To plot the V-I characteristic curve of a TRIAC and study its behavior during both positive and negative cycles of AC voltage
VI Characteristics:
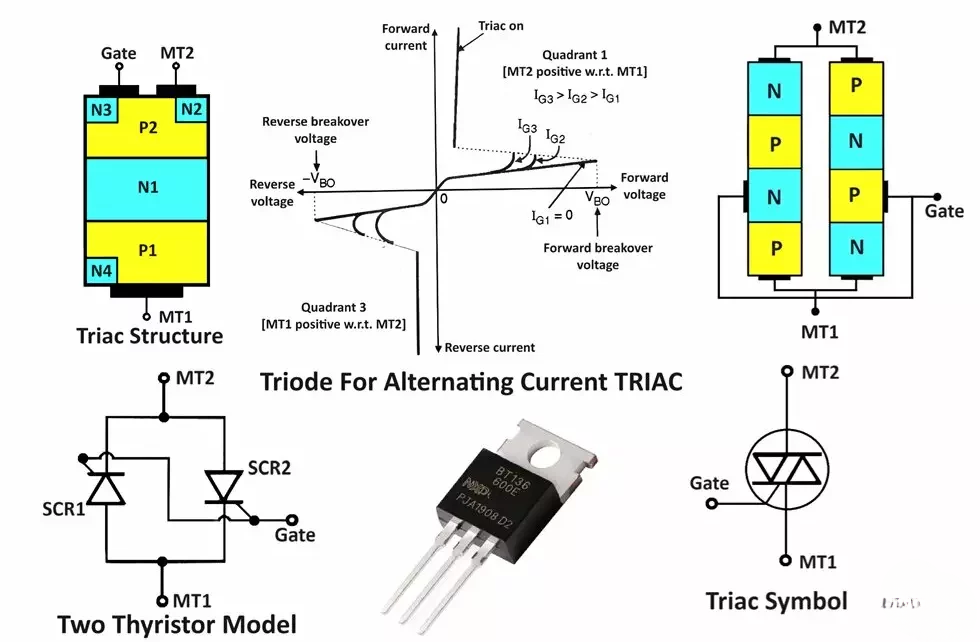
The characteristics of the triac are as shown in Figure 1 and they are similar to those of an SCR both in blocking and conducting states. The only difference is that the SCR conducts only in the forward direction (anode-cathode) whereas the triac conducts in both directions.
The other difference in the operation is the triggering mechanism. The triac can be turned on by applying either a positive or negative voltage to the gate with respect to terminal MT. Whereas the SCR can be triggered only by a positive gate signal.
The different States of Triac working (operation):
The three important states of triac operation are:1) Forward blocking state.
2) Reverse blocking state.
3) Conduction or on the state.
The different States of Triac working (operation):
Forward blocking state : (MT2 positive with respect to MT1):
When a forward voltage less than the break-over voltage Vn is applied with the gate terminal open the triac can successfully block the forward voltage without getting turned on.Reverse blocking state: (MT1 positive with respect to MT2):
When the reverse voltage is less than the breakover voltage Vpo with the gate open-circuited, the triac will block the reverse voltage without getting turned on.Conduction or ON state:
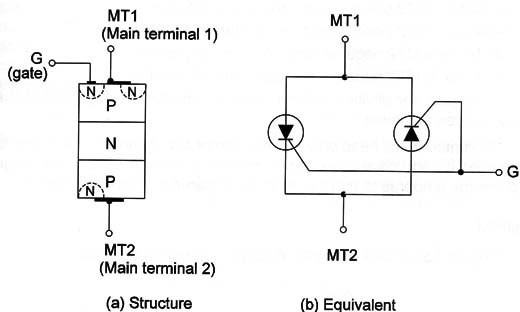
The triac is equivalent to two SCRs connected back to back. Therefore it is a bidirectional device that can conduct positive as well as negative half cycles of the supply voltage. As shown in Figure 2.The gate current can be positive or negative.
The forward and reverse break-over voltage reduces with an increase in the gate current.