Emission spectra
Procedure
For Doing Simulation
- Move the slider in Calibrate Telescope and click the START button.
- Click on the combo box to select the lamp.
- Click Switch On Light.
- Set Vernier reading to 0° and telescope to 90° by adjusting both sliders.
- Click the Place Grating button.
- Turn the telescope to the left. Align the vertical cross wire with the green line on the pattern.
- Note the readings of Vernier 1 and Vernier 2.
- Move the telescope to the right side of the direct image and align the vertical cross wire with the green line on the pattern.
- Note the readings of Vernier 1 and Vernier 2 again.
- Use the slider under Fine Angle to get more precise readings.
- Calculate the difference between the two readings on the same Vernier.
- Take the mean value of this difference to get 2θ, twice the angle of diffraction. From this, θ is obtained for the green line.
- Assuming the wavelength of the green line is 546 nm, calculate the number of lines per mm using the equation: N = sinθ / (mλ) where m is the order.
For Doing the Real Lab
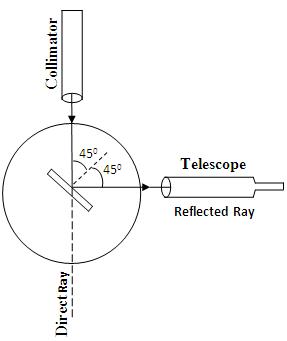
Setting the Grating for Normal Incidence Position
- Fix the Vernier table after making the preliminary adjustments.
- Illuminate the slit with a mercury vapour lamp and make the slit narrow.
- Bring the telescope in line with the collimator. Align the direct image of the slit with the vertical cross wire.
- Note down any one of the Vernier readings.
- Turn the telescope exactly through 90° and clamp it.
- Place the grating on the prism table with its ruled surface facing the collimator and perpendicular to the line joining the two leveling screws of the prism table.
- Unclamp the Vernier and rotate until the reflected image coincides with the vertical cross wire.
- Fix the prism table and note the Vernier readings.
- Unclamp the Vernier table and rotate exactly 45° in the proper direction so that the surface of the grating becomes normal to the collimator.
- Clamp the Vernier table.
Standardizing the Grating
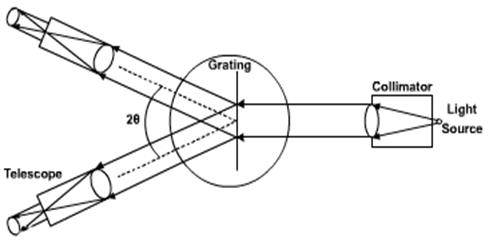
- Move the telescope to observe the direct image. Diffraction patterns will be seen on either side of the direct image.
- Turn the telescope to the left and align the vertical cross wire with the green line on the pattern.
- Note the readings of Vernier 1 and Vernier 2.
- Move the telescope to the right side of the direct image and align the vertical cross wire with the green line on the pattern.
- Note the readings of Vernier 1 and Vernier 2 again.
- Calculate the difference between the two readings on the same Vernier.
- Take the mean value of this difference to get 2θ. From this, calculate θ for the green line.
- Assuming the wavelength of the green line is 546 nm, calculate the number of lines per mm using the equation: N = sinθ / (mλ).
To Determine the Wavelength of Other Lines
Repeat the same procedure as above for other lines, and calculate their wavelengths using the equation:
λ = sinθ / (N × m)
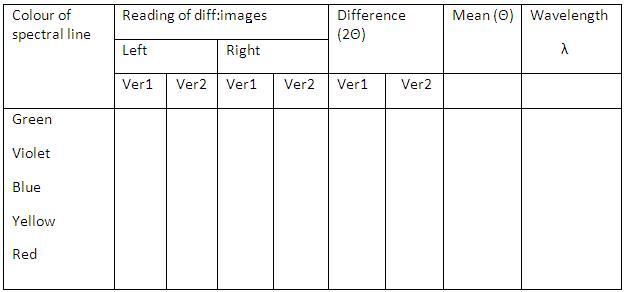
Results
The wavelength of the prominent lines of the mercury spectrum are given in nanometre in the tabular column.
Number of grating per metre=................/m
