Differentiating Blockchain Databases from Conventional Databases
This simulation demonstrates the differentiating properties of blockchain such as Immutability, Decentralization, and Performance.
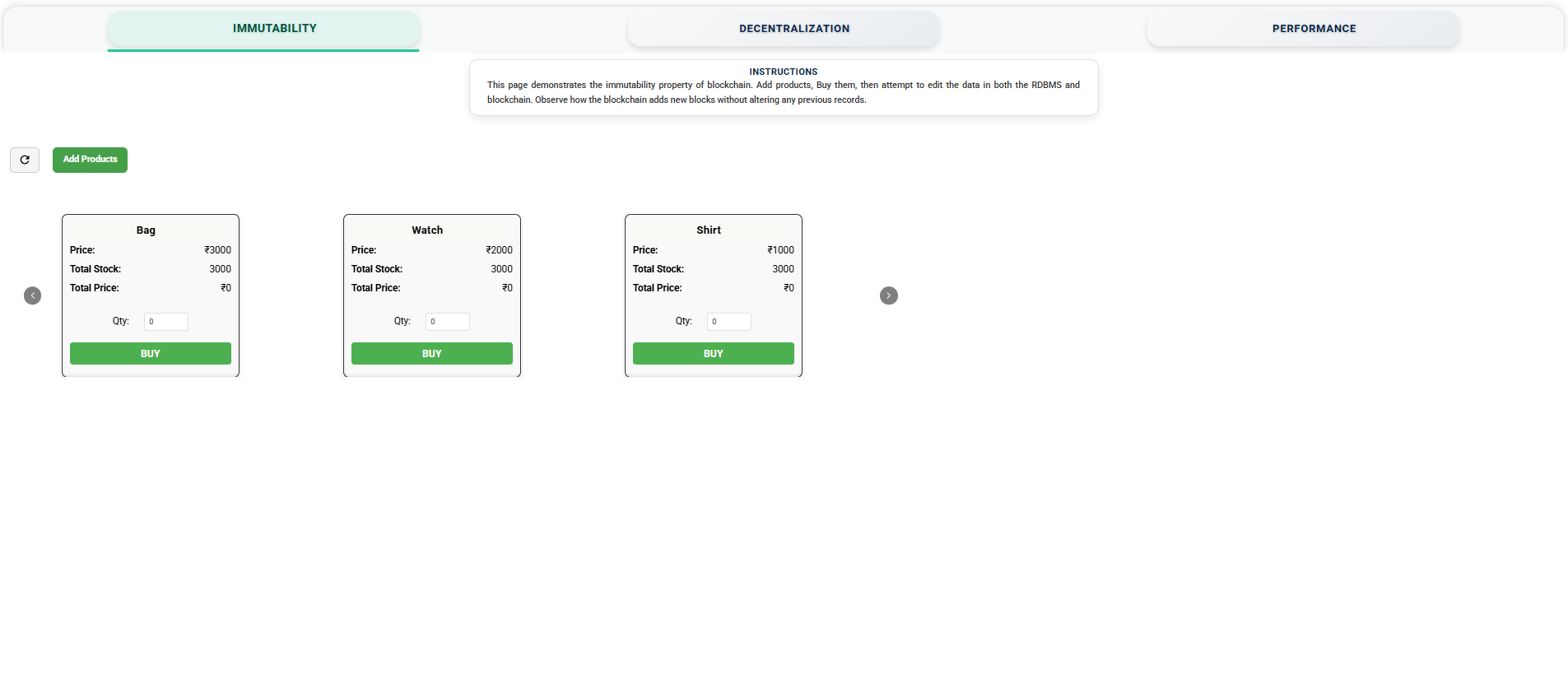
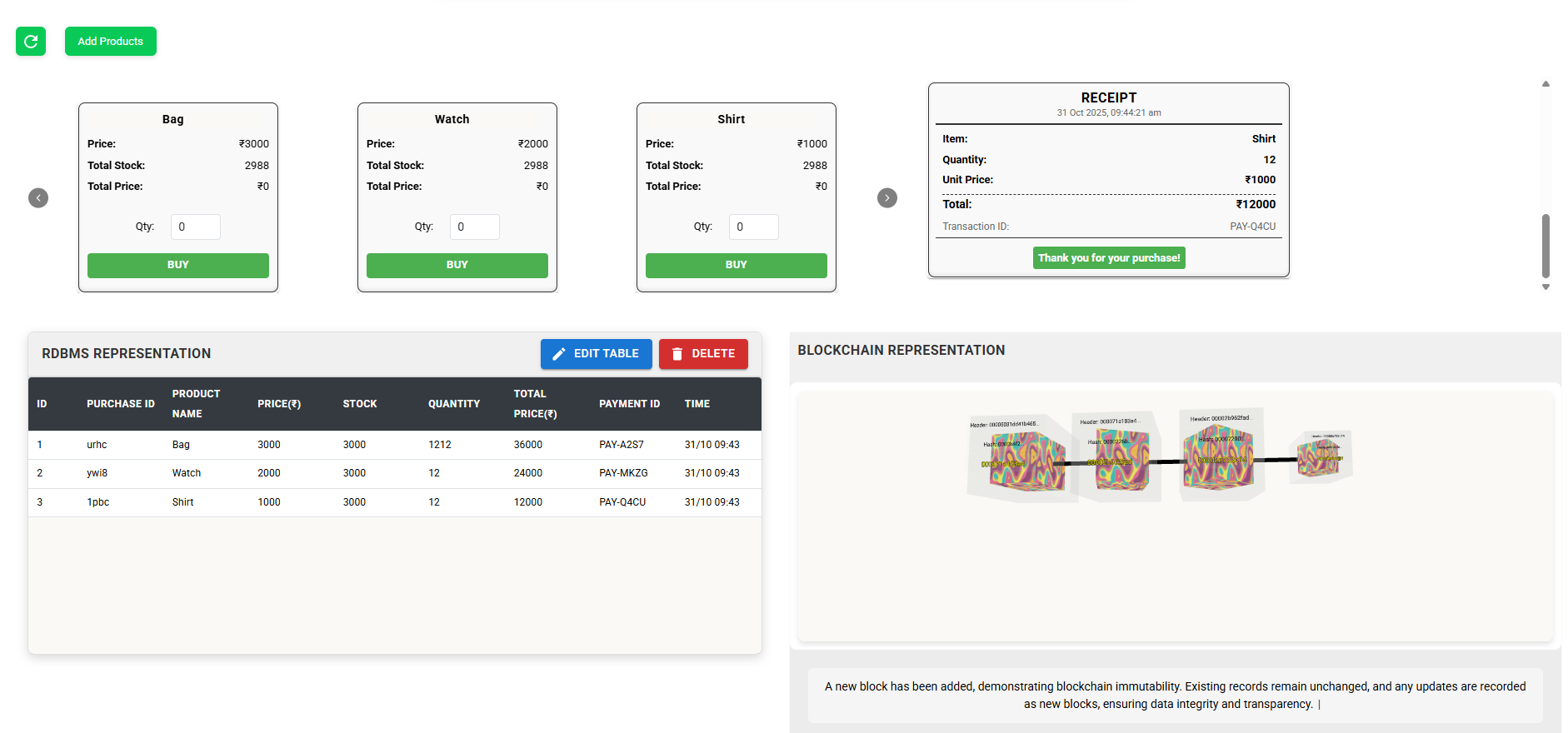
Immutability
This page demonstrates the immutability of blockchain. Add products and click the BUY button to purchase them.
Click the EDIT TABLE button to modify the data in the RDBMS Representation Table.
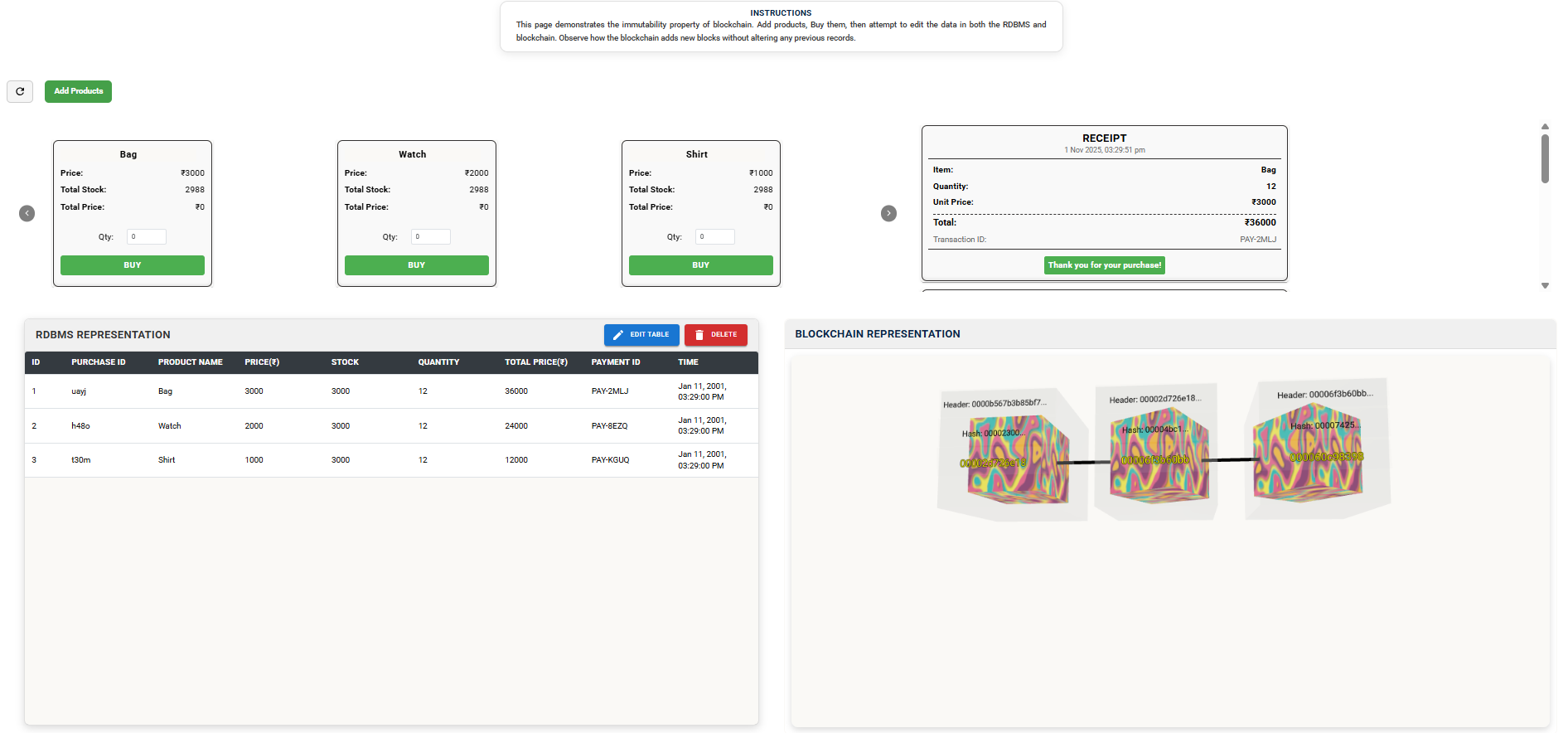
Once you have successfully edited the data in the RDBMS Representation Table, click the EDIT BLOCKCHAIN button under the Blockchain Representation section.
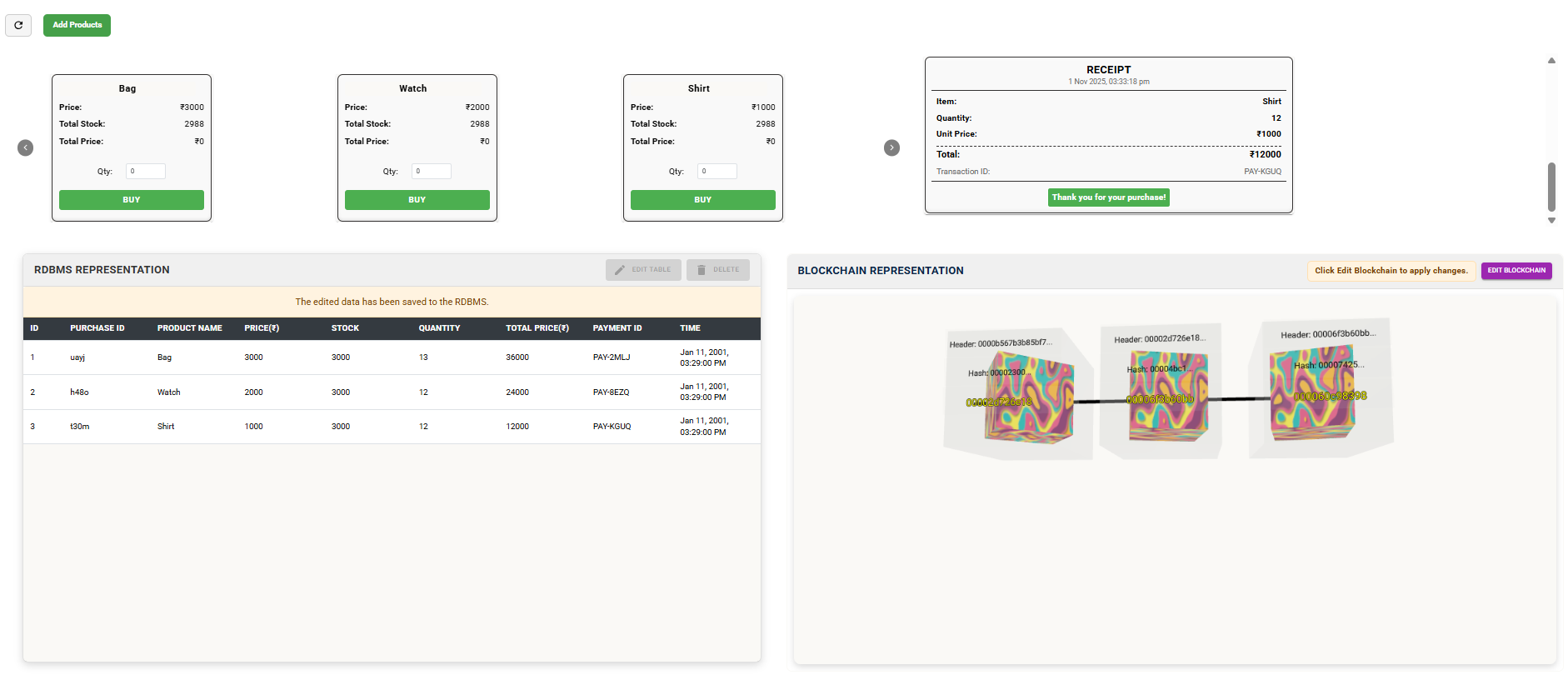
Observe how the blockchain reflects these updates immutably, ensuring that any modification creates a new linked block.
Decentralization
This page demonstrates the concept of decentralization in blockchain.
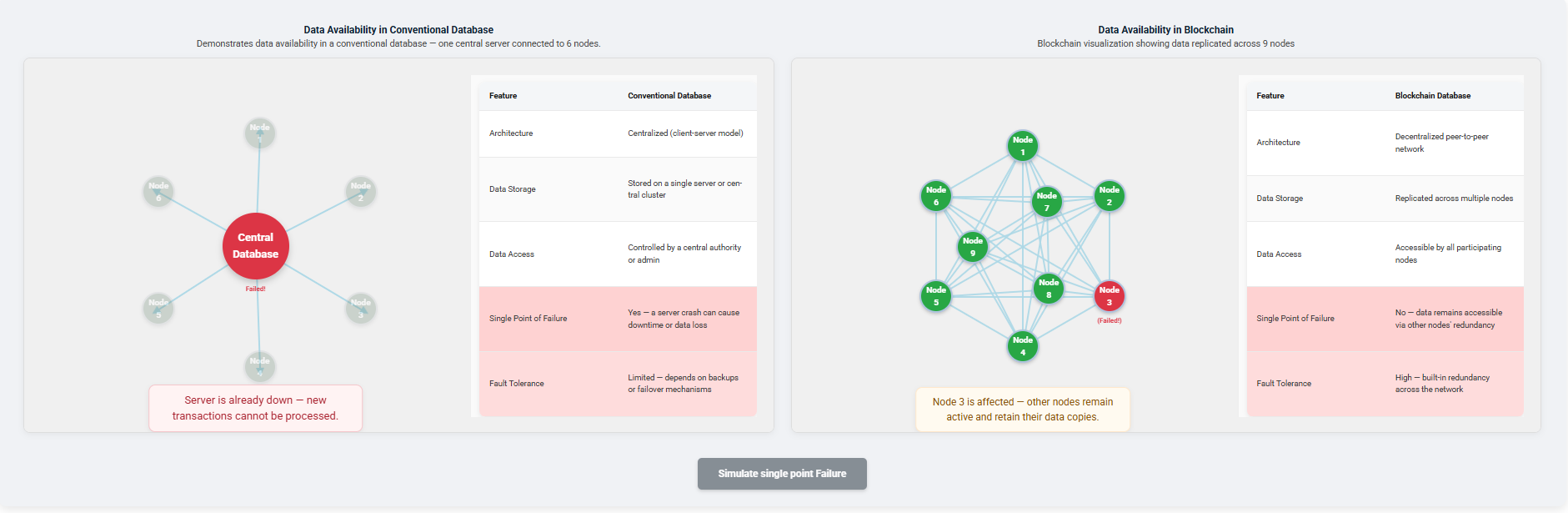
To demonstrate data availability, create a transaction by clicking the BUY button.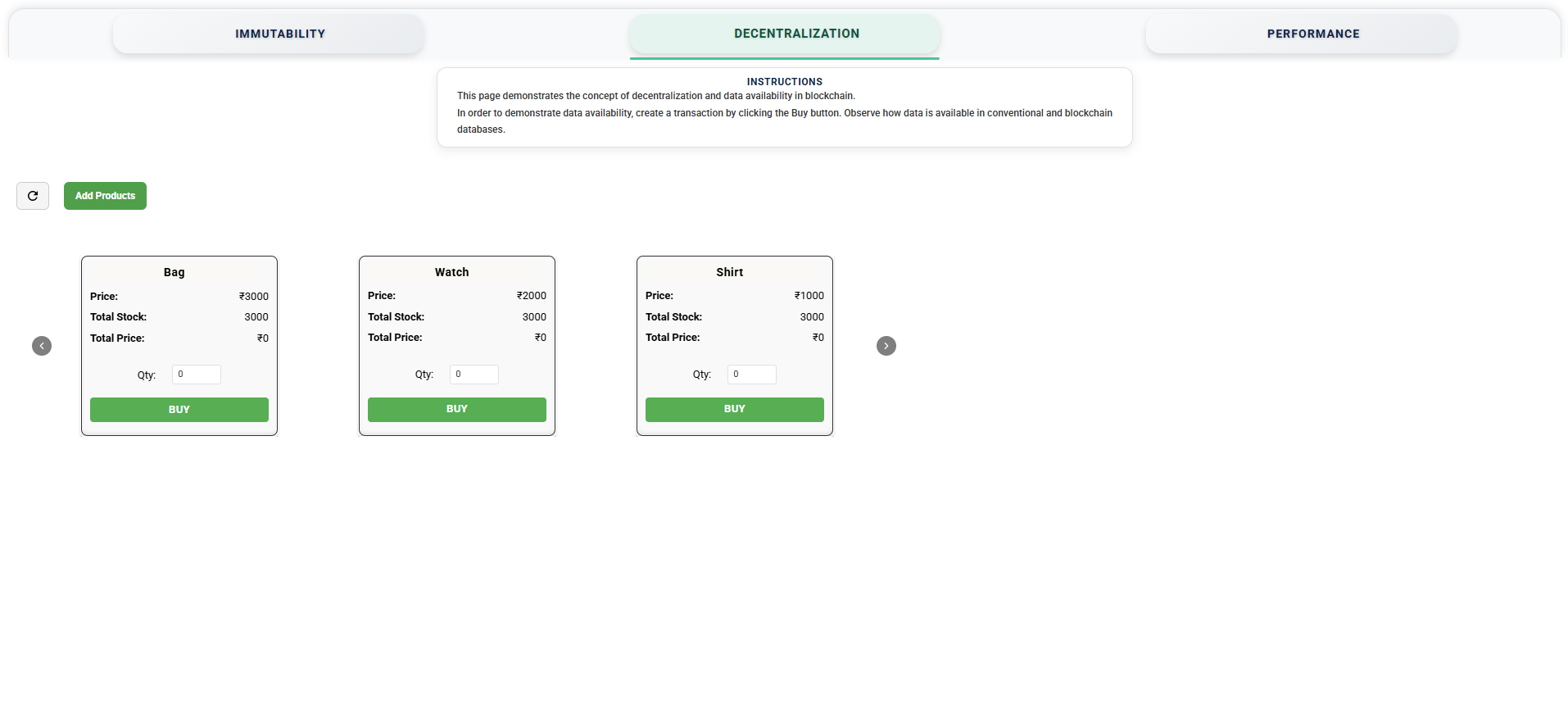
Observe how data is managed in the conventional and blockchain databases.
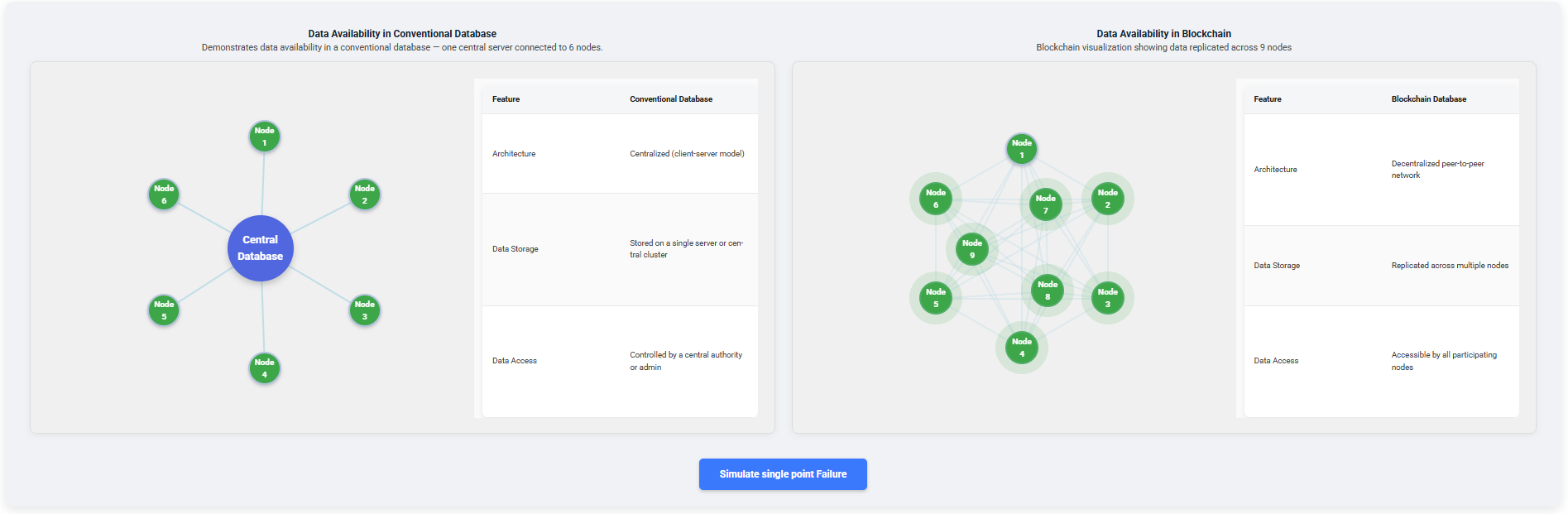
Click Simulate Single Point Failure to observe how a failure impacts the conventional and blockchain databases.
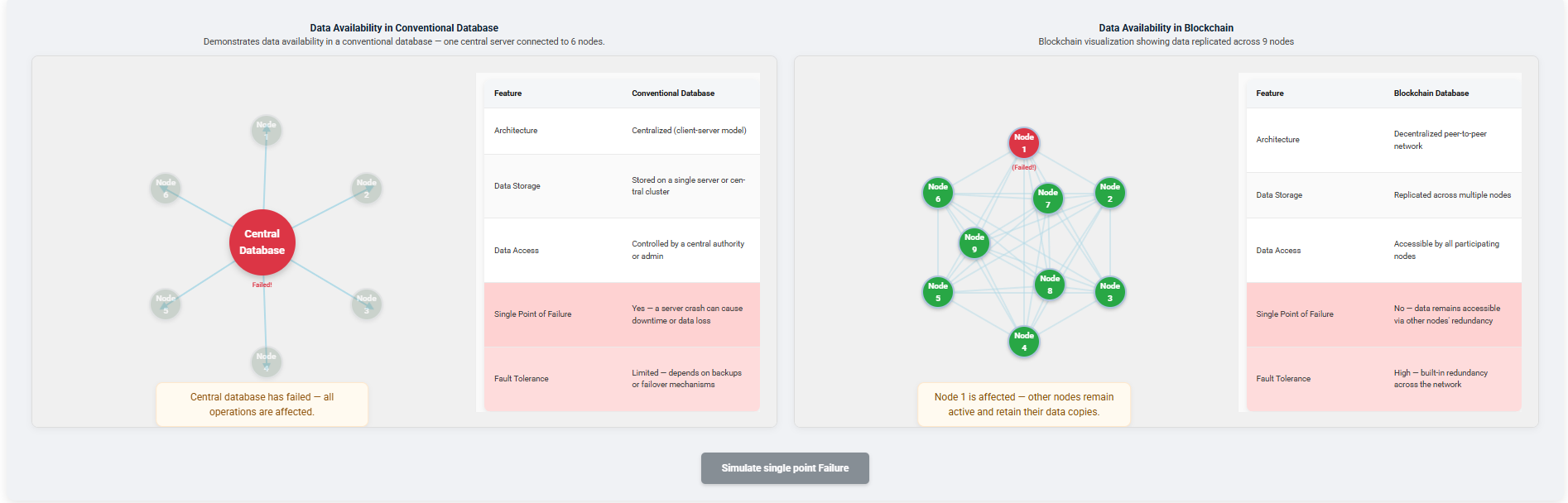
When the server fails, try to buy a new item. A message will appear stating:
“The server is currently down. Choose an option to proceed.”
You will be given two options: Fix and Continue or Continue Without Fix.
- Fix and Continue – Repairs the failed server and restores normal operation.
- Continue Without Fix – Proceeds while the server remains down.
In this case:
- In the Conventional Database, new transactions cannot be processed because the central server has failed.
- In the Blockchain Database, even if one node fails, other nodes remain active.
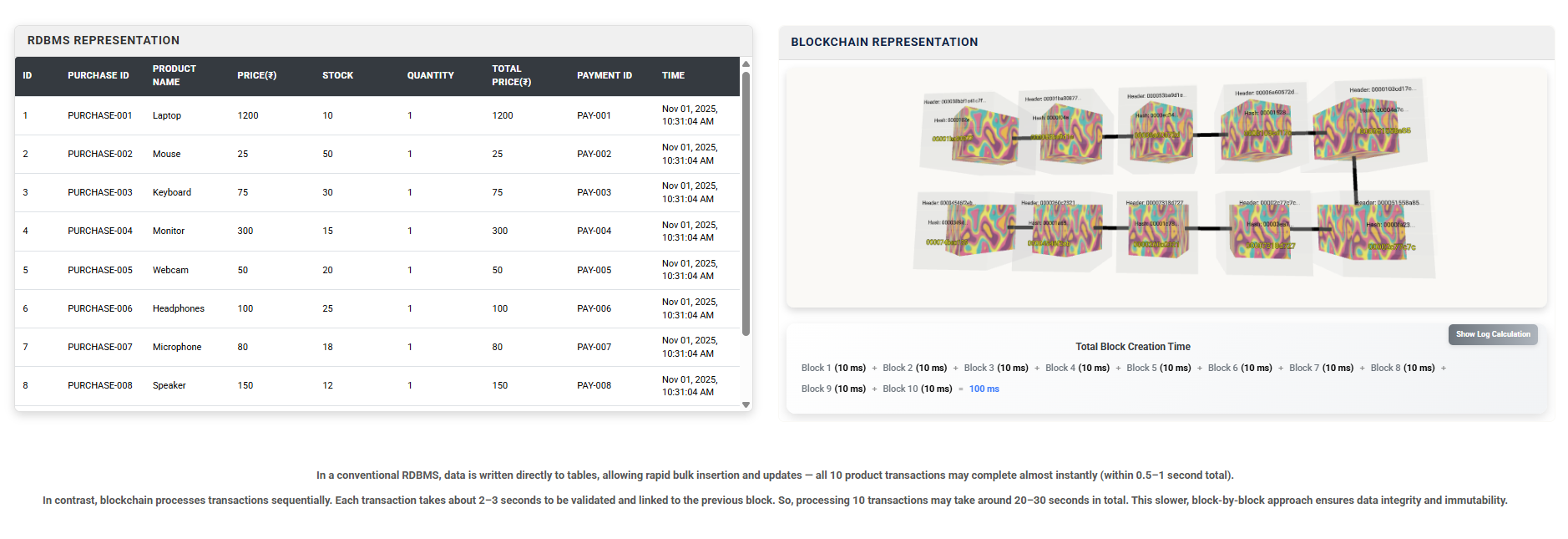
Performance
This page simulates multiple transactions to demonstrate and compare the performance of RDBMS and Blockchain systems.
Click Buy All Products in the cart and observe how each system processes and updates the data.
The RDBMS REPRESENTATION table shows records stored in a centralized database.
Observe how the RDBMS updates instantly, while Blockchain processes transactions sequentially, block by block.