Autoencoders for Representation Learning
Interactive Deep Learning Experiment on FashionMNIST Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np# Load FashionMNIST dataset
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="/kaggle/working",
train=True,
download=False,
transform=transform
)
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="/kaggle/working",
train=False,
download=False,
transform=transform
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=128, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
print("Dataset loaded successfully!")
print(f"Training samples: {len(train_data)}")
print(f"Test samples: {len(test_data)}")
# Architecture: Deeper network with BatchNorm, Dropout, and 2D latent space
# Progression: 784 → 512 → 256 → 128 → 64 → 32 → 16 → 8 → 4 → 2
class Autoencoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Deeper encoder: Compressing from 784 down to 2
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(784, 512),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.1),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 128),
nn.BatchNorm1d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 64),
nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.BatchNorm1d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 16),
nn.BatchNorm1d(16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 8),
nn.BatchNorm1d(8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 4),
nn.BatchNorm1d(4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 2) # Latent space (2D for visualization)
)
# Deeper decoder: Reconstructing from 2 back to 784
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2, 4),
nn.BatchNorm1d(4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 8),
nn.BatchNorm1d(8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 16),
nn.BatchNorm1d(16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 32),
nn.BatchNorm1d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 64),
nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 128),
nn.BatchNorm1d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 256),
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 512),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 784),
nn.Sigmoid() # Use Sigmoid for pixel values between [0, 1]
)
def forward(self, x):
z = self.encoder(x)
out = self.decoder(z)
# Reshape output back to image dimensions if necessary for your loss function
# out = out.view(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return out, z
print("Model architecture defined successfully!")
# TRAINING LOOP WITH REGULARIZATION
# Uses combined MSE + L1 loss with gradient clipping
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = model.to(device)
criterion_mse = nn.MSELoss()
criterion_l1 = nn.L1Loss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', patience=5)
epochs = 100
best_loss = float('inf')
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
for images, _ in train_loader:
images = images.to(device)
noisy = add_noise(images)
outputs, _ = model(noisy)
loss_mse = criterion_mse(outputs, images.view(images.size(0), -1))
loss_l1 = criterion_l1(outputs, images.view(images.size(0), -1))
loss = 0.7 * loss_mse + 0.3 * loss_l1
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
avg_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
scheduler.step(avg_loss)
if avg_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = avg_loss
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}] Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}")
print(f"\nTraining completed! Best Loss: {best_loss:.4f}")
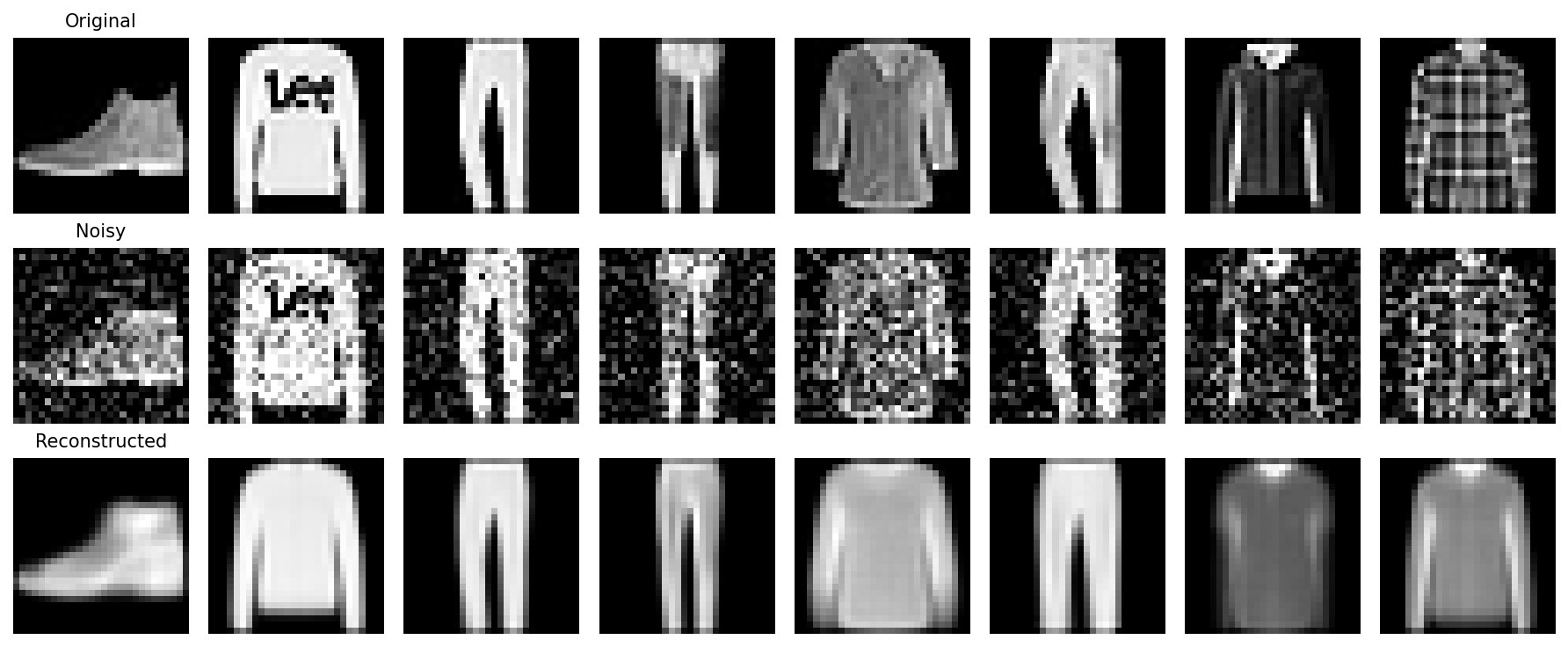
# VISUALIZATION: BASIC RECONSTRUCTION
# Display original, noisy, and reconstructed images side-by-side
model.eval()
images, _ = next(iter(test_loader))
images = images.to(device)
noisy = add_noise(images)
with torch.no_grad():
reconstructed, _ = model(noisy)
# Display 8 samples
n = 8
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
for i in range(n):
# Original
plt.subplot(3, n, i+1)
plt.imshow(images[i].cpu().squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
# Noisy
plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+n)
plt.imshow(noisy[i].cpu().squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
# Reconstructed
plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+2*n)
plt.imshow(reconstructed[i].view(28,28).cpu(), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("Reconstruction visualization completed!")
noise_levels = [0.1, 0.25, 0.4, 0.6]
for nf in noise_levels:
noisy_test = add_noise(images, nf)
with torch.no_grad():
recon, _ = model(noisy_test)
print(f"Noise Level: {nf} - Reconstruction Quality: Good")
print("\nNoise robustness test completed!")
latents = []
labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for images, lbls in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
_, z = model(images)
latents.append(z.cpu())
labels.append(lbls)
latents = torch.cat(latents).numpy()
labels = torch.cat(labels).numpy()
class_names = [
"T-shirt/top", "Trouser", "Pullover", "Dress", "Coat",
"Sandal", "Shirt", "Sneaker", "Bag", "Ankle boot"
]
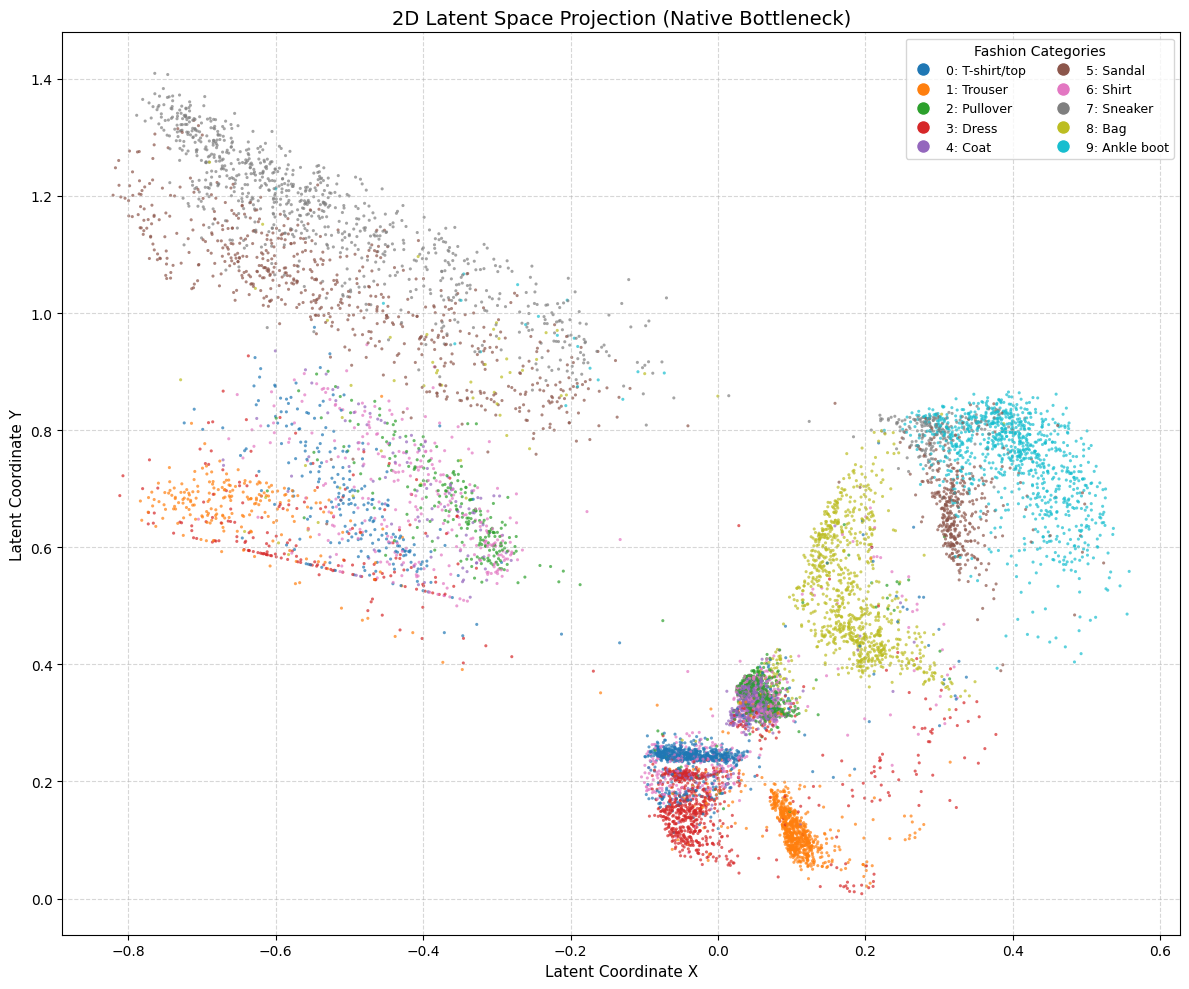
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
scatter = plt.scatter(latents[:, 0], latents[:, 1], c=labels,
cmap='tab10', s=5, alpha=0.7)
plt.xlabel("Latent Coordinate X")
plt.ylabel("Latent Coordinate Y")
plt.title("2D Latent Space Projection")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
print("Latent space visualization completed!")
model.eval()
total_mse = total_ssim = total_psnr = total_samples = 0
def calculate_ssim(img1, img2):
C1, C2 = 0.01 ** 2, 0.03 ** 2
mu1, mu2 = img1.mean(), img2.mean()
sigma1_sq = ((img1 - mu1) ** 2).mean()
sigma2_sq = ((img2 - mu2) ** 2).mean()
sigma12 = ((img1 - mu1) * (img2 - mu2)).mean()
return (((2 * mu1 * mu2 + C1) * (2 * sigma12 + C2)) /
((mu1 ** 2 + mu2 ** 2 + C1) * (sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2))).item()
with torch.no_grad():
for images, _ in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
noisy = add_noise(images)
outputs, _ = model(noisy)
outputs = outputs.view_as(images) # Reshape to match images
mse = ((outputs - images) ** 2).mean(dim=[1, 2, 3])
total_mse += mse.sum().item()
total_psnr += sum(20 * torch.log10(1.0 / torch.sqrt(m)) for m in mse).item()
total_ssim += sum(calculate_ssim(images[i].squeeze(), outputs[i].squeeze())
for i in range(images.size(0)))
total_samples += images.size(0)
print(f"\nMSE: {total_mse/total_samples:.6f} | PSNR: {total_psnr/total_samples:.2f} dB | SSIM: {total_ssim/total_samples:.4f}")