Hydraulic Conductivity-Constant Head Test
Objective:
To determine the hydraulic conductivity how easily water can pass through the rock or the soil.
Apparatus used:
Trowel, Test Cylinder, Coarse Sand, Filter Paper
.png)
Calculation of the cross sectional area of the cylinder: Take the caliper and measure the diameter of the cylinder. From this cross sectional area is getting as section is cylinder.
.png)
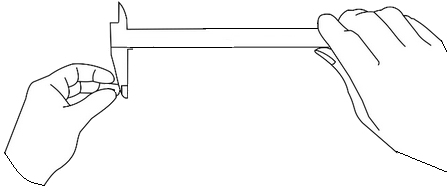
Diameter=13.79cm2
Area=d2π⁄4= cm2/s
Please Enter Value to proceedPrepare the Soil Sample
STEP 2Take one killogram of coarse soil sample and place it in conatiner and measure the sample.




Mass of the container and initial volume of the soil (g>) = _________

Put the screen at the bottom of the test cylinder and place the soil sample. Soil sample should be arranged in layers and each layer is levelled by using hammer.
.png)
.png)







.png)






















 (1).png)
 (1).png)
 (1).png)
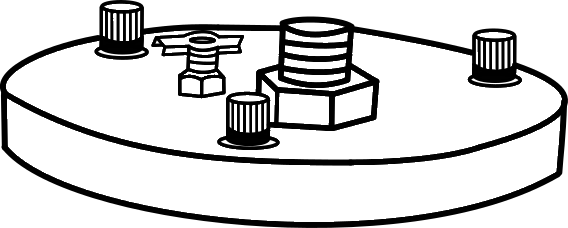
The top of the column should level so that small gaps are filled properly and covered with screen and a separator. Top should be covered with the cap and three screws.

.png)
After that weigh the remaining soil sample.





Mass of the container and remaining soil = _________

Connect the intake line of the reservoir to the top of the test cylinder and other two lines to the other two nominals of the test cylinder. This is to measure the pore water pressure of the water at specific points.
.png)
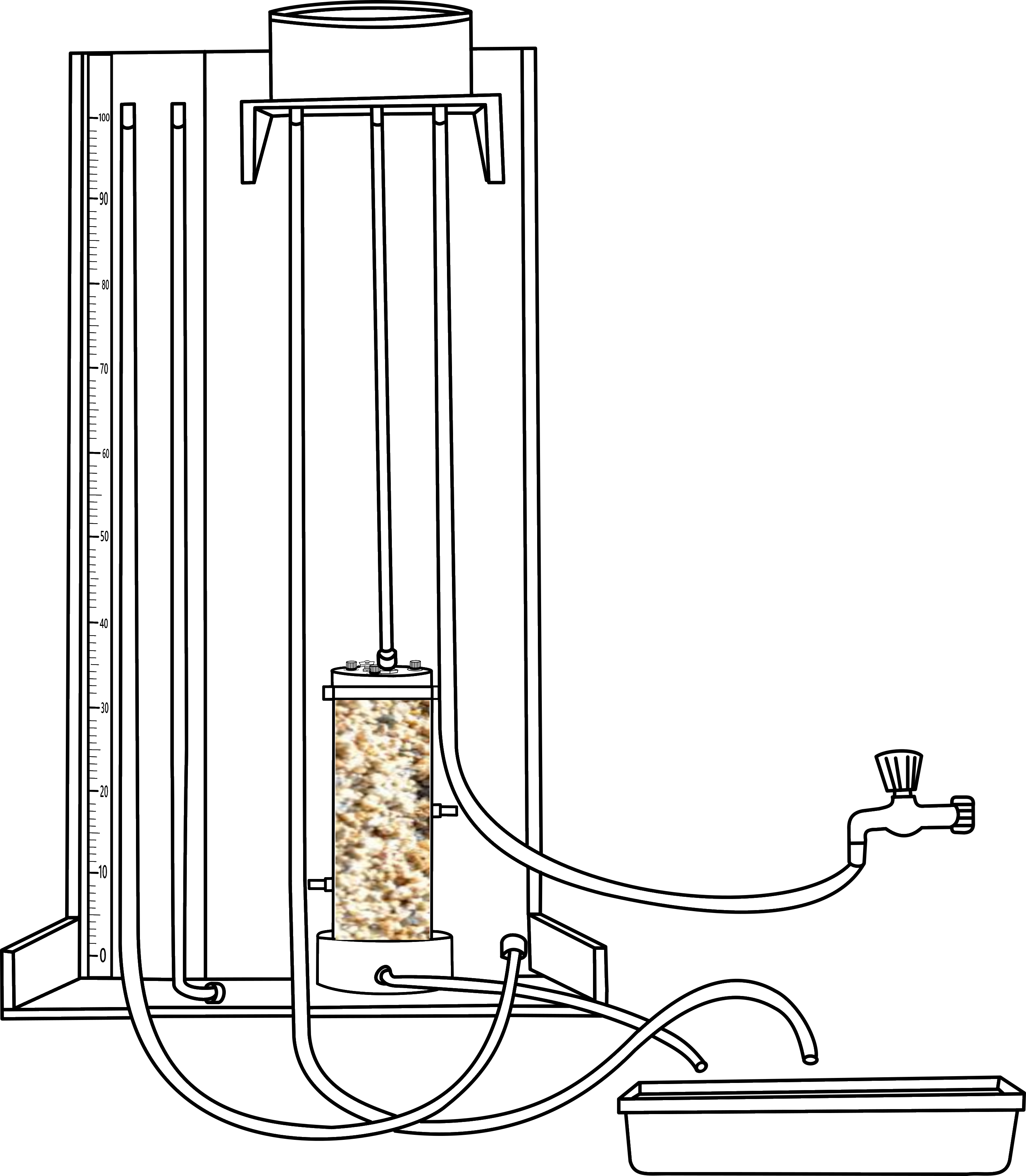
.png)






.png)
.png)






Close the valve of the intake line and turn the tap so that intake line will fill up and extra water will come from the discharge tube so that water level is constant in the reservoir



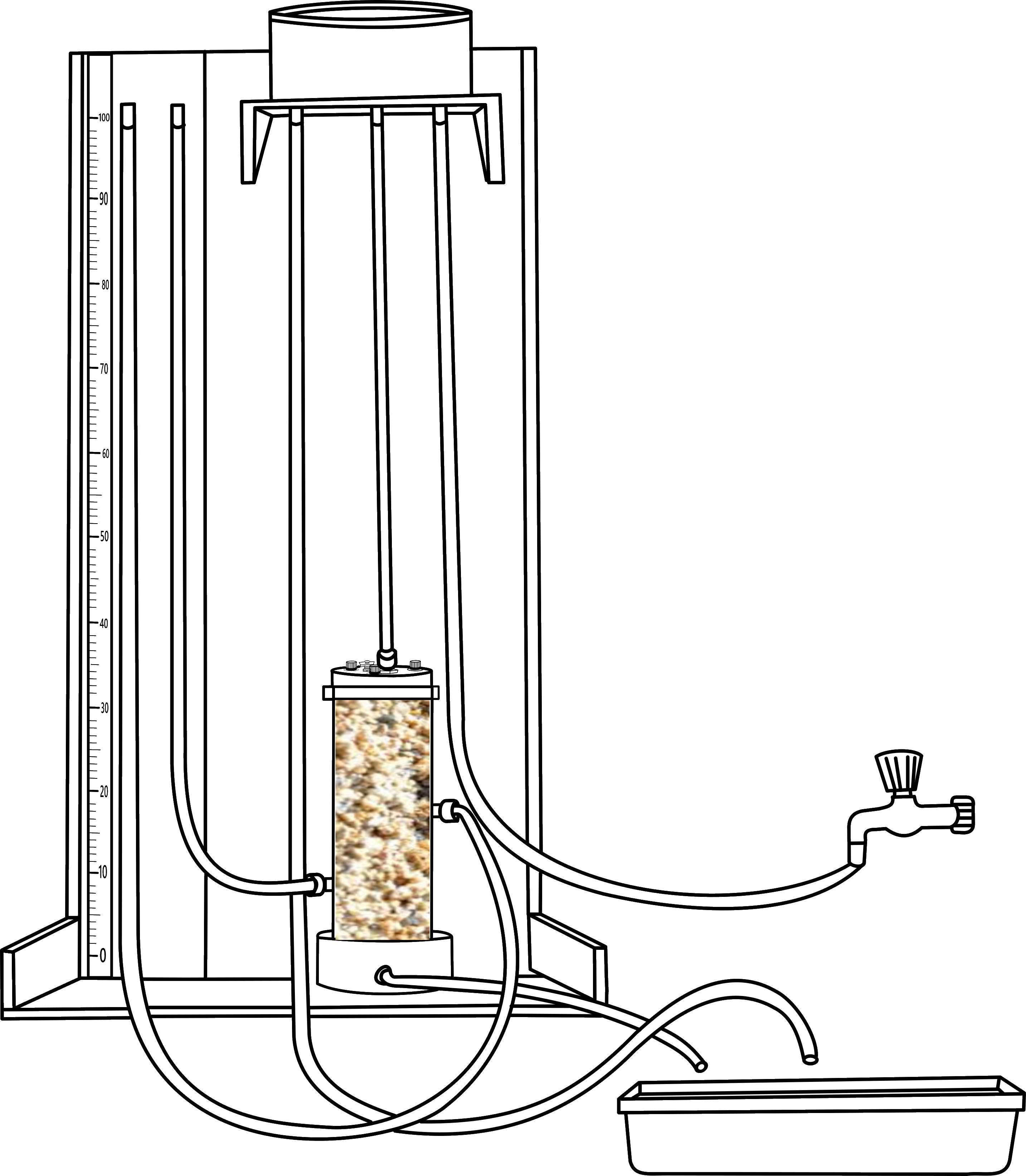


.png)

Constant Head Test Permeability
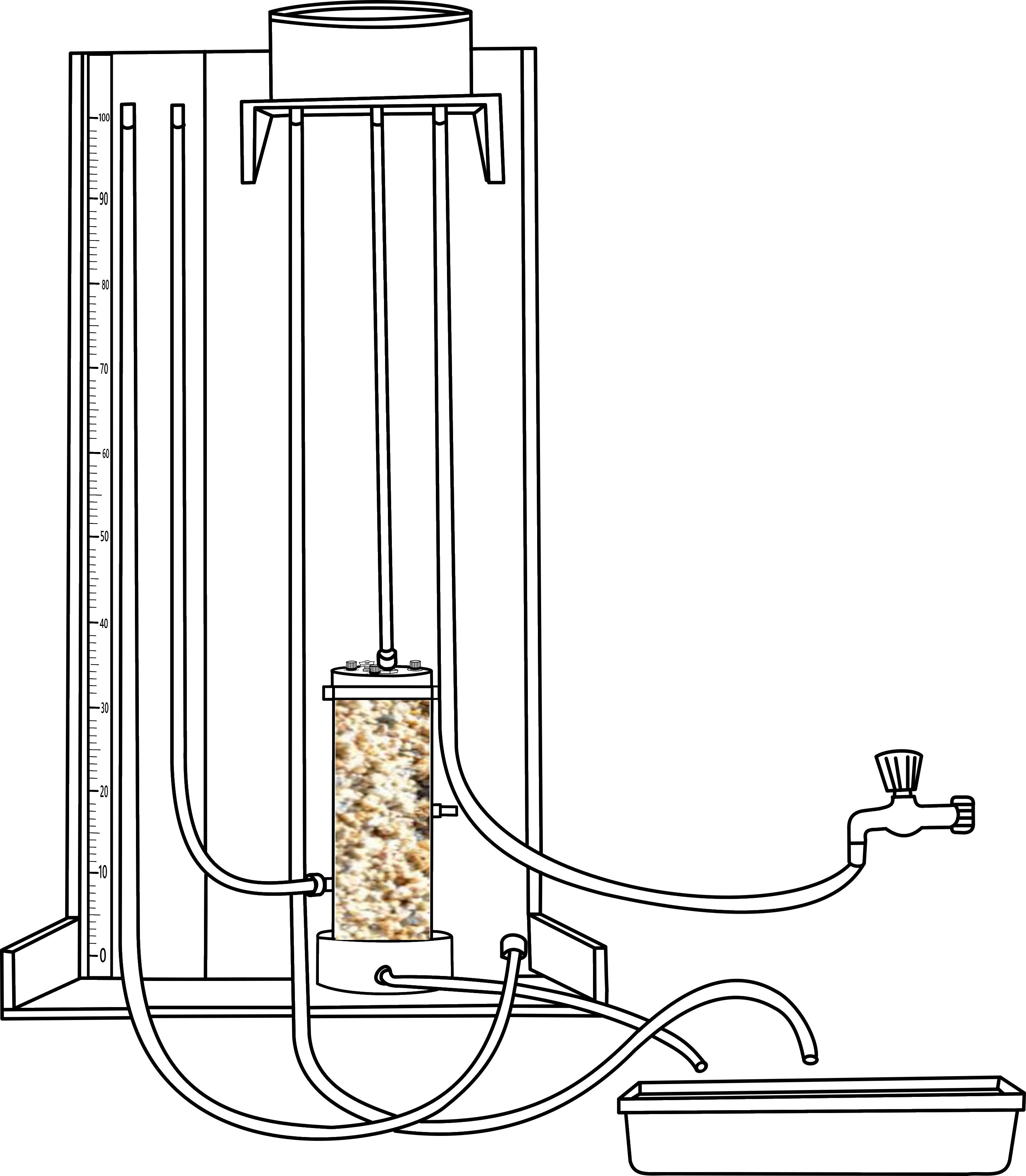
STEP 8Now open the valve so that water flow to the sample. For measure the flow rate water should run to the system for few minutes.





.png)
.png)


.png)
For the water flow rate measurement take a water beaker and measure its weight. And record the values in the table.




Mass of the empty container = _________

Use and the stopwatch allow the discharge tube to the beaker. Collect the 300 ml of the water and stop the watch and remove the discharge tube.
Trial : 1

.png)


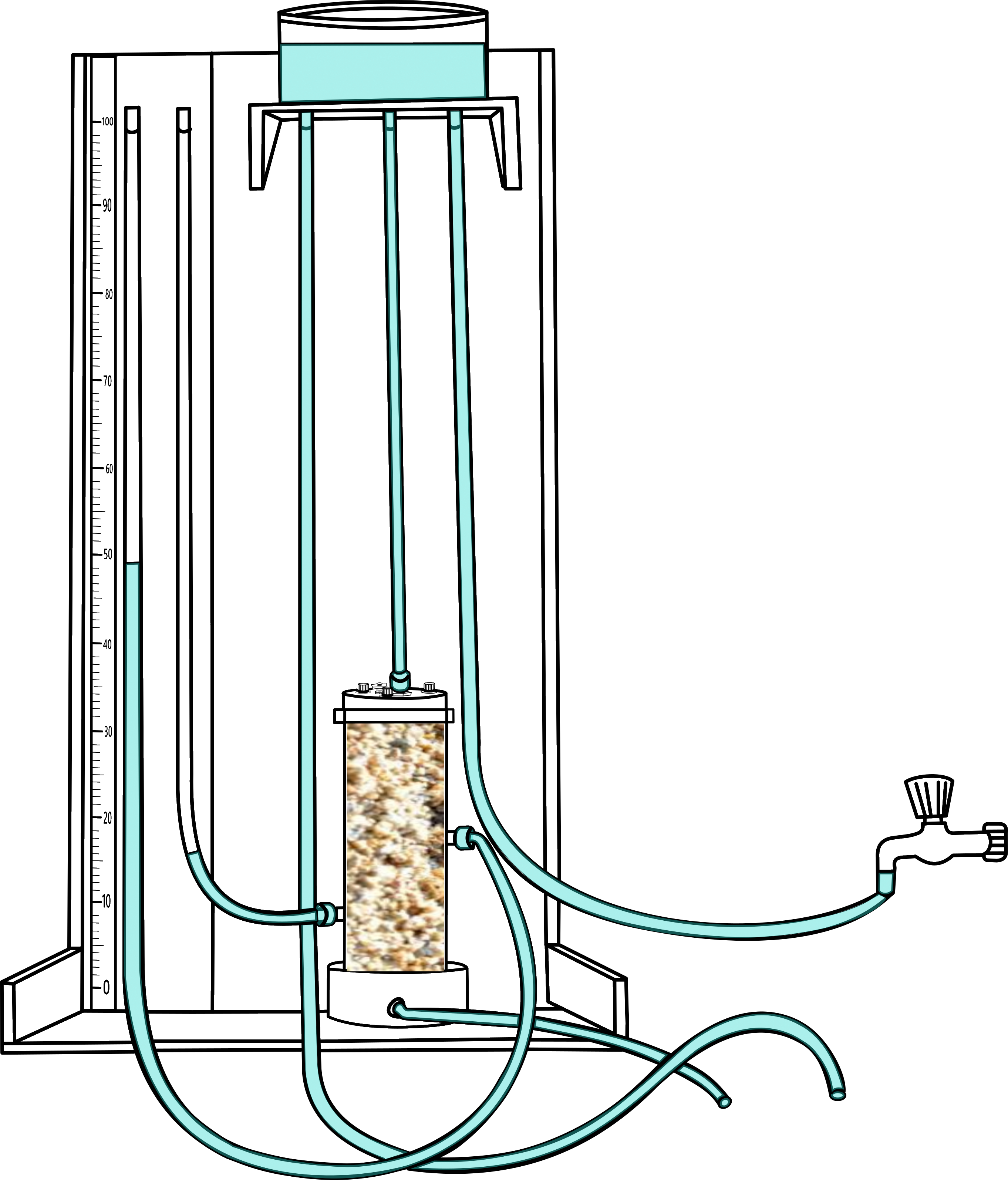
.png)

Measure the mass of container and water.


.png)
.png)
Mass of the beaker and water = _________

Add the measured values to the table.
| Test Number | 1 |
|---|---|
| Time to accumulate water | 8 sec |
| Mass of beaker +water | 419.4 |
| Mass of water | 304.9 |
Use and the stopwatch allow the discharge tube to the beaker. Collect the 300 ml of the water and stop the watch and remove the discharge tube.
Trial : 2



.png)



.png)


Measure the mass of container and water.



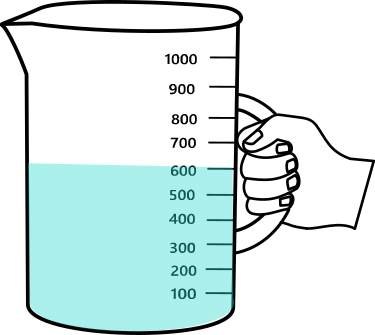
Mass of the beaker and water = _________

Add the measured values to the table.
| Test Number | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Time to accumulate water | 8 sec | 13 sec |
| Mass of beaker +water | 419.4 | 621.6 |
| Mass of water | 304.9 | 507.1 |
Use and the stopwatch allow the discharge tube to the beaker. Collect the 300 ml of the water and stop the watch and remove the discharge tube.
Trial : 3







.png)


Measure the mass of container and water.



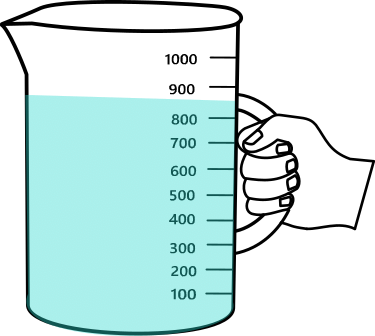
Mass of the beaker and water = _________

Add the measured values to the table.
| Test Number | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to accumulate water | 8 sec | 13 sec | 19 sec |
| Mass of beaker +water | 419.4 | 621.6 | 811.5 |
| Mass of water | 304.9 | 507.1 | 697 |
Calculate the head applied to the sample. Measure the total head at the top monometer and total head at the bottom monometer.


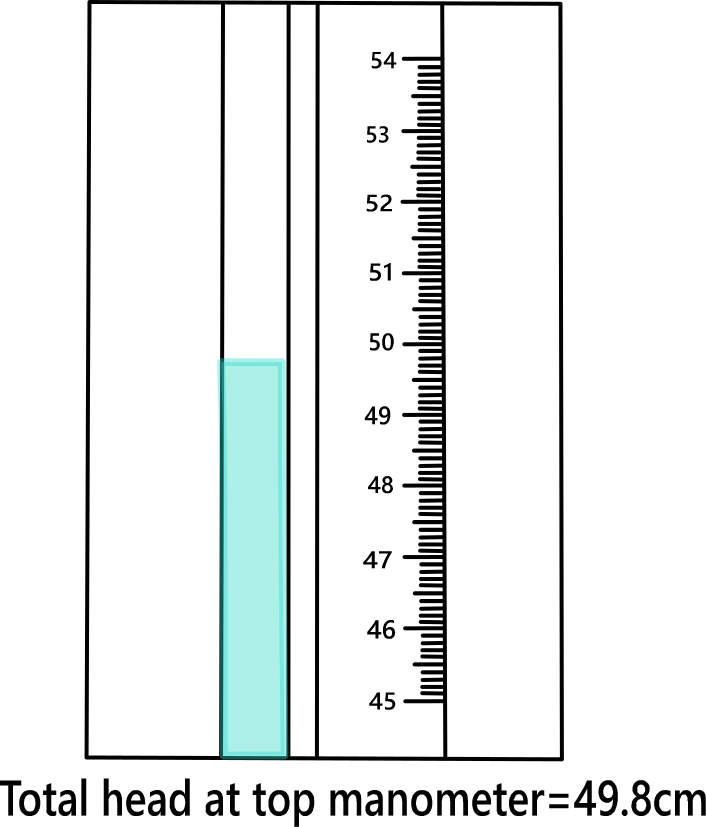
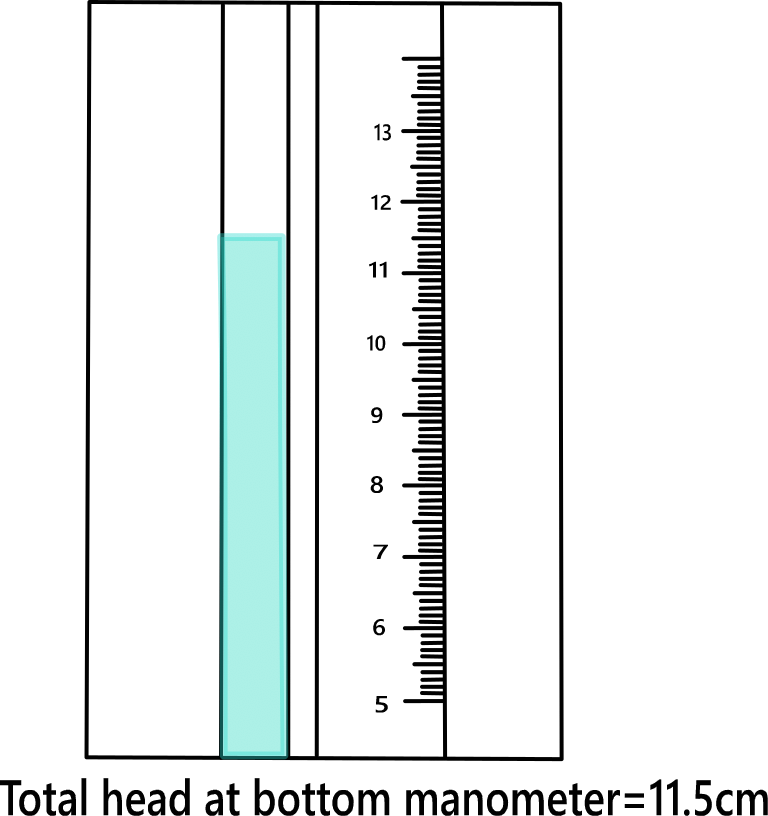
Observation & Calculation.
| Test Number | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to accumulate water | 8sec | 13sec | 19sec |
| Mass of beaker+water | 419.4 | 621.6 | 811.5 |
| Mass of water | 304.9 | 507.1 | 697 |
| Coefficient of Permeability |
Coefficient of Permeability (Kavg) = Please Enter Value to proceed

