Implement association relationship between classes using C++/Java
Theory
Aggregation relationship:
In Object-Oriented programming, an Object communicates to another object to use functionality and services provided by that object.
If a class have an entity reference, it is known as Aggregation.
Aggregation represents HAS-A relationship.
It is a unidirectional association i.e. a one-way relationship.
In Aggregation, both the entries can survive individually which means ending one entity will not affect the other entity.
Consider the class diagram
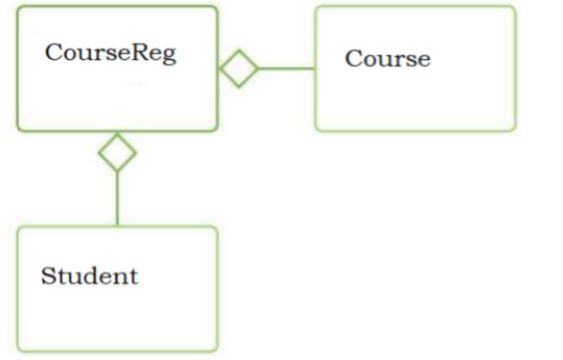
Student class
public class Student
{
public String name; // Student's name.
public double test1, test2, test3; // Grades on three tests.
public Student()
{
System.out.printin(“ Creating Student 1! *);
}
public double getAverage()
{ // compute average test grade
return (test1 + test2 + test3) / 3;
}
}// end of class Student
Course Class
public class Course{
private String courseName;
private int courselevel;
private final int courseCredits;
public Course (String courseName, int courselevel, int courseCredits )
{
this.courseNeme= courseName;
this.courselevel=courselevel;
this. courseCredits=courseCredits;
}
}
Course Registration
public class CourseRegistartion
{
private Course courseObj:
private Student studentObj;
public Course ( Course courseObj, Student studentObj)
{
this.courseObj
this. studentObj
}
}
Composition relationship:
Composition is a restricted form of Aggregation in which two entities are highly dependent on each other.
It represents part-of relationship.
In composition, both entities are dependent on each other.
When there is a composition between two entities, the composed object cannot exist without the other entity.
Composition is a strong Association whereas Aggregation is a weak Association.
Consider the following class diagram:
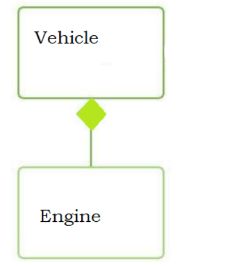
The class diagram shows that the Engine is a part-of Vehicle and the Vehicle cannot exist without the Engine object. The Engine object cannot be changed once assigned to a Vehicle.
Use the final Keyword on the variable as a modifier. Using final means the value once assigned to a variable cannot be changed.
