CONTOUR MAP
Objective:
- Draw a geological cross-section along XY.
- Determine the Dip and Strike of the formations.
- A horizontal tunnel is proposed at an altitude of 1200m.
Pre-requisites:
Topographic map
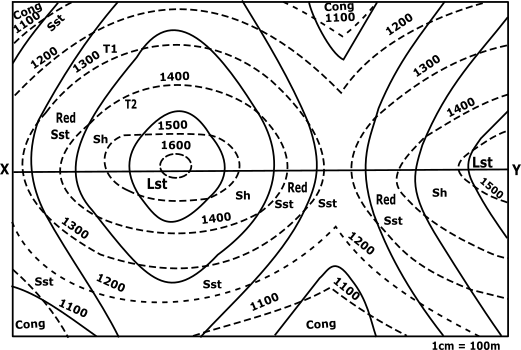 Description
True and Apparent Dip: Apparent dip is the inclination of geologic beds as seen from any vertical cross section not perpendicular to the strike of the geologic beds. When a vertical cross-section is perpendicular to the strike of the beds, the inclination seen in the cross section is called the true dip.
Description
True and Apparent Dip: Apparent dip is the inclination of geologic beds as seen from any vertical cross section not perpendicular to the strike of the geologic beds. When a vertical cross-section is perpendicular to the strike of the beds, the inclination seen in the cross section is called the true dip.Angle of Dip: is the angle made by the Earth’s magnetic field lines with the horizontal.For any tilted bed, the dip helps in the providing the steepest angle of descent relative to a horizontal plane. The angle of dip is represented between zero degrees to 90 degrees
Identify the line about which the profiles are to be drawn.



Line to be considered for profiles to be drawn:
Mark all the points of XY line that is obtained by the intersection of the dotted line with this XY of the contour map.

| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| a | x1 | 1300 |
| b | x2 | 1400 |
| c | x3 | 1500 |
| d | x4 | 1600 |
| e | x5 | 1600 |
| f | x6 | 1500 |
| g | x7 | 1400 |
| h | x8 | 1300 |
| i | x9 | 1300 |
| j | x10 | 1400 |
| k | x11 | 1500 |
Identify X-axis and Y-axis taking X as origin and define scale.Mark X' at a height of 1000 as the new x-axis.
Plot the points taking its distance from X as x coordinate and the index values of the corresponding line as y coordinate along with the points Y’(1535,0) on the graph.
| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| a | 30 | 1300 |
| b | 140 | 1400 |
| c | 290 | 1500 |
| d | 450 | 1600 |
| e | 550 | 1600 |
| f | 690 | 1500 |
| g | 840 | 1400 |
| h | 960 | 1300 |
| i | 1050 | 1300 |
| j | 1190 | 1400 |
| k | 1380 | 1500 |
Mark all the points of XY line that is obtained by the intersection of the solid line with this XY of the contour map.

| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| p | x1 | y1 |
| q | x2 | y2 |
| r | x3 | y3 |
| s | x4 | y4 |
| t | x5 | y5 |
| u | x6 | y6 |
| v | x7 | y7 |
| w | x8 | y8 |
| x | x9 | y9 |
Name the points as p,q,r … respectively taking its distance from X as x-coordinate.
| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| p | x1 | y1 |
| q | x2 | y2 |
| r | x3 | y3 |
| s | x4 | y4 |
| t | x5 | y5 |
| u | x6 | y6 |
| v | x7 | y7 |
| w | x8 | y8 |
| x | x9 | y9 |
To Calculate the index value of the solid line.Search for the first dotted line on both the sides of the solid line.
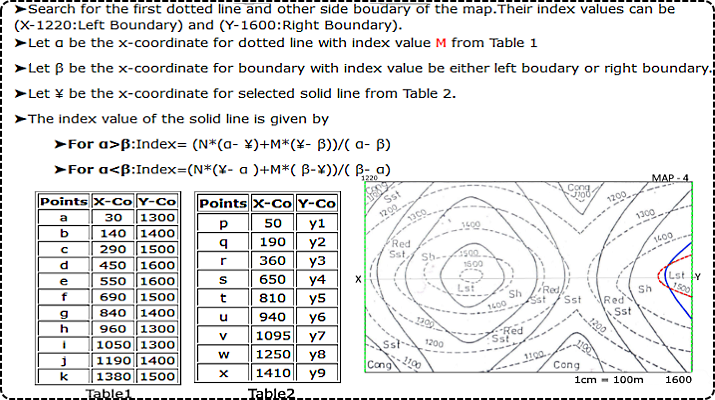 ▼
▼
If Found
If Not Found
▼
▼
If Found
If Not Found
Calculate the index value of all solid lines.
Hint: Found
| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| a | 30 | 1300 |
| b | 140 | 1400 |
| c | 290 | 1500 |
| d | 450 | 1600 |
| e | 550 | 1600 |
| f | 690 | 1500 |
| g | 840 | 1400 |
| h | 960 | 1300 |
| i | 1050 | 1300 |
| j | 1190 | 1400 |
| k | 1380 | 1500 |
| Y'Axis | 1535 | 1600 |
| Table 2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
| p | 50 | y1 |
| q | 190 | y2 |
| r | 360 | y3 |
| s | 650 | y4 |
| t | 810 | y5 |
| u | 940 | y6 |
| v | 1095 | y7 |
| w | 1250 | y8 |
| x | 1410 | y9 |


➤For the solid line p:
Plot the above points (p to x) with the plotted points (a to k) along with the points Y’ (1535,0) on the graph.
| Points | X-Co | Y-Co |
|---|---|---|
| p | 50 | 1318 |
| q | 190 | 1433 |
| r | 360 | 1544 |
| s | 650 | 1529 |
| t | 810 | 1420 |
| u | 940 | 1317 |
| v | 1095 | 1332 |
| w | 1250 | 1432 |
| x | 1410 | 1519 |
Join all the plotted points on the graph free hand. And extrapolate it between the bounds.
A horizontal tunnel is proposed at an altitude of 1200m from the x axis parallel to it, between the bounds.
Calculation for Angle of dip.
➤Search for the points of intersection between the solid line and the dotted line on the contour map.

From the points (p,q,r,s,t,u,O,M,N) find angle of dip θ

| Points | θ(°) |
|---|---|
| p | |
| q | |
| r | |
| s | |
| t | |
| u | |
| v | |
| w | |
| x | |
| O | |
| M | |
| N |
From the points (p,q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,o,m,n) draw a line at an angle θ with horizontal in anticlockwise direction and its point of intersection on x-axis be (p’,q’,r’,s’,t’,u’,v’,w’,x’,o’,m’,n’) respectively.
➤p-p’☚
➤q-q’☚
➤r-r’☚
➤s-s’☚
➤t-t’☚
➤u-u’☚
➤v-v’☚
➤w-w’☚
➤x-x’☚
➤o-o’☚
➤m-m’☚
➤n-n’☚
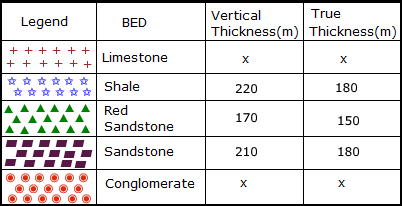
Location of Types of stones on the contour.
➤LimeStone☚
➤Shale☚
➤Redsandstone☚
➤Standstone☚
➤Conglomerite☚
Profile View Graph
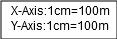

Both ends of the pipe must be trimmed to ensure parallel faces.