Cryptographic Hash Function Properties
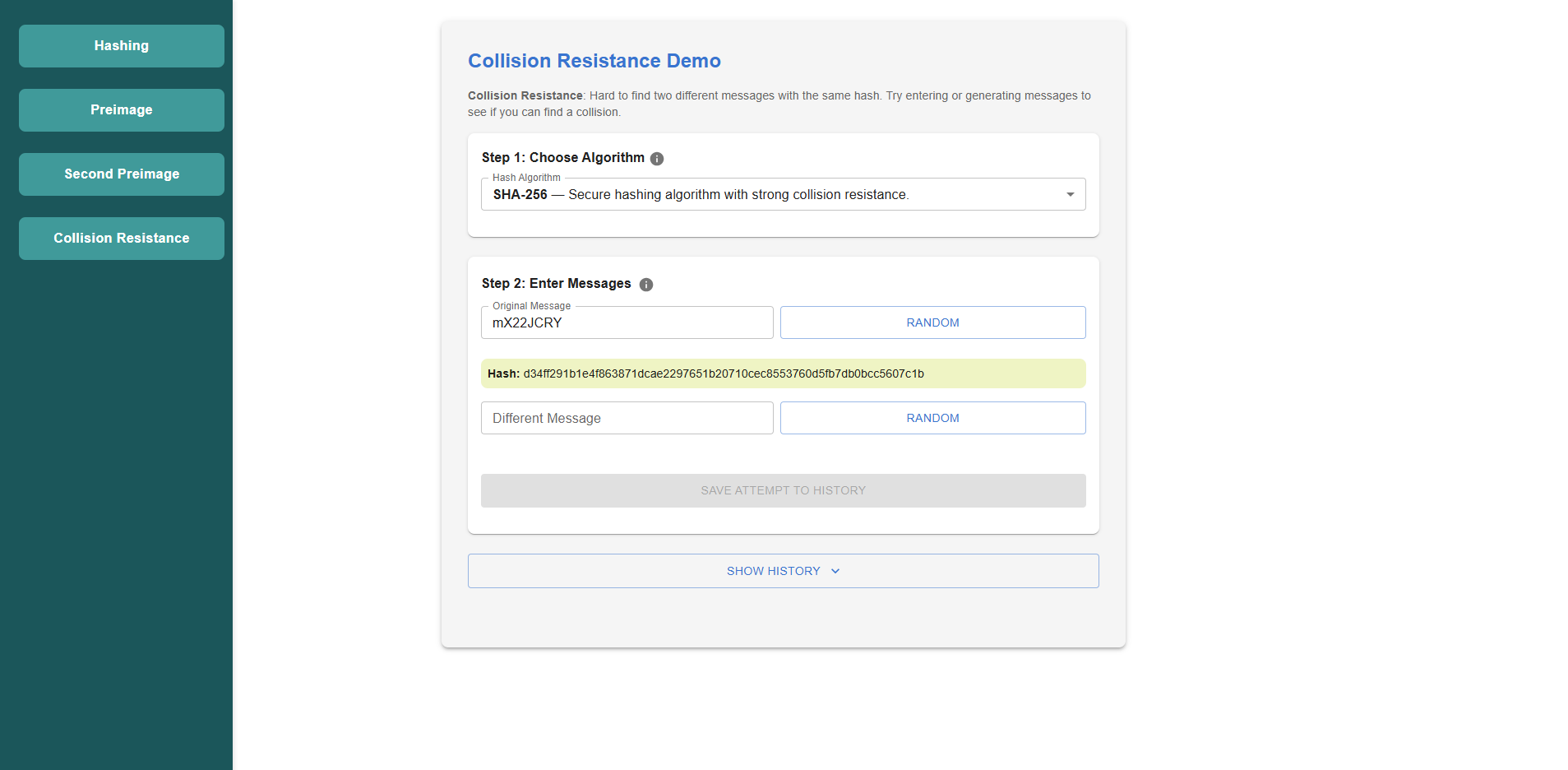
Hashing
- Click on the Hashing button from the left panel.
- Enter the text you want to hash in the Enter Text input box.
- (Optional) Click the Random Input button to generate a random message.
- Select the hashing algorithm (e.g., SHA-256, MD5, etc.) from the dropdown list.
- The hashed value of the input will be displayed in the output section.
Preimage
- Click on the Preimage button from the left panel.
- Step 1: A hidden input is hashed using the selected algorithm (e.g., SHA-256). Click Generate Hash to see the hash value.
- Step 2: Try to guess the hidden input by entering your guess in the text box.
- Click Submit Guess to check if your guess produces the same hash.
- If the hash matches, the hidden input is correctly guessed. If not, it demonstrates Preimage Resistance – showing that it is computationally hard to recover the original input from its hash.

Second Preimage
- Click on the Second Preimage button from the left panel.
- Step 1: Observe the Original Input and its corresponding hash generated using the selected algorithm (e.g., SHA-256).
- Step 2: Enter a different input into the text box.
- Click Check Match to see if the new input produces the same hash.
- If the hashes do not match, it demonstrates Second Preimage Resistance – meaning it is computationally infeasible to find another input that generates the same hash as the original one.
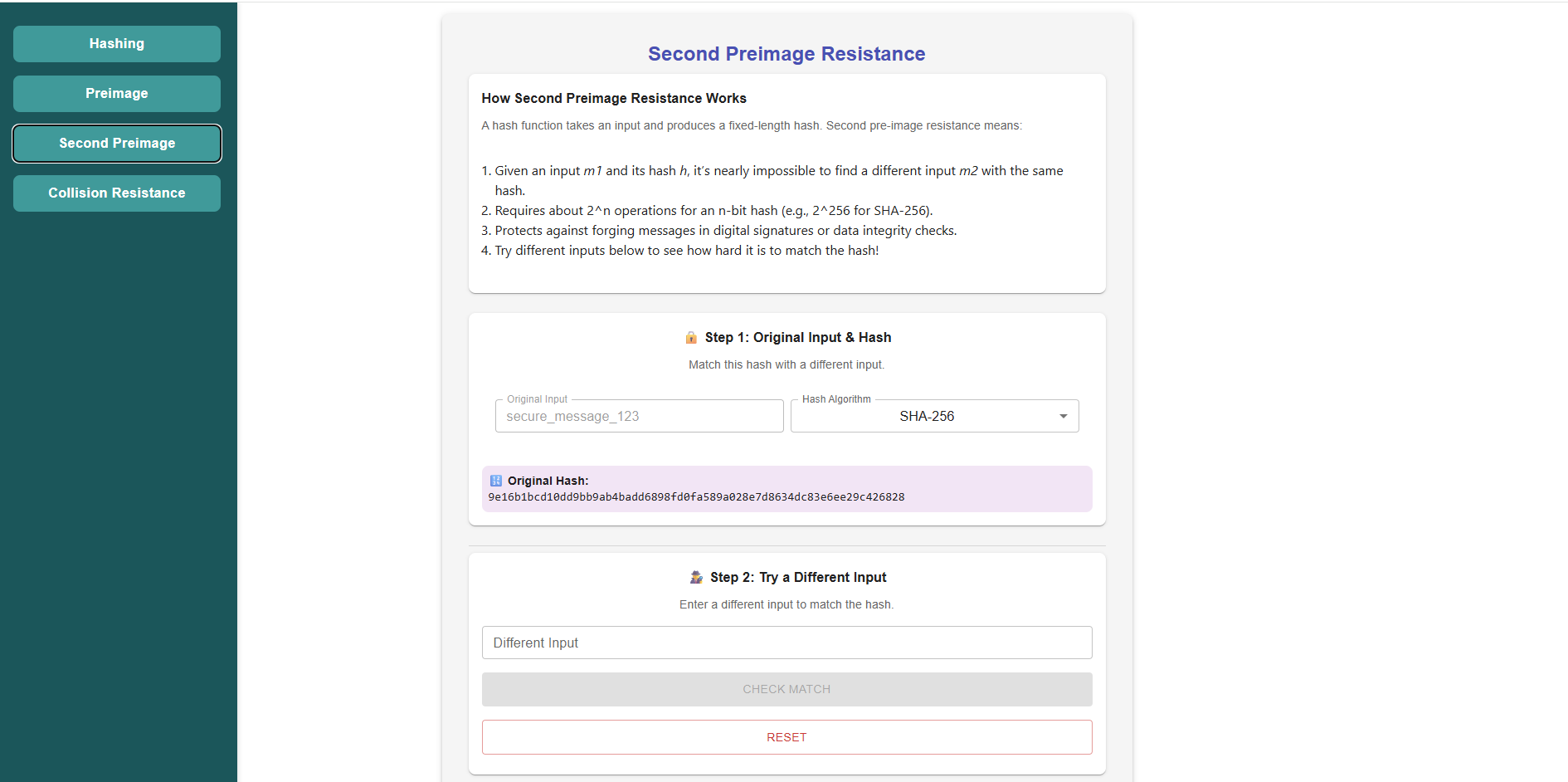
Collision Resistance
- Click on the Collision Resistance button from the left panel.
- Step 1: Select the hashing algorithm (e.g., SHA-256) from the dropdown.
- Step 2: Enter the Original Message manually or click Random to generate one automatically. Its hash will be displayed.
- Enter a Different Message manually or generate one using Random. Its hash will also be displayed.
- The system checks if the two hashes are identical:
- If the hashes are different, it confirms Collision Resistance, meaning it is very difficult to find two distinct inputs with the same hash.
- If the hashes are the same (collision), it would demonstrate a weakness in the algorithm.