conditions.
- Use Hg manometer for higher flow rates.
- Collect the the fluid present in the static bed after closing the main valve, to calculate the void volume.
Data :
Column Diameter = D = cm
Height of static bed = Lmf =
Viscosity of fluid = .gif) = cp
= cp
Density of fluid = kg/m3
Density of CCl4 = kg/m3
Density of Hg = kg/m3
Packing type =
Density of packing material= .gif) p = kg/m3
p = kg/m3
.gif) = Sphericity =
= Sphericity =
Specific surface area of packing = S = m2/m3=surface area/unit bed volume
Observations :
Volume of voids = m3
| Sl No. |
Manometer reading  |
Height of bed(L)cm |
Rotameter reading | Volumetric flow rate m3/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Calculations :
Minimum bed porosity = .gif) =void volume/volume of bed
=void volume/volume of bed
Volume of Bed =.gif)
Superficial velocity = .gif)
Cross sectional area of the tube, .gif)
.gif) = m H2o
= m H2o
.gif) m = density of manometric fluid
m = density of manometric fluid
.gif) = N/m2
= N/m2
Bed Porocity .gif)
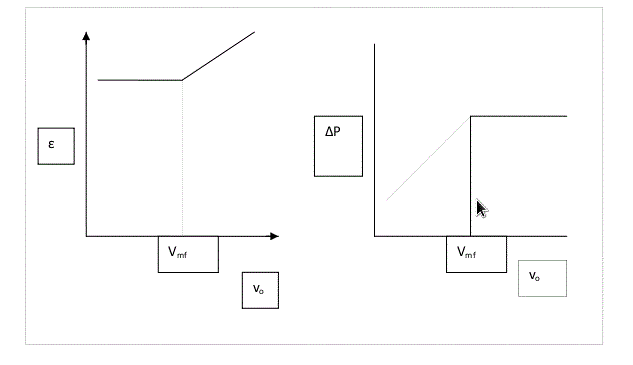
Plot .gif) vs
vs .gif) on a log-log graph
on a log-log graph
Plot .gif) vs
vs .gif) on a log-log graph.
on a log-log graph.
Determine minimum fluidization velocity (Vmf) from both the plots.
Theoretical value of minimum fluidization velocity:
Determine pressure drop per unit bed height under minimum fluidization condition.
.gif)
Ergun’s equation:
.gif)
Solve equation 1 and determine Vmf.
Results :
Report the values of minimum fluidization velocity obtained from plots and from Ergun's equation. Comment on effect of superficial velocity on .gif) and
and .gif) .
.
