Floating Point Numbers Representation
What are floating point numbers
As the name implies, floating point numbers are numbers that contain floating decimal points. For example, the numbers 5.5, 0.001, and -2,345.6789 are floating point numbers. Numbers that do not have decimal places are called integers.Computers recognize real numbers that contain fractions as floating point numbers. When a calculation includes a floating point number, it is called a "floating point calculation." Older computers used to have a separate floating point unit (FPU) that handled these calculations, but now the FPU is typically built into the computer's CPU.
Floating-Point Format
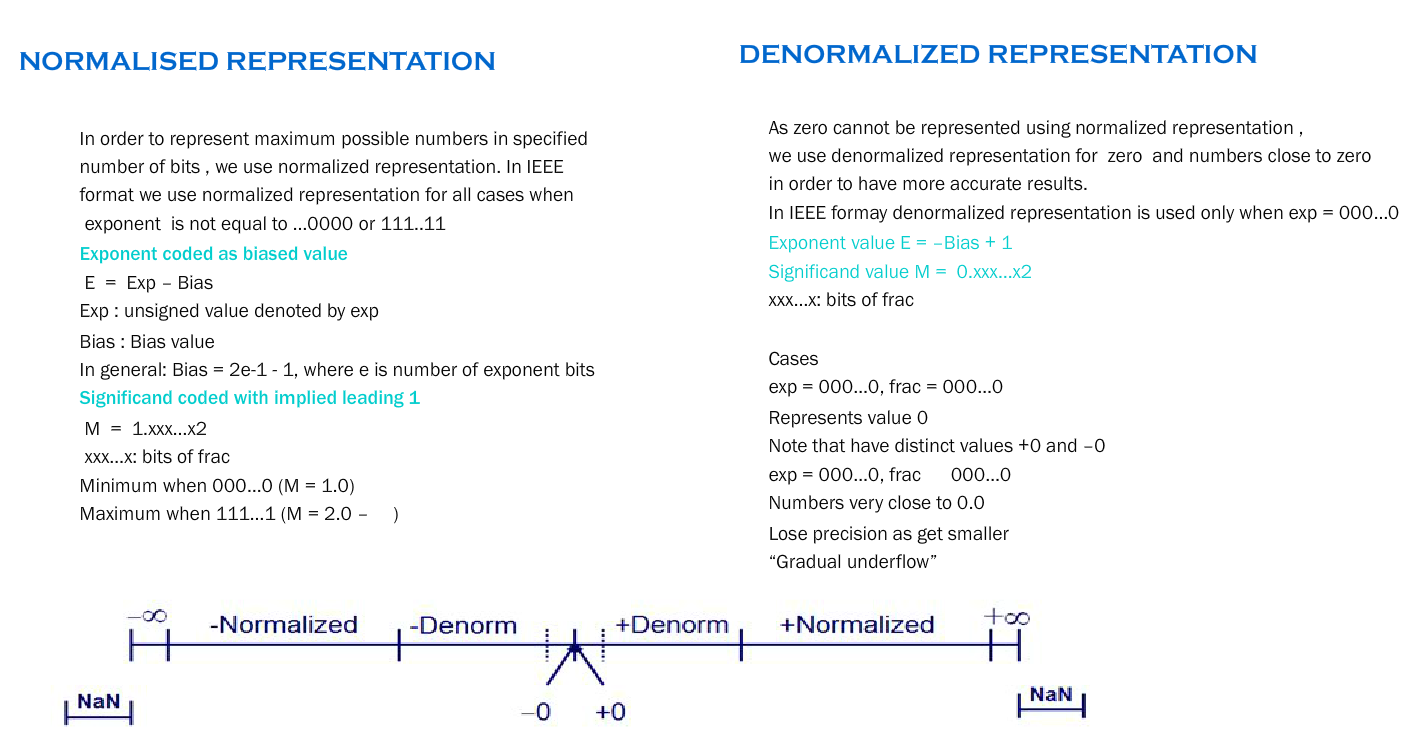
Computers store floating point numbers in a specific format . As our aim is to maximize the range of numbers that can be stored .FPUs typically represent real numbers in a binary floating-point format. In this format, a real number has three parts: a sign, a significand, and an exponent. The following explaination is in accordance with the standard IEEE format of 32 bit representation .

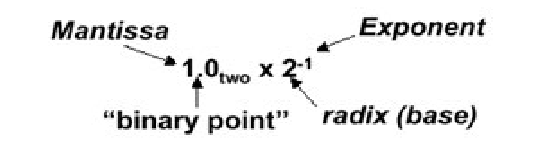
Exponent Field
-> 8 - Bits Long
-> Determines The Range Of Numbers That Can be Represented
-> Increasing The Bits Will Increase The Range , Not Precision
-> To Cover For -ve Numbers , exp = 127 + real exp
Sign Bit
-> 1- Bit Long
-> Dtermines The +ve or -ve number
-> 1 = -ve Number 0 = +ve Number
Mantissa Field
-> 23 - Bits Long
-> Determines the precision of Numbers
-> Increasing bits Will Increase precision, not range.
Consequence #1: Values are unevenly spaced
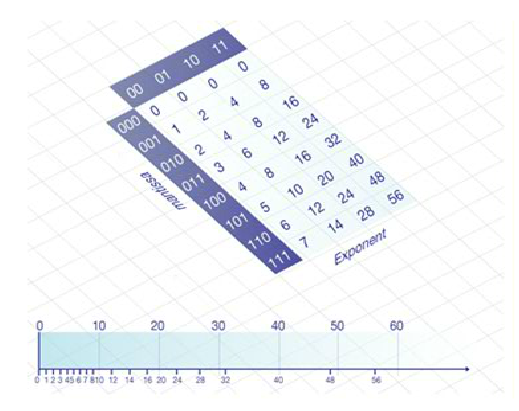
-> Imagine we only had 6 bits for each floating-point number (1 sign, 3 mantissa, 2 exponent)
-> Means less absolute precision for numbers with larger magnitudes
-> More bits ....More The Accuracy
-> That is why the numbers are more densed near the zero as compared to far away from the number line.
Consequence #2: Roundoff errors
-> Our system can represent 6, and it can represent ¼, but not 5¾
-> So 6 - 0.25 is 6, not 5.75
-> And if 6 - 0.25 - 0.25 - 0.25 - 0.25 is evaluated left to right, the answer is still 6
-> This is not random Happens exactly the same way every time