Objective:
Determine the angularity number of aggregate.
Apparatus used:
BS test sieves: 20.0 mm, 14.00 mm, 10.00 mm, 6.30 mm, 5.0 mm, a balance of capacity 10kg and accurate to 1, a metal cylinder (150mm * 150mm).

Angularity Number of Coarse Aggregate
Step
1
Objective: Determine the angularity number of aggregate. Apparatus used: BS test sieves: 20.0 mm, 14.00 mm, 10.00 mm, 6.30 mm, 5.0 mm, a balance of capacity 10kg and accurate to 1, a metal cylinder (150mm * 150mm). 
Step
2
Place the metal cylinder on the weighing balance. Press the TARE button to read the balance zero.


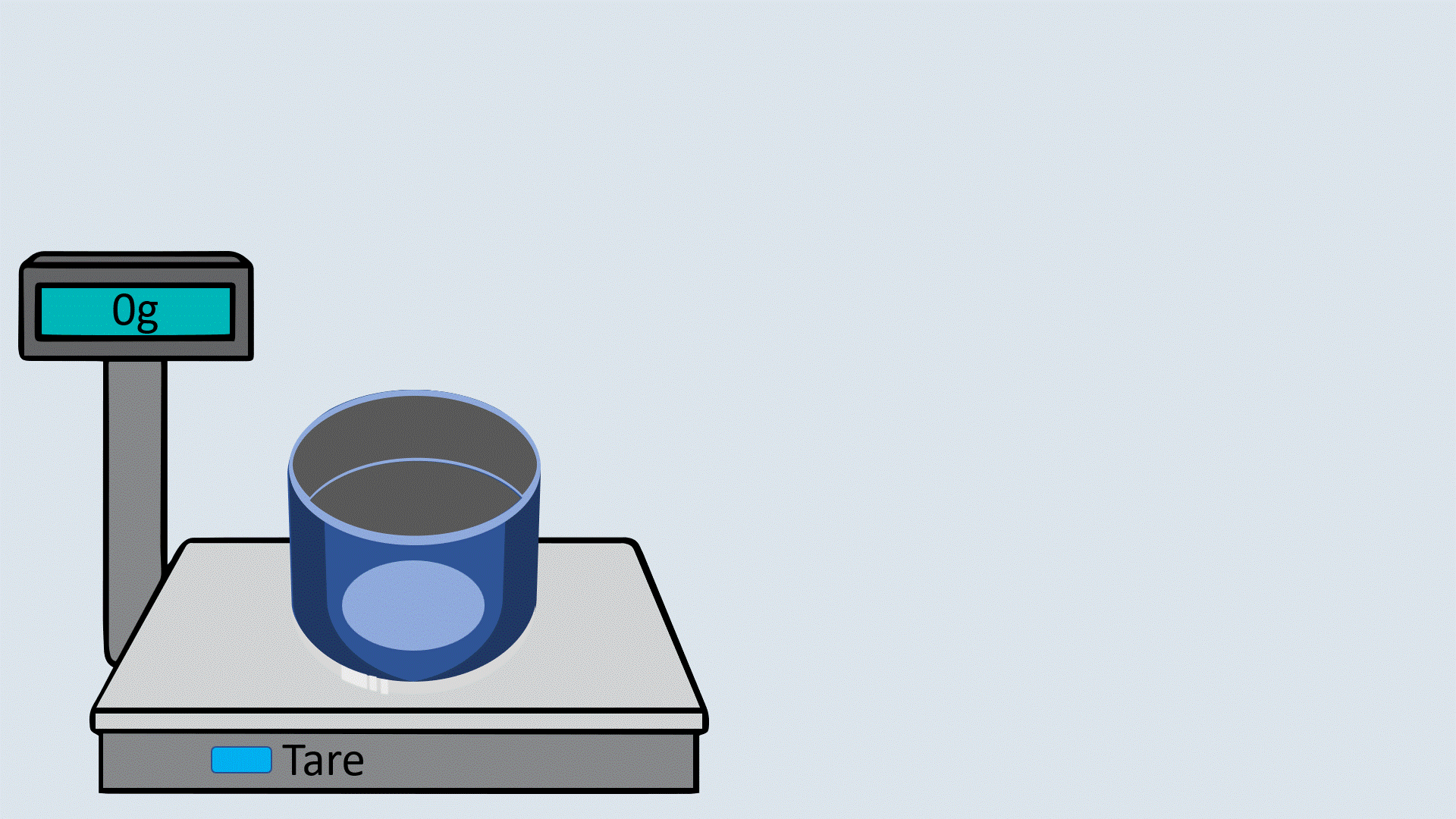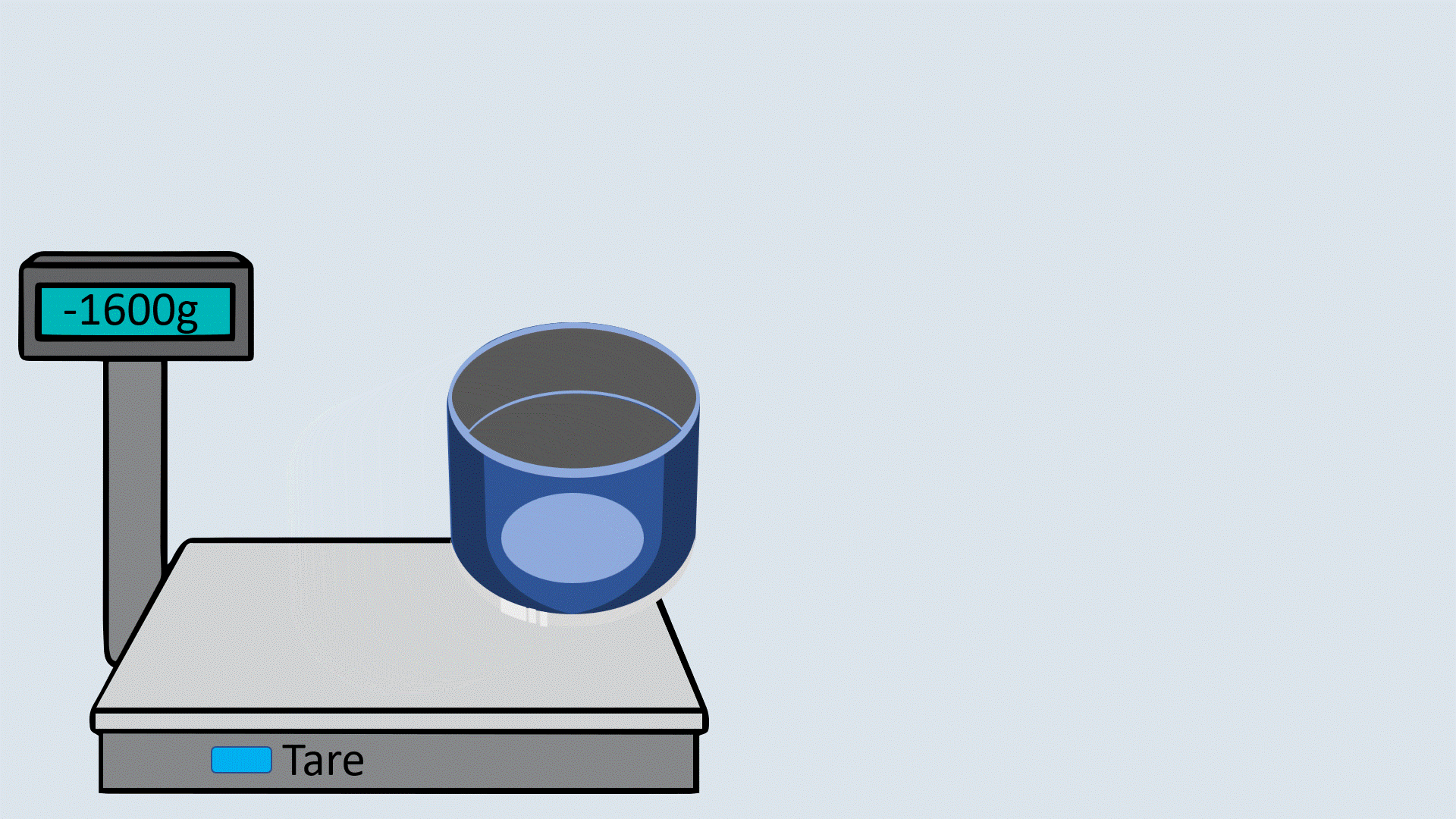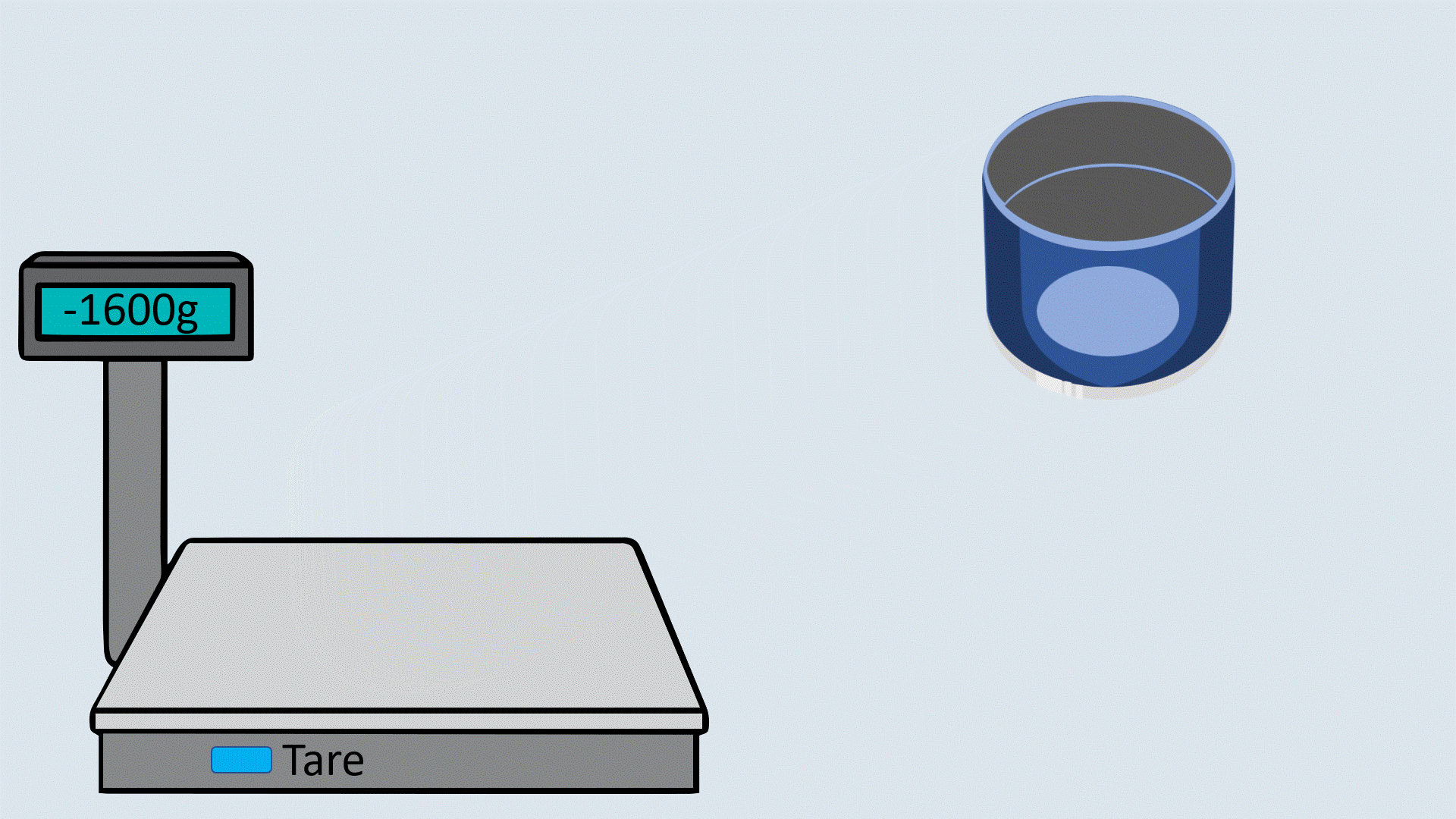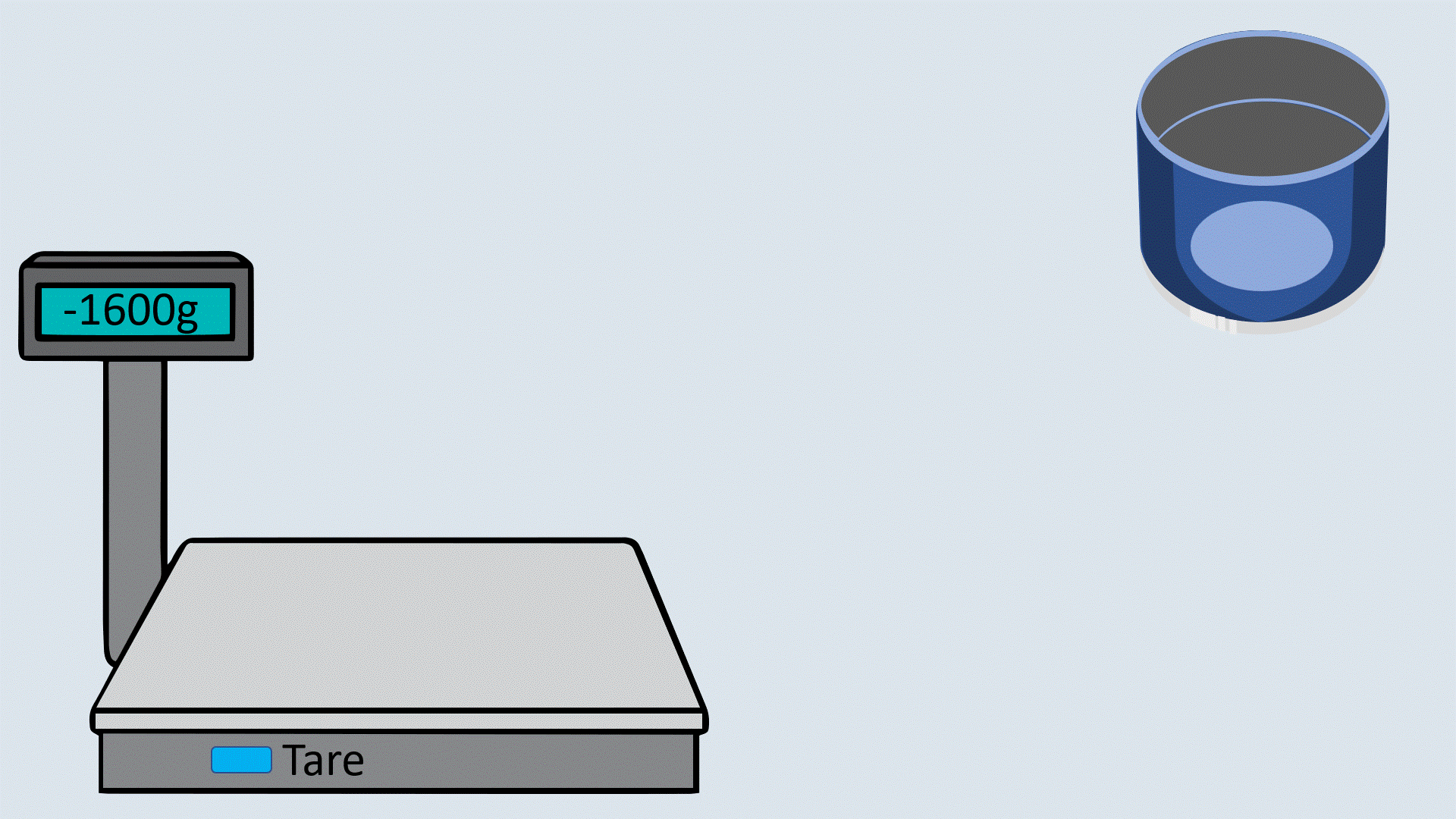



Step
3
Pour the water into the cylinder carefully.




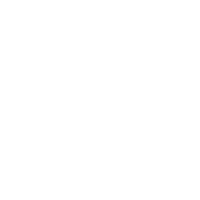
Step
4
Note down the volume of water filled inside the metal cylinder.



Step
5
Place the tray on the balance and again press the TARE button.


Step
6
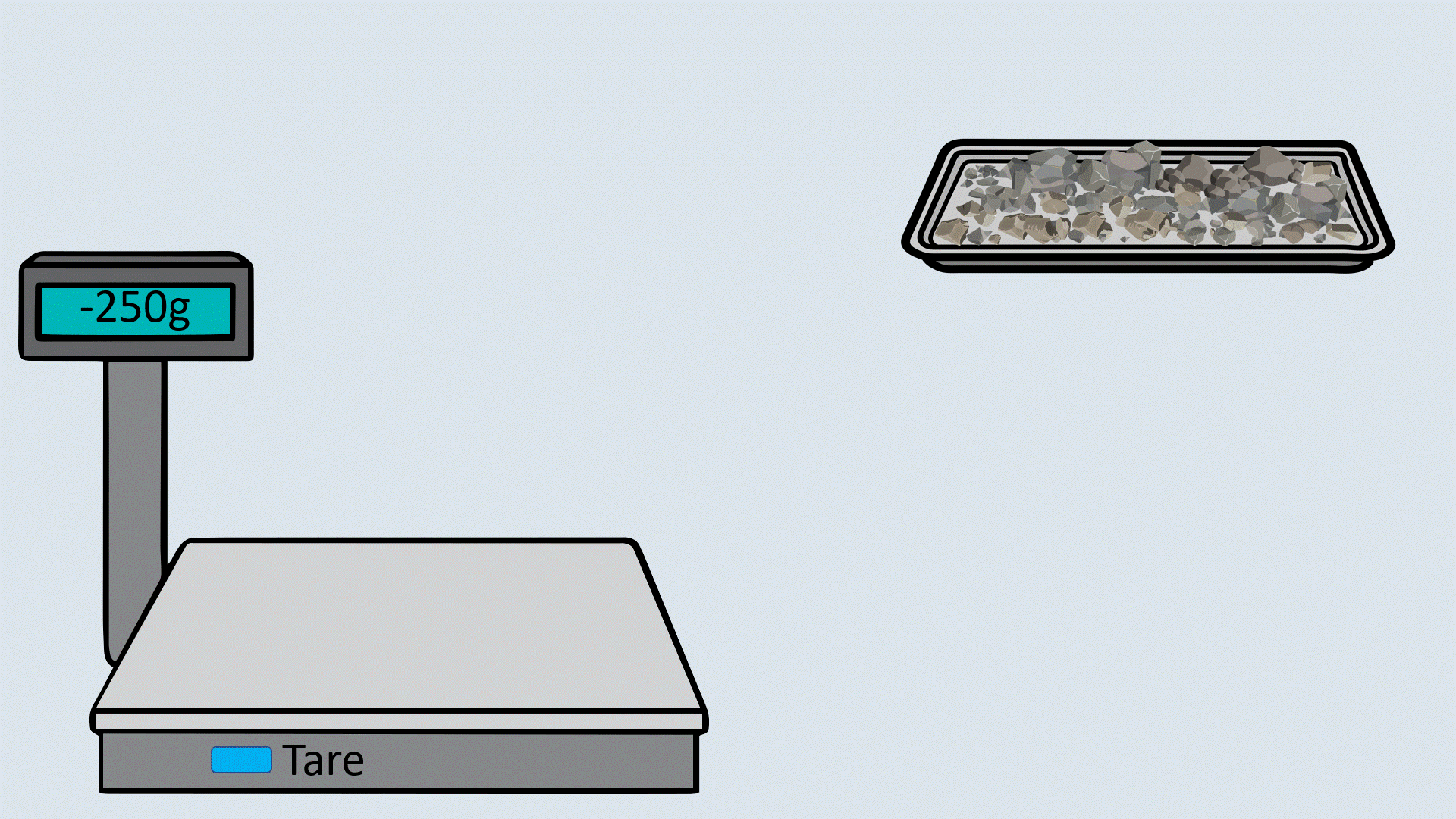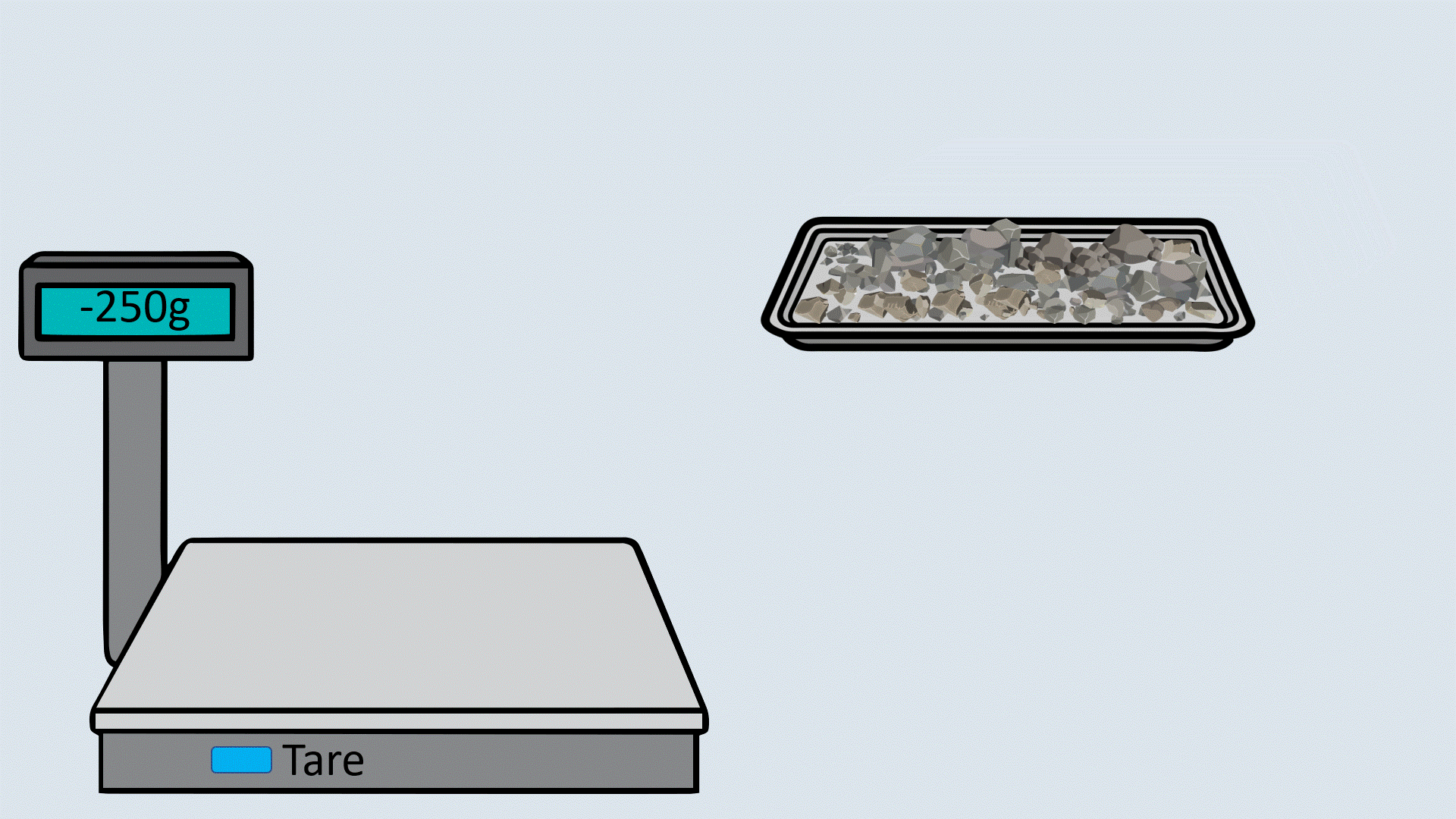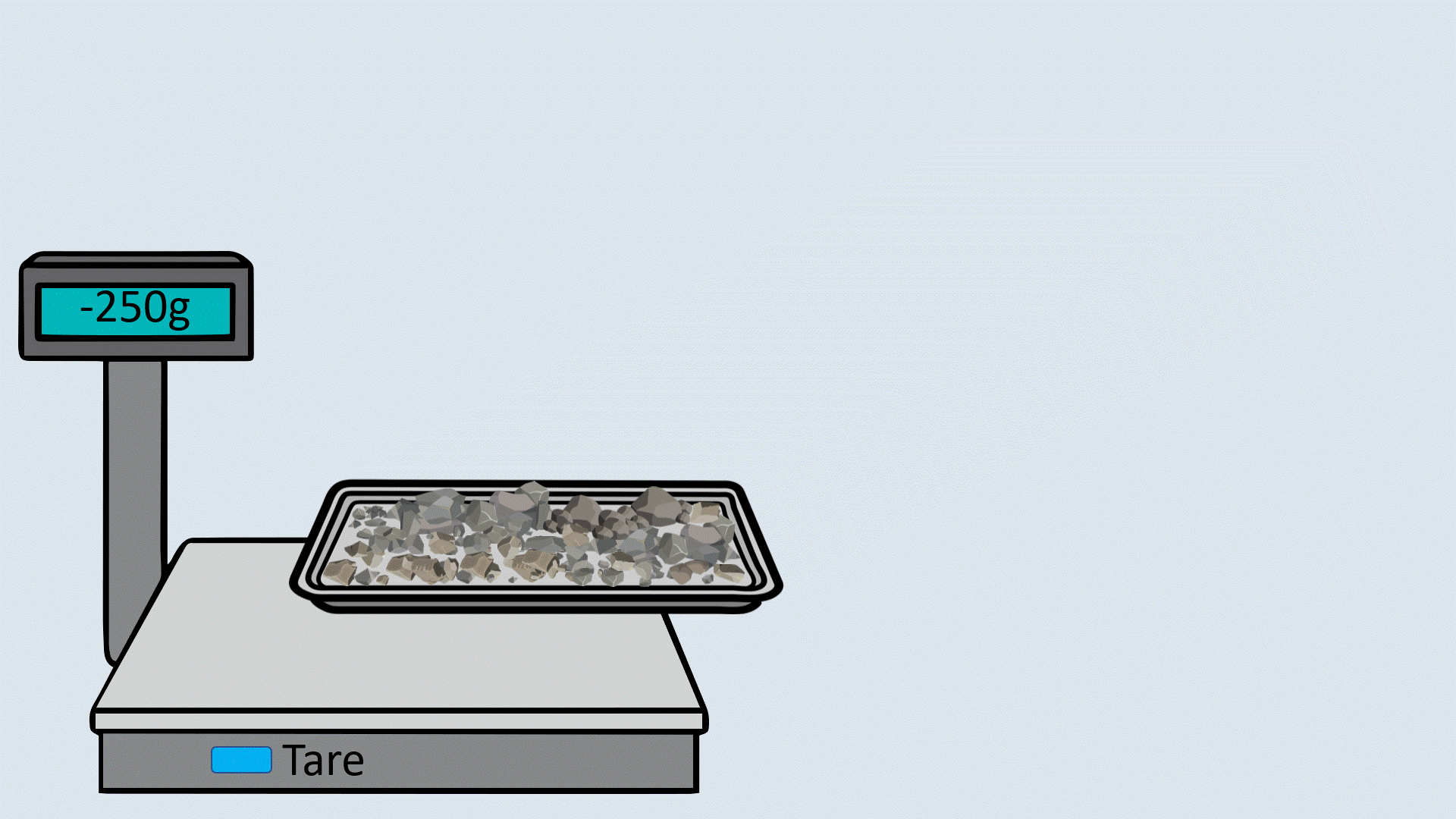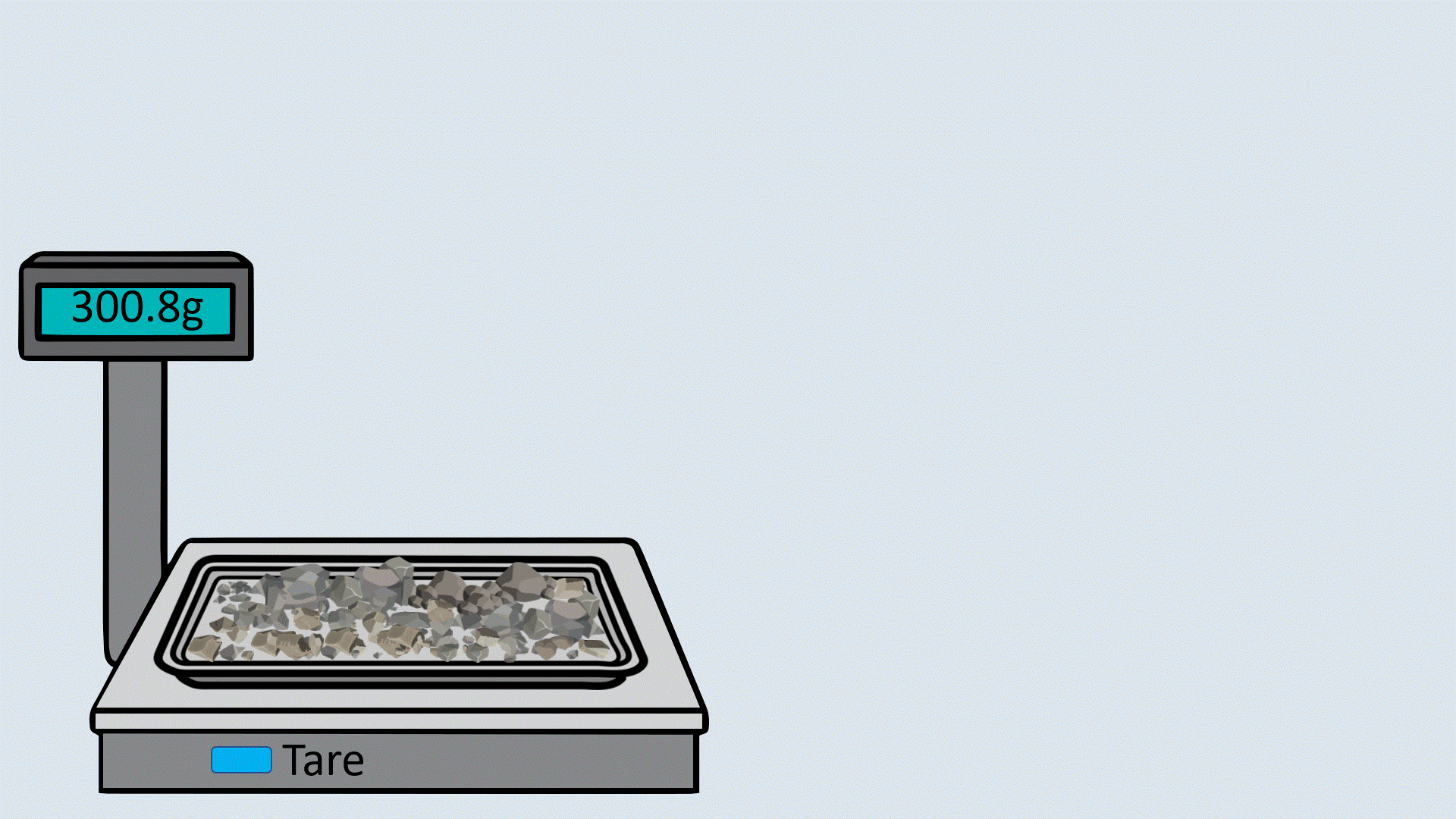
Take sufficient quantity of aggregate in the tray and weigh them.

Step
7
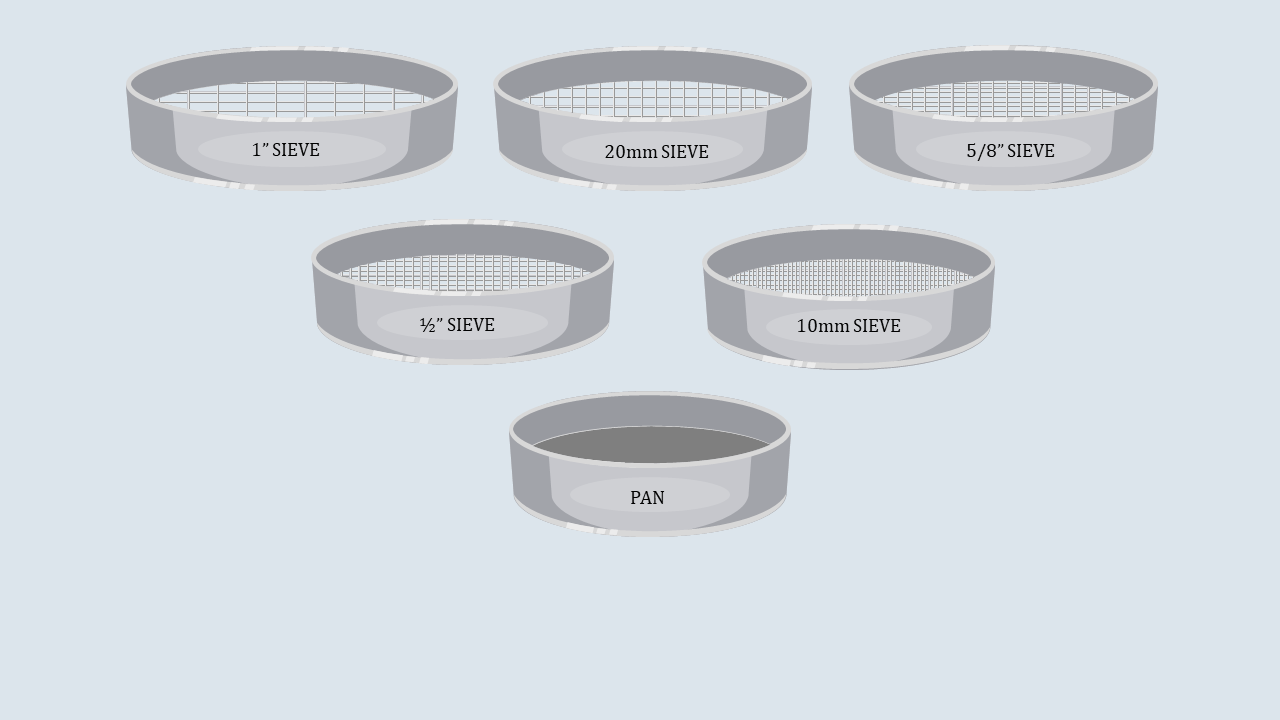
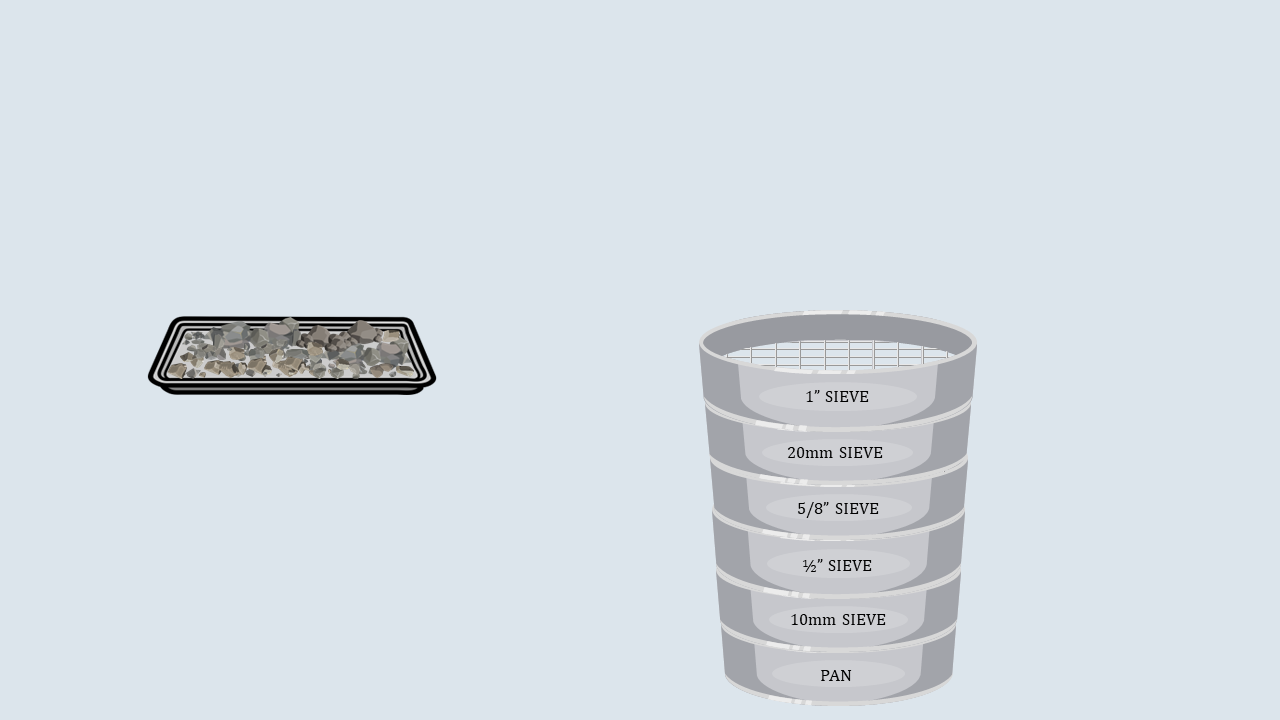
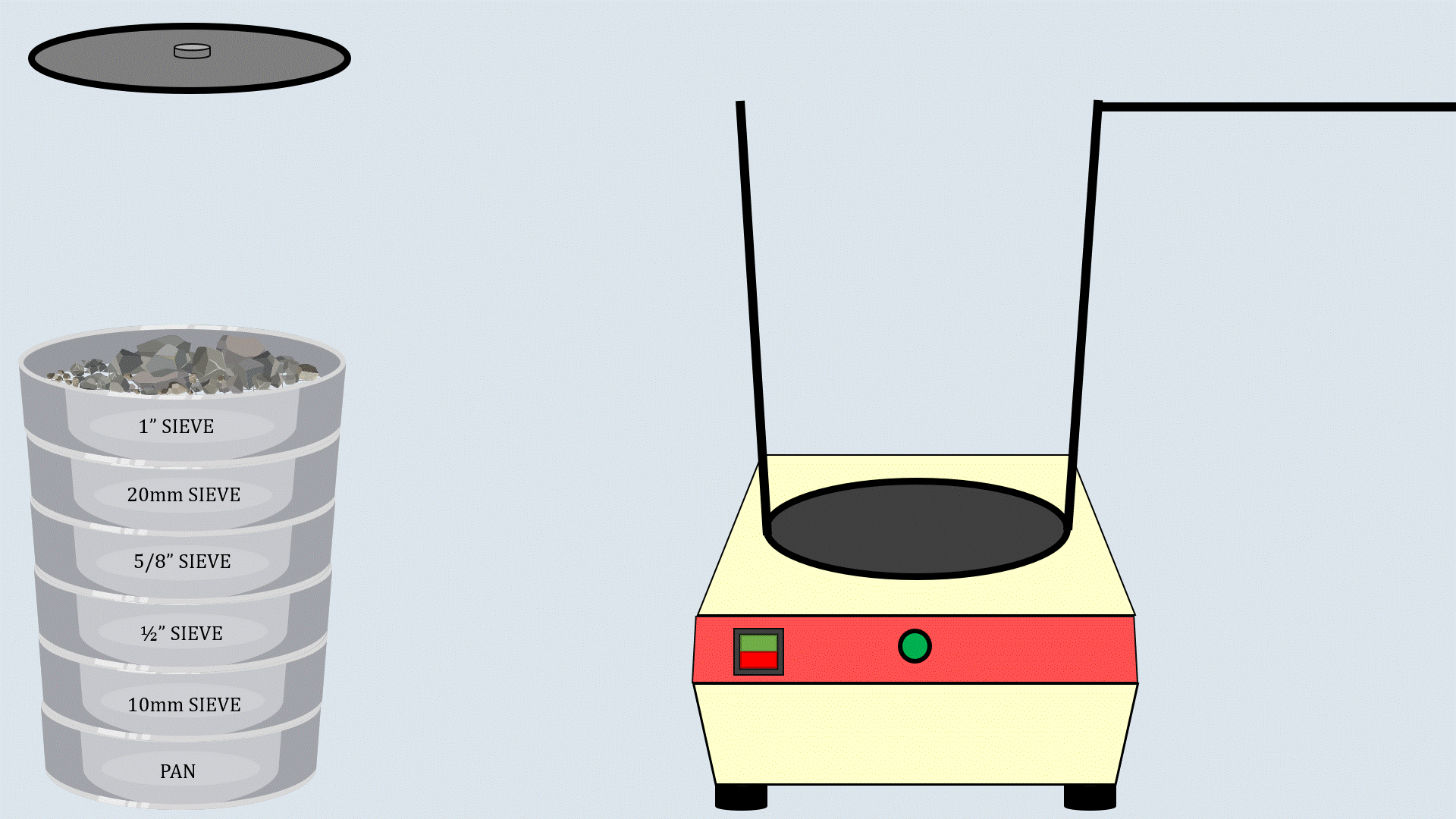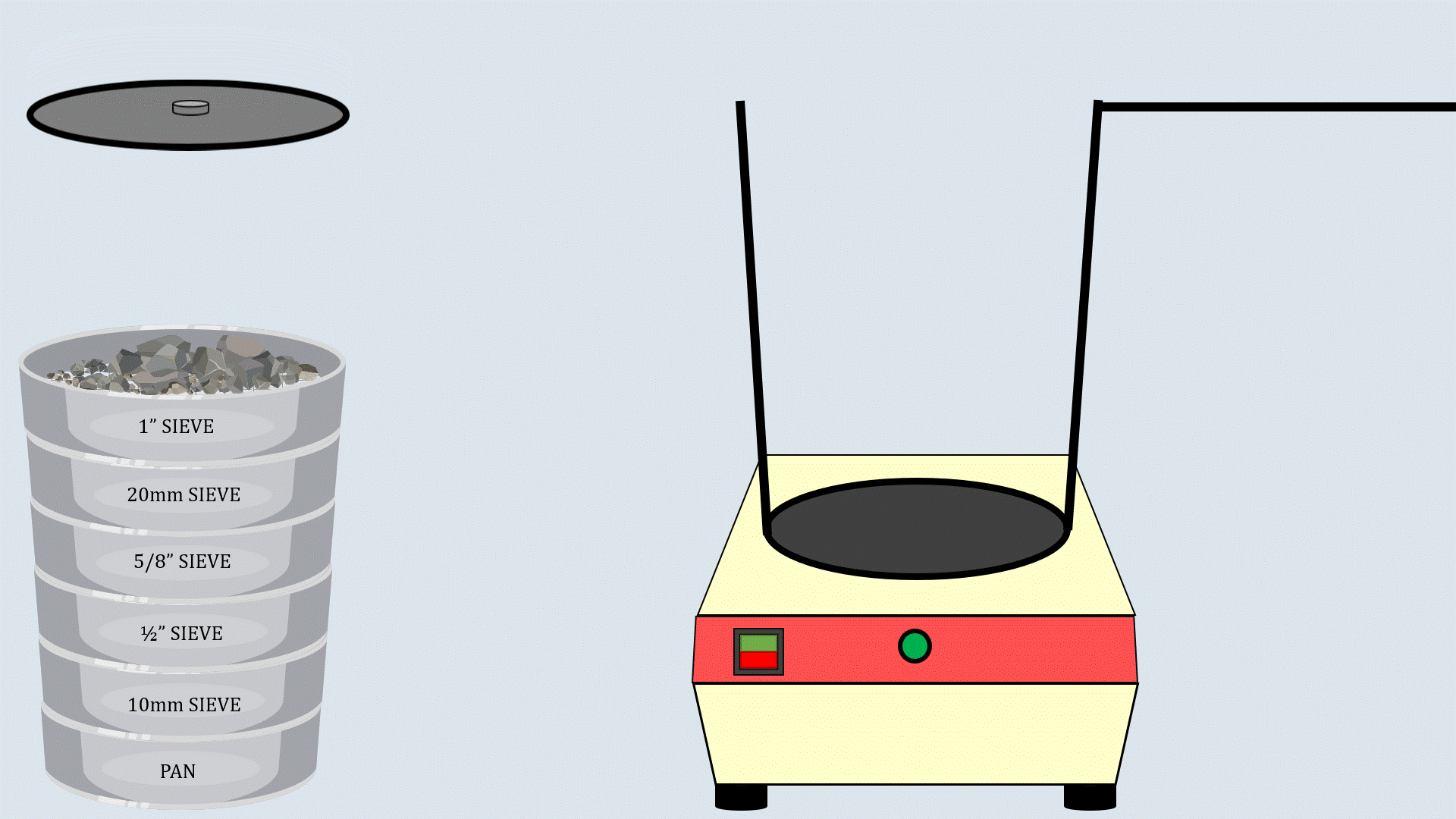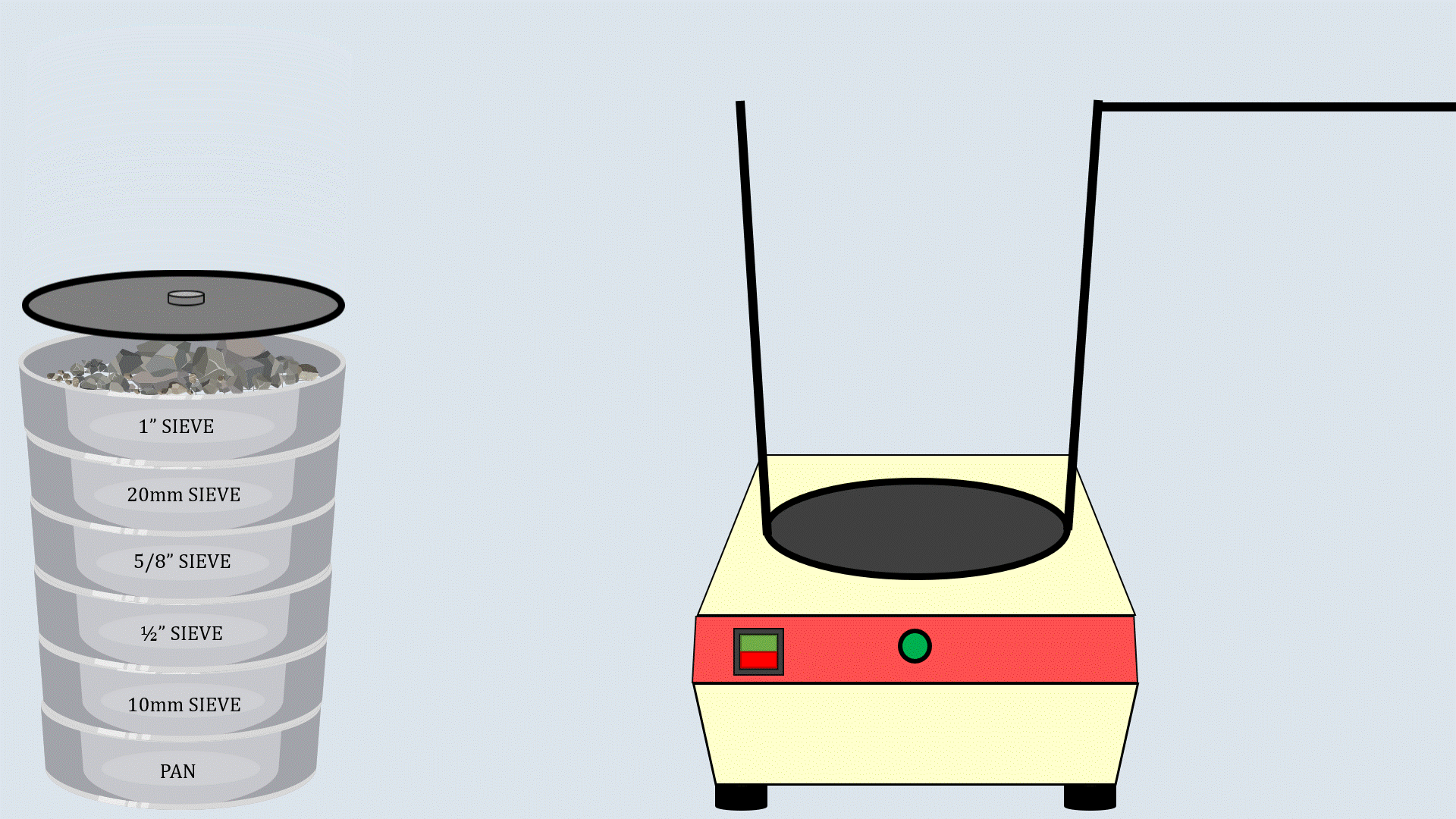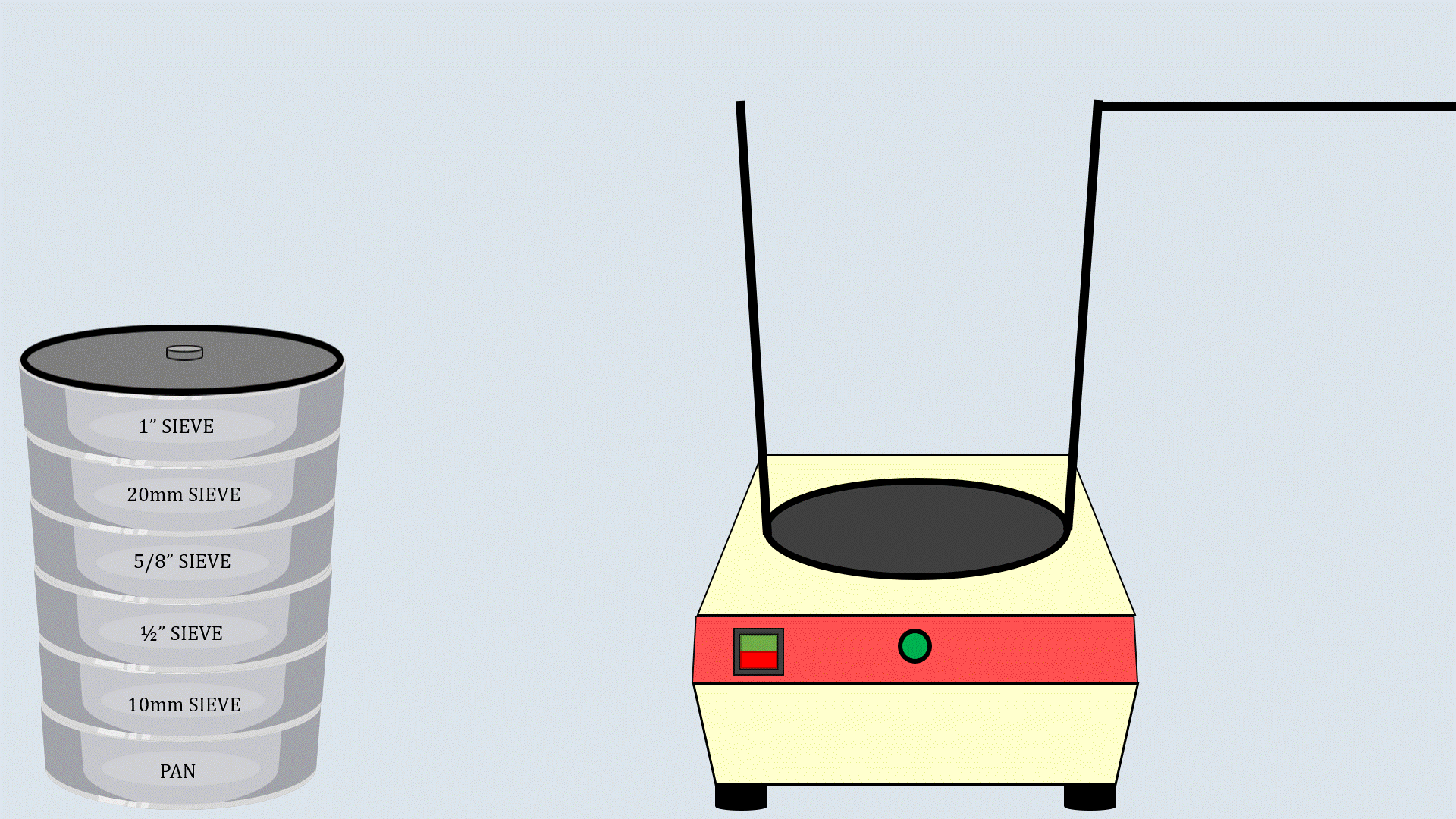
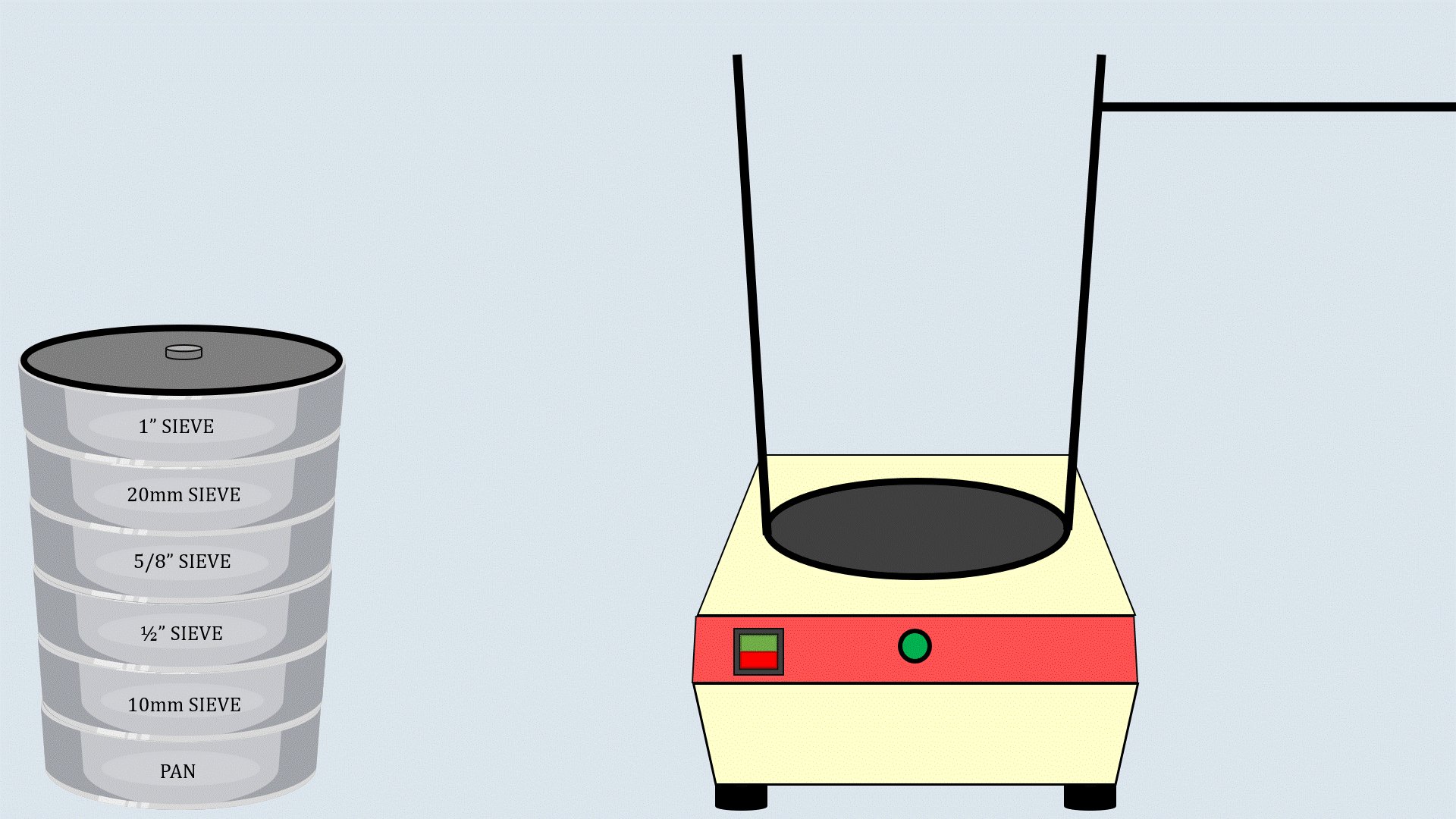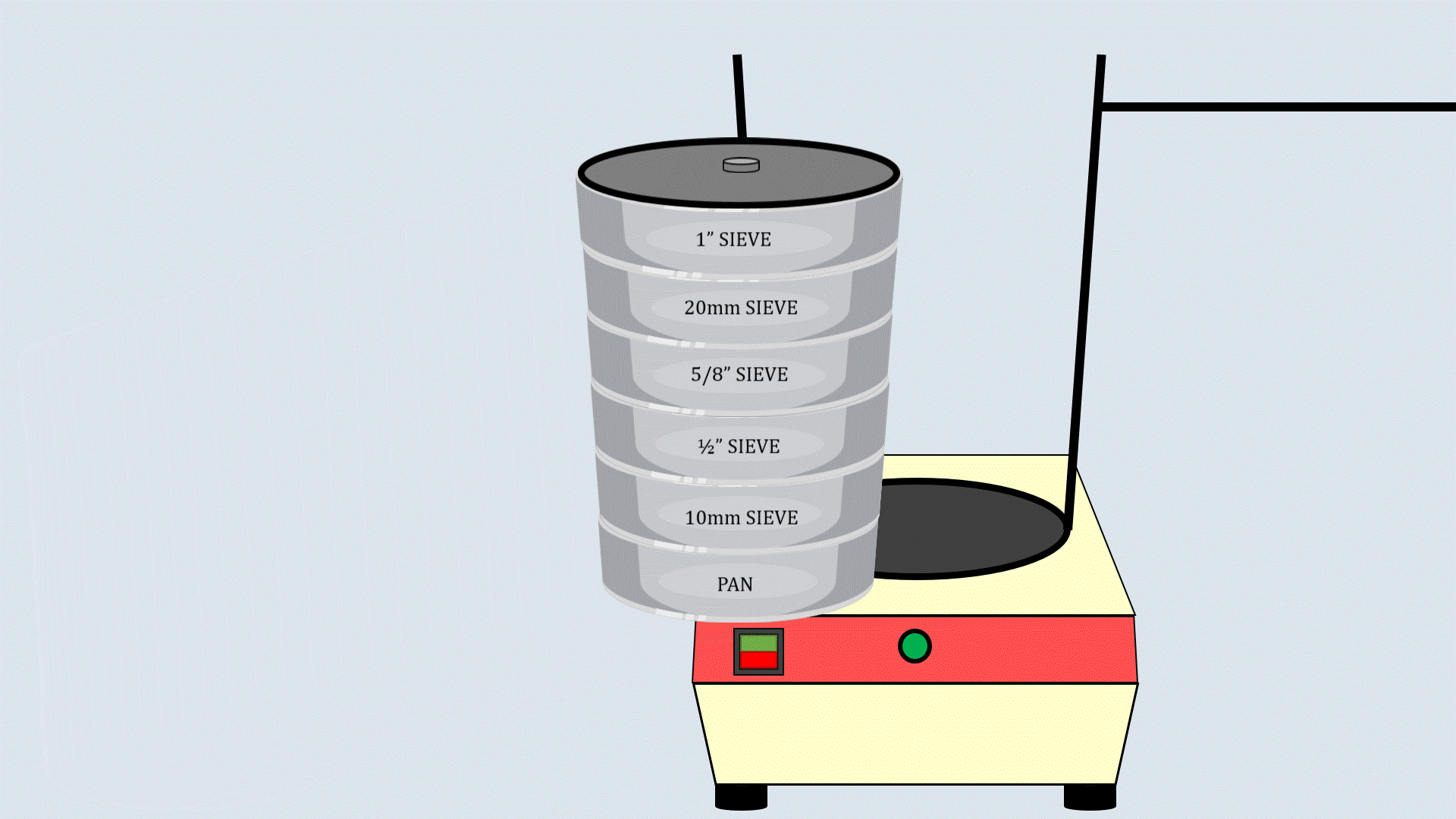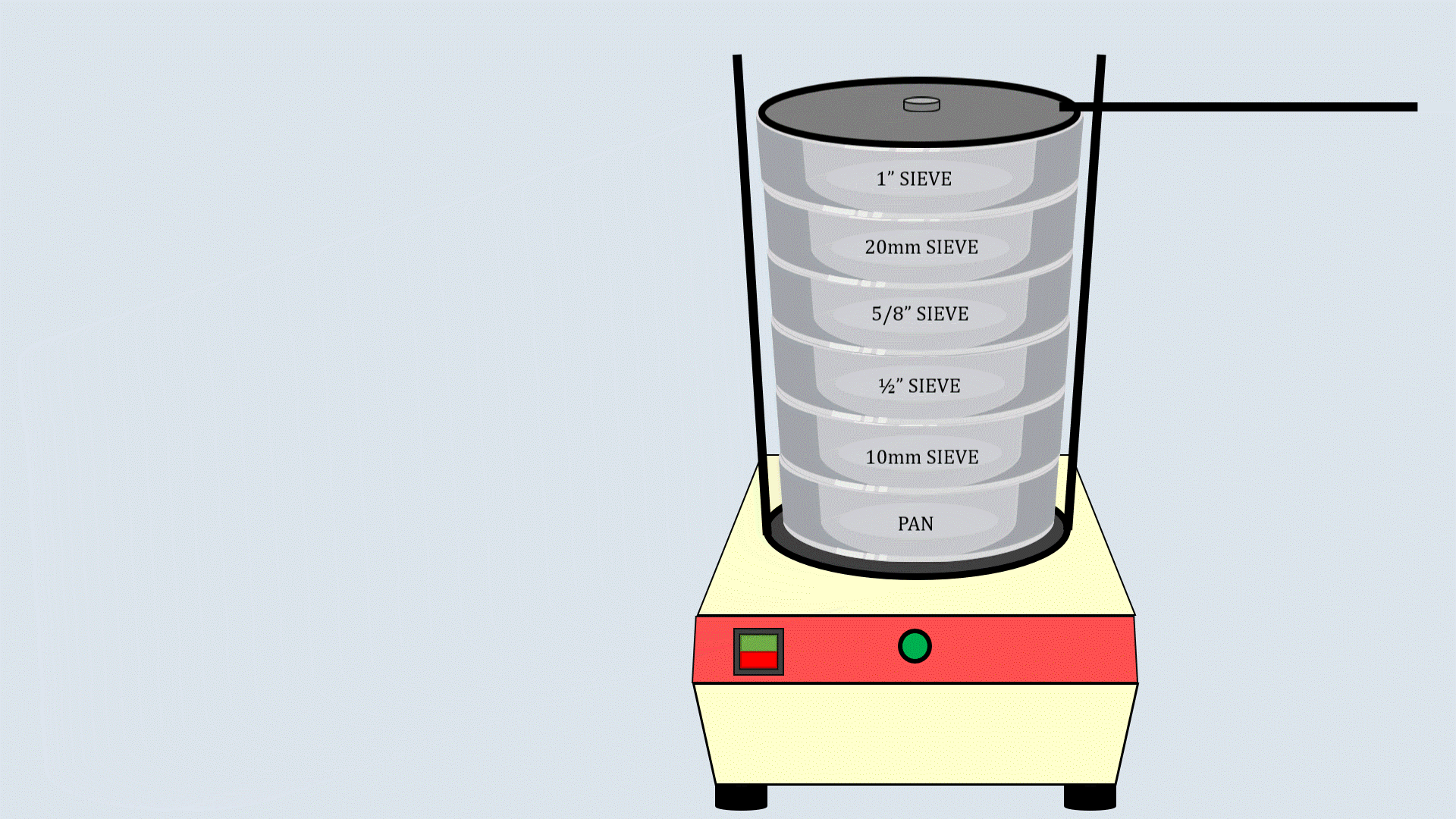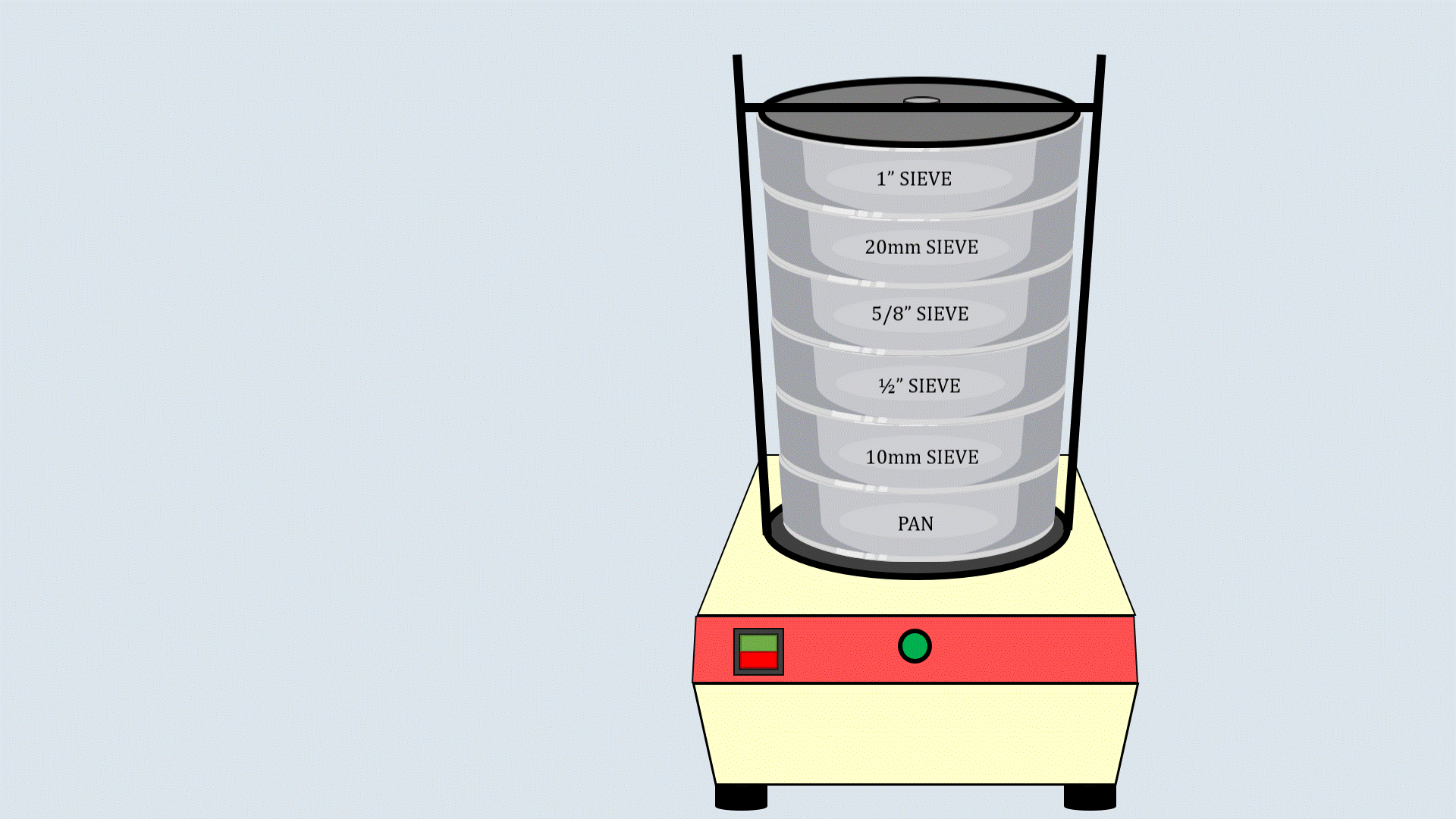
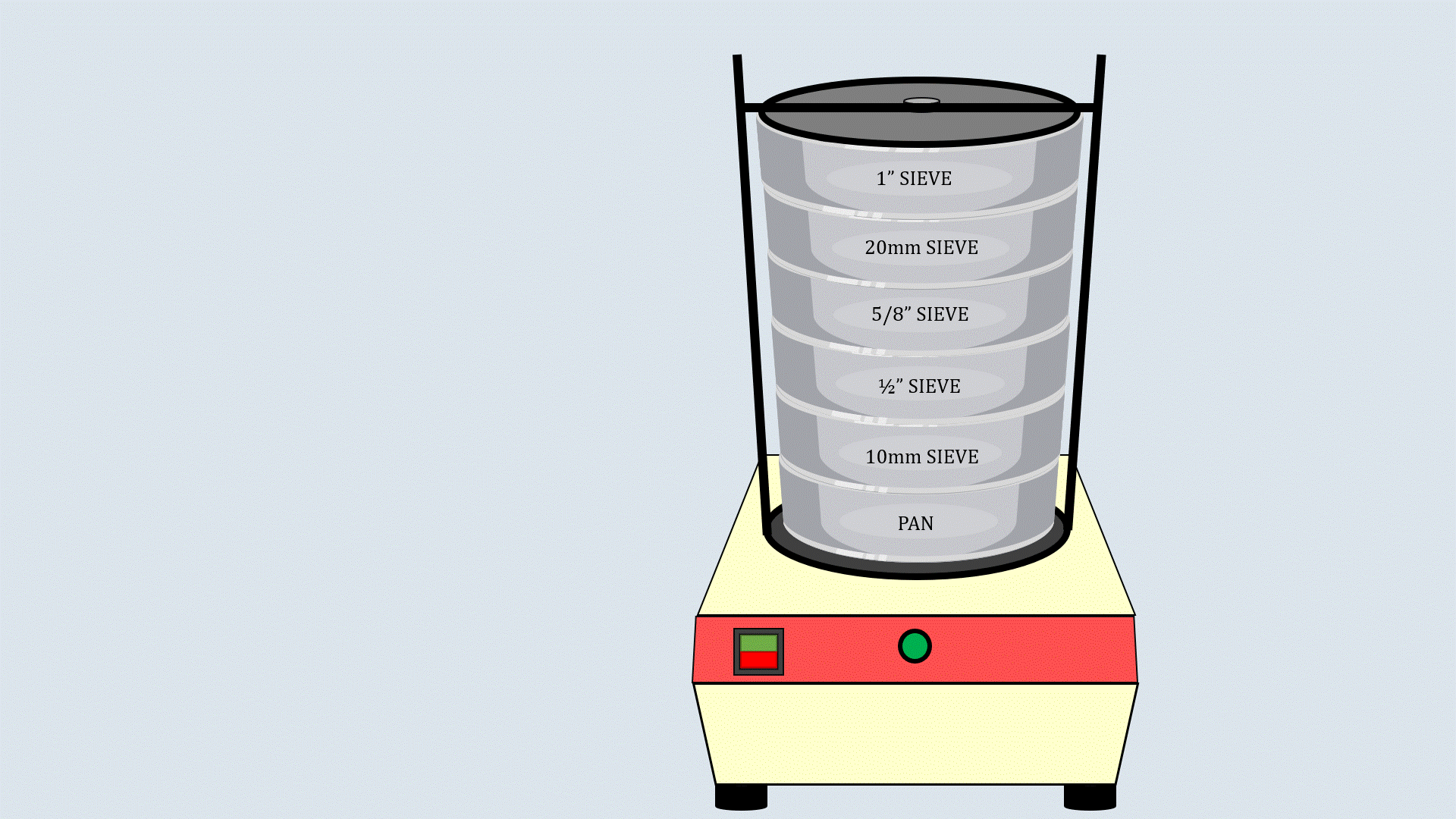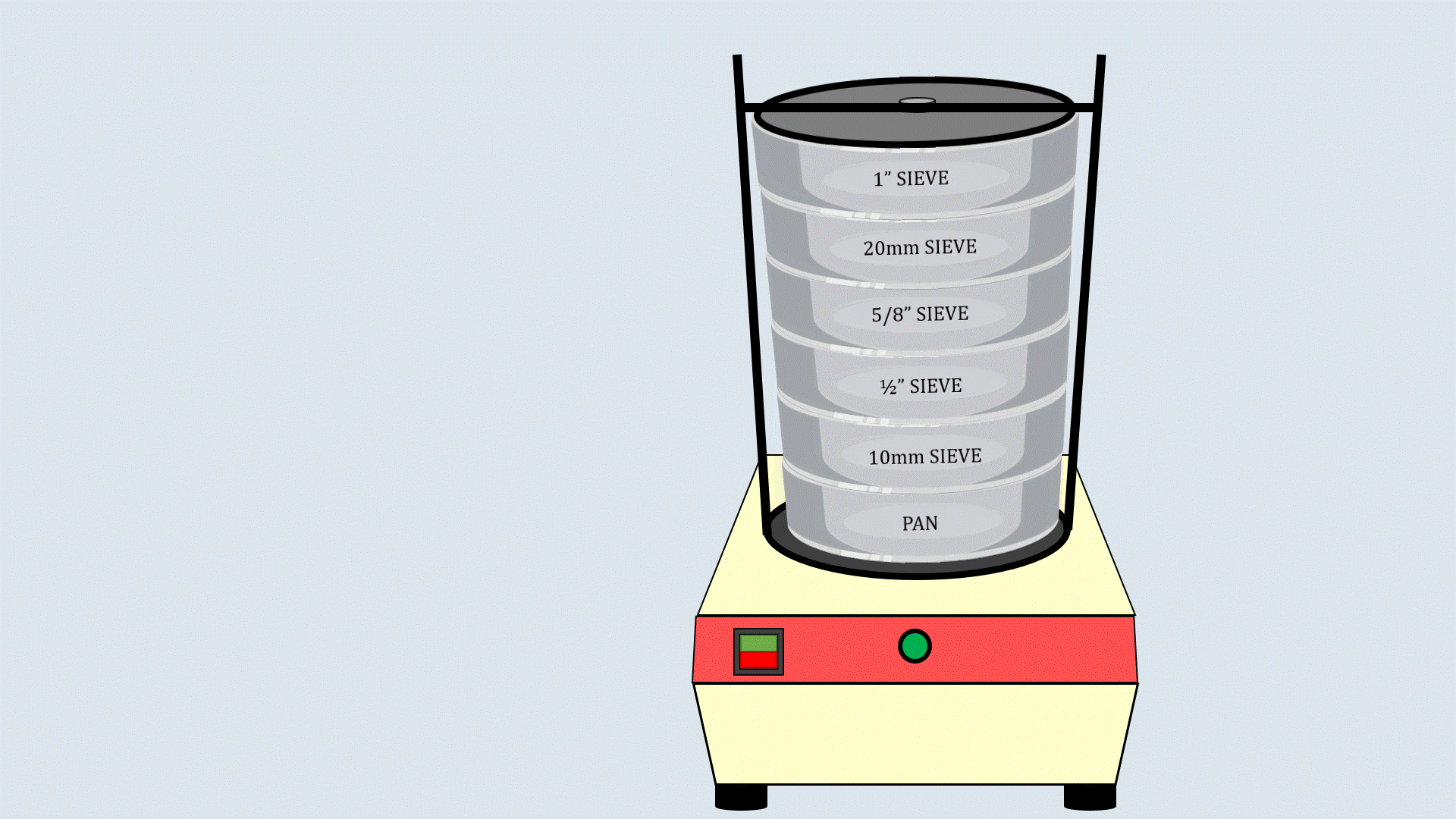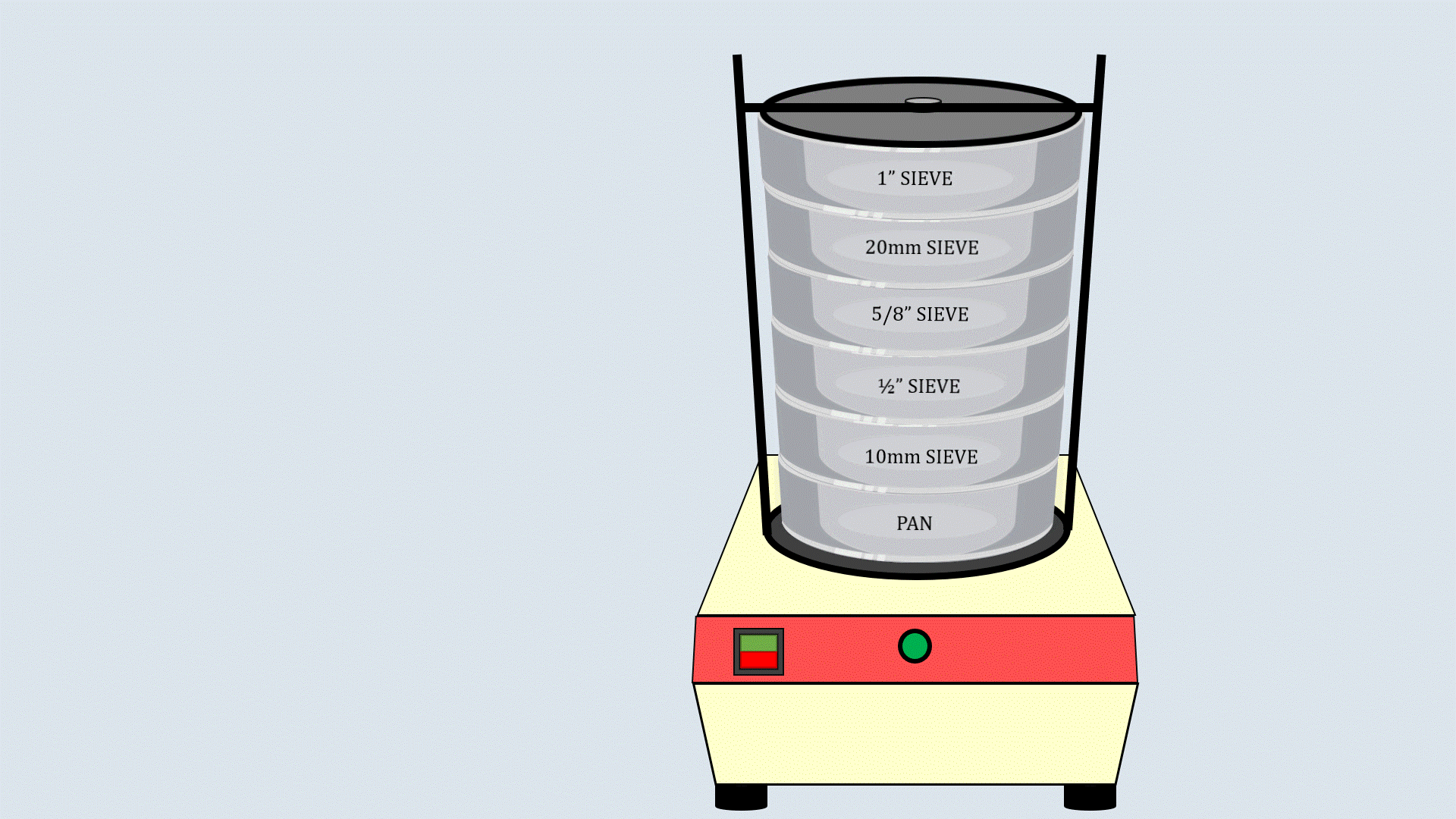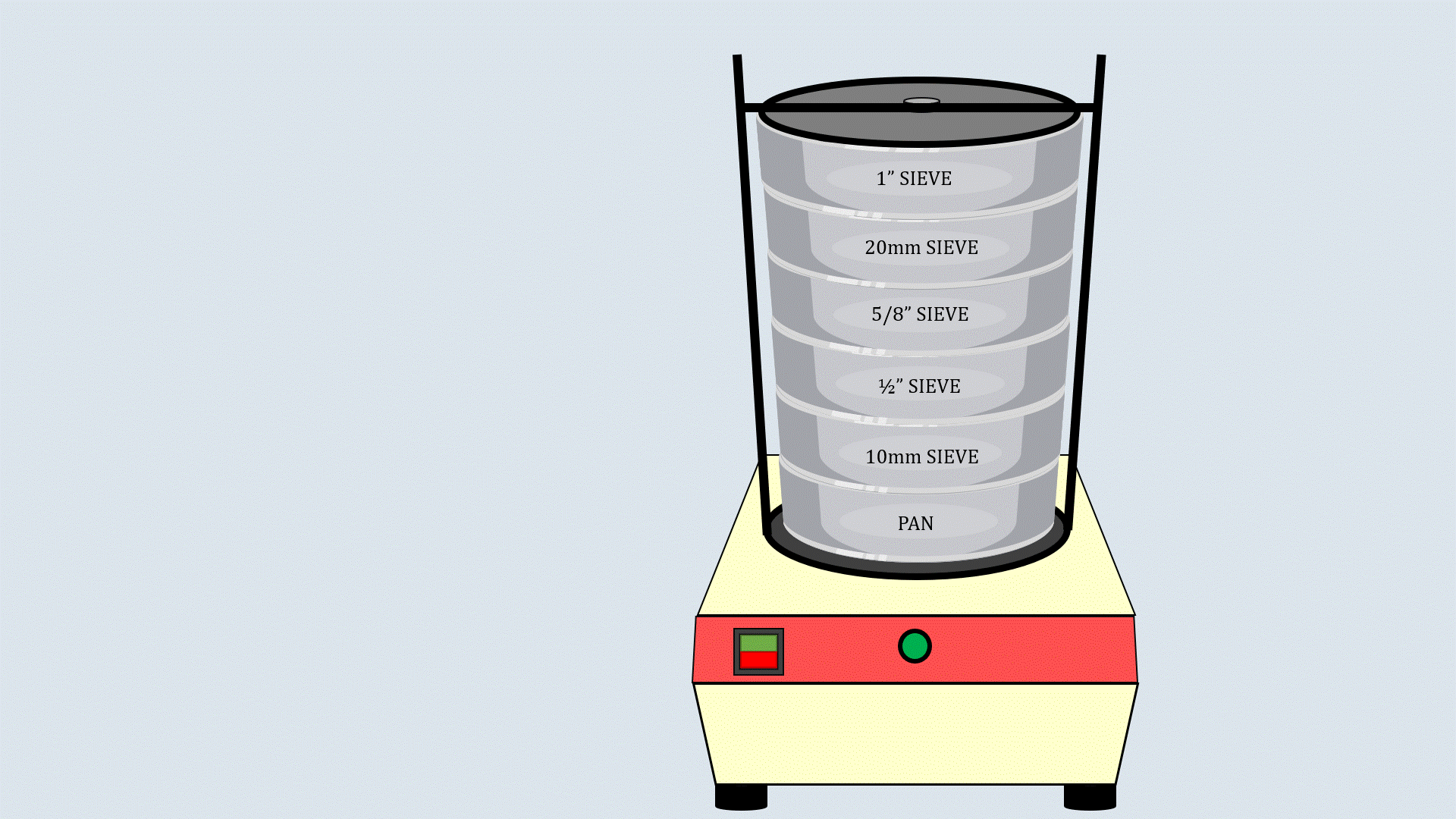
Arrange the sieves in descending order, with the
largest aperture size at the top and the smallest one at the
bottom and place a pan below the lower most sieve.

Step
8
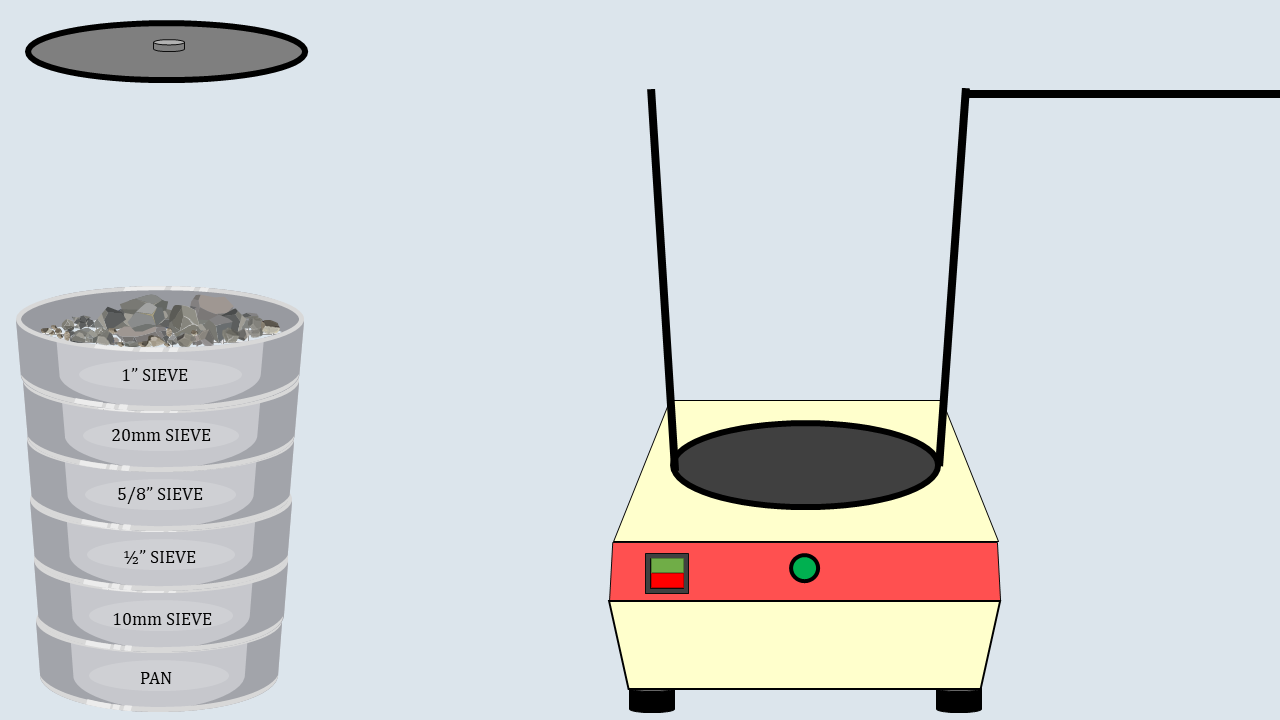
Now, put the weighed aggregates on the sieve
stack.



Step
9
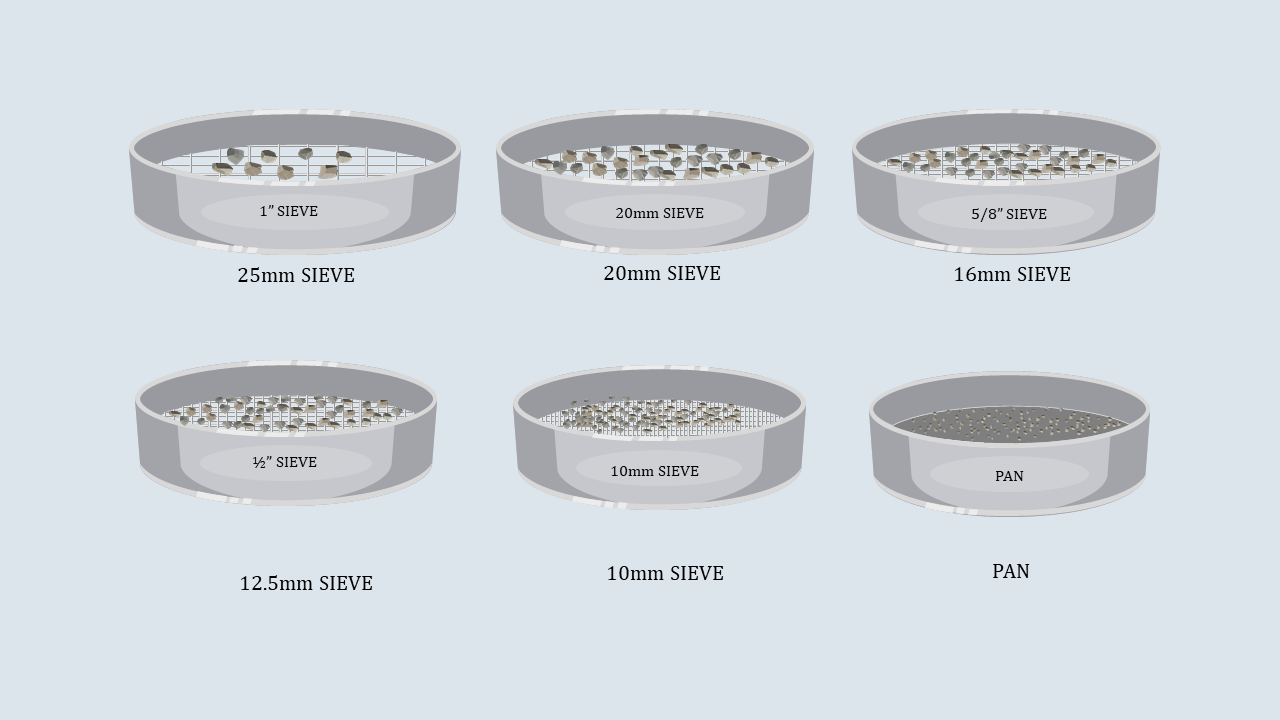
Cover the sieve stack with the lid and place it on the
sieve shaker. Start the sieve shaker, and after some time,
remove the sieves and record the aggregates collected in
each sieve.





Step
10
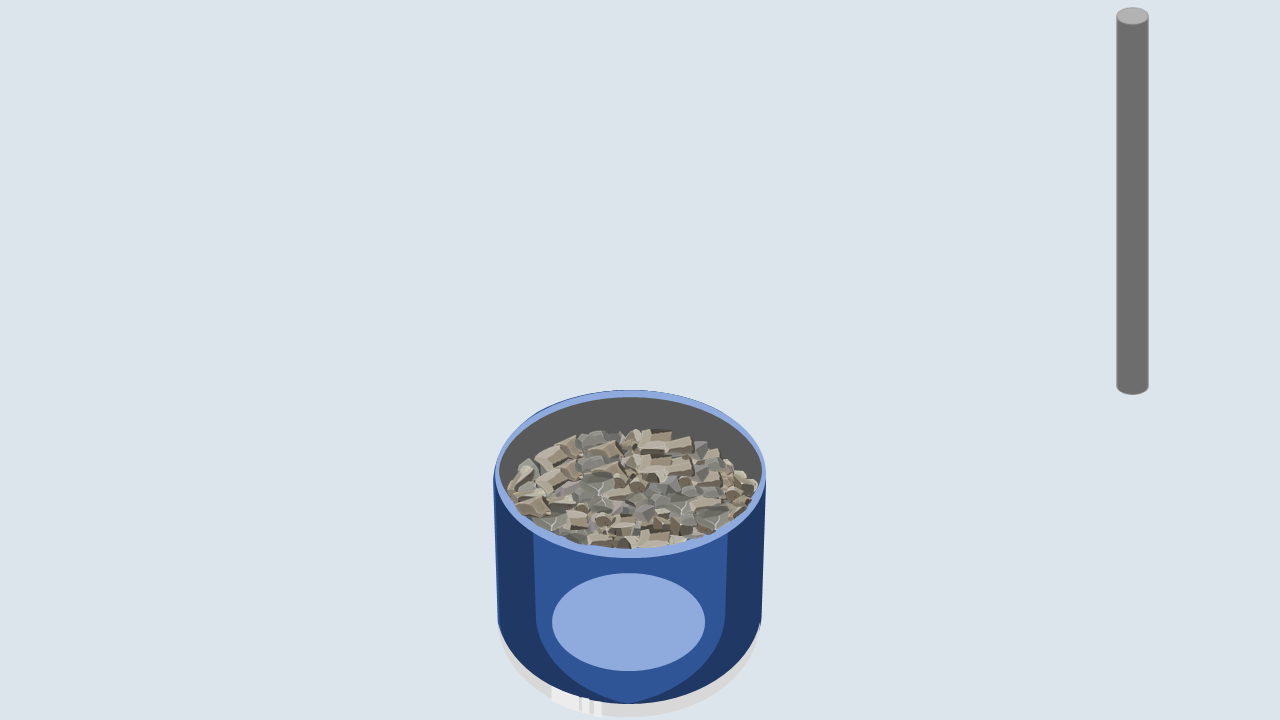
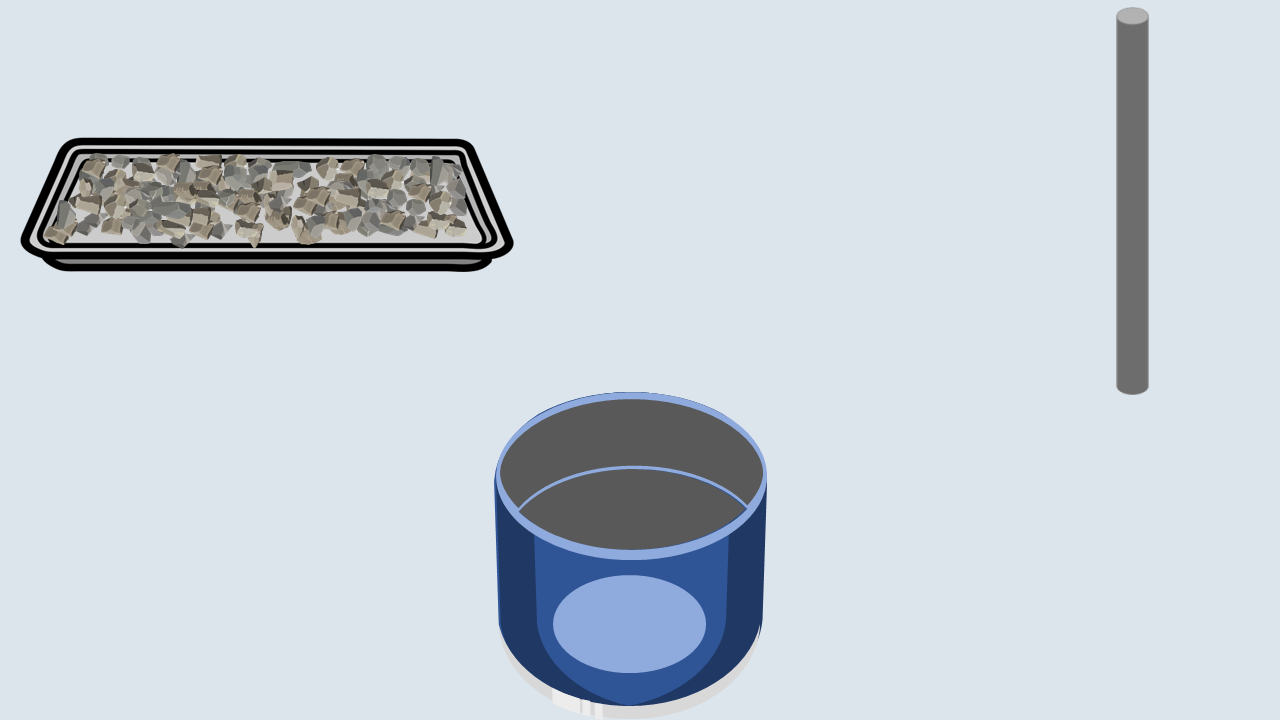
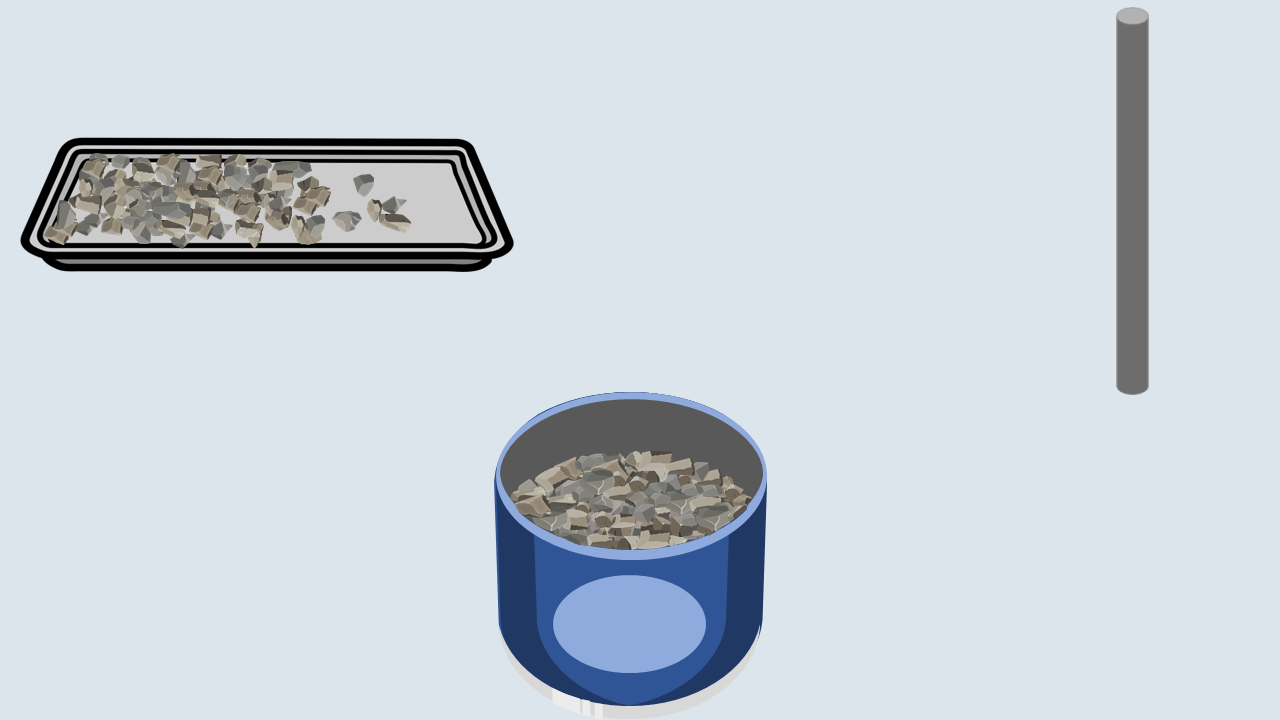
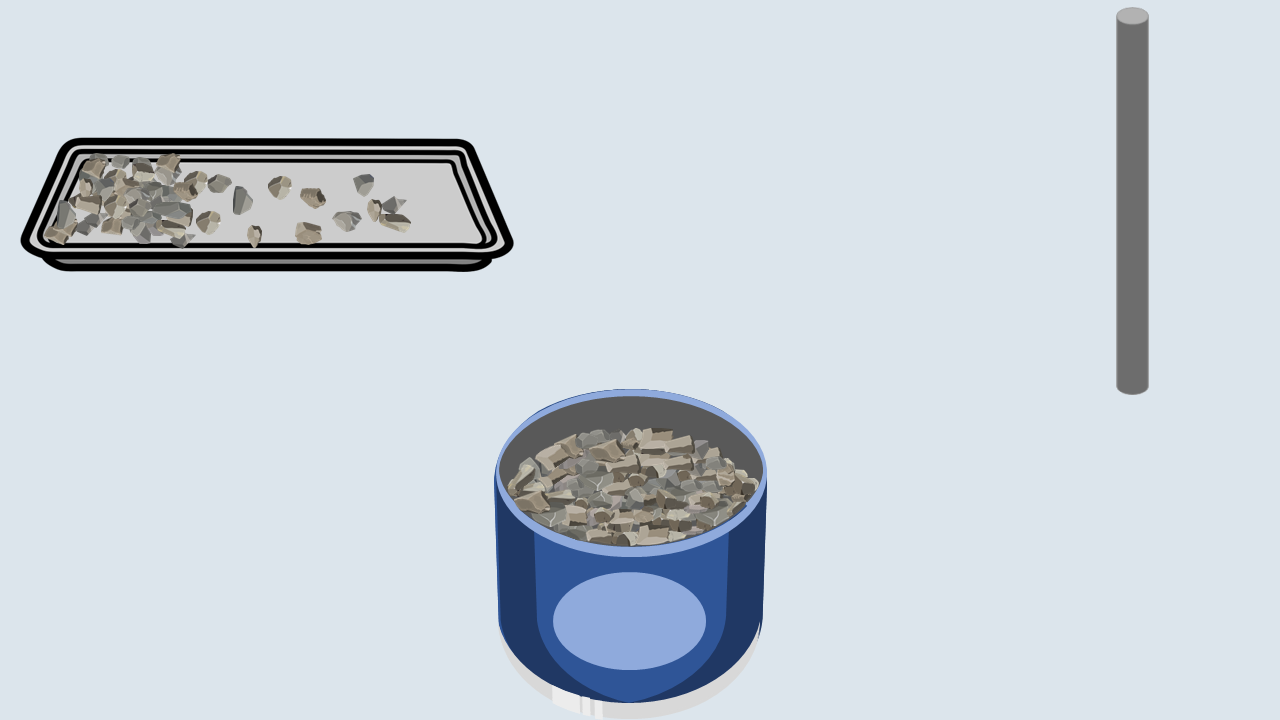
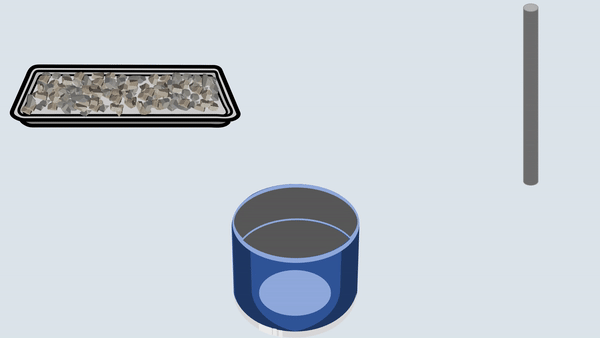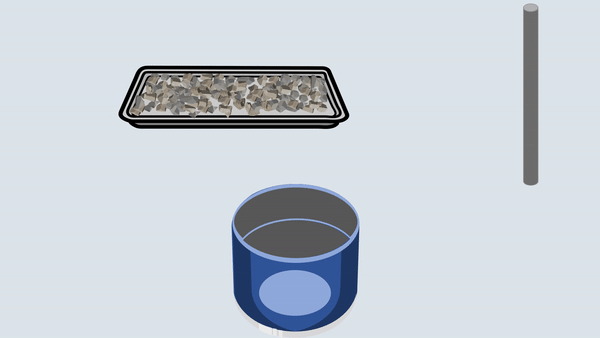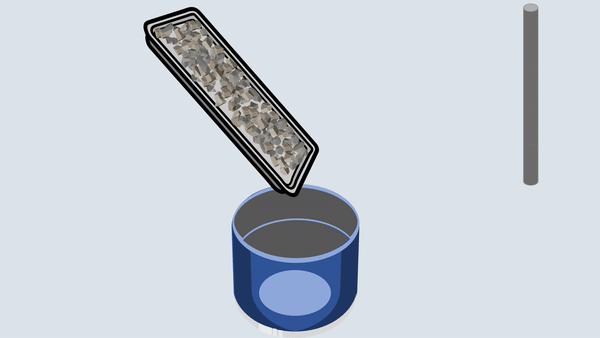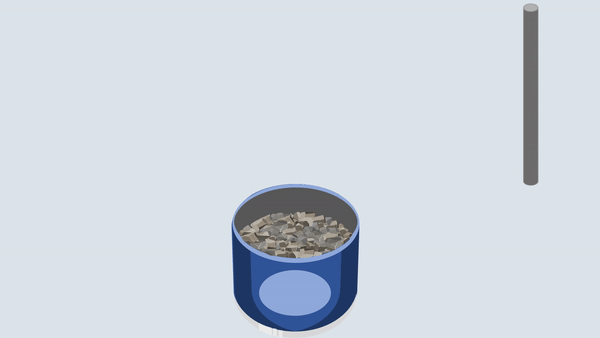
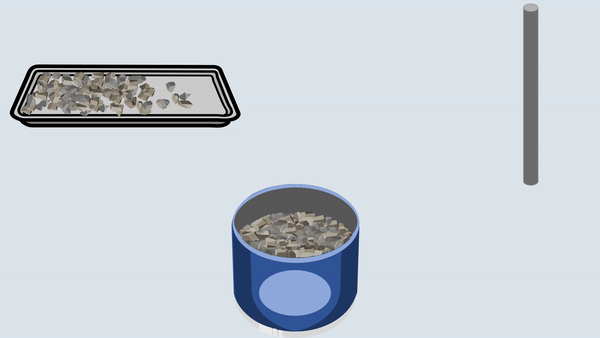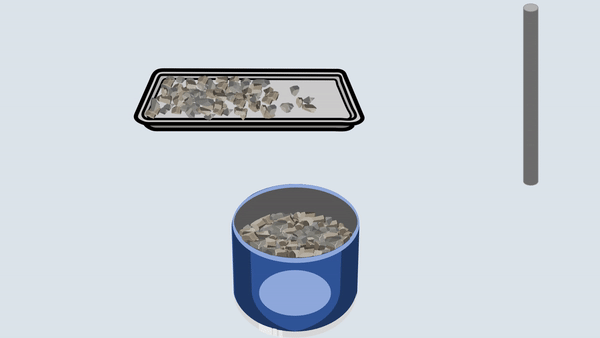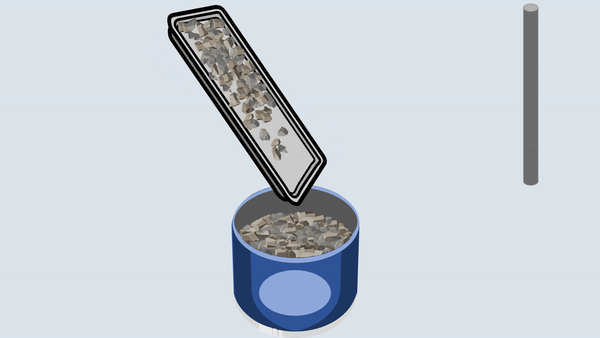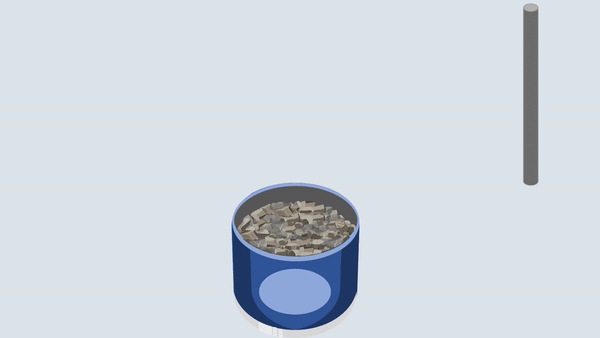
Fill the aggregate in the metal cylinder in three layers. Compact each layer uniformly by giving 100 blows using a tamping rod and then remove off the excess aggregate with the tamping rod.














Step
11
Weigh the aggregates with the cylinder.



Step
12
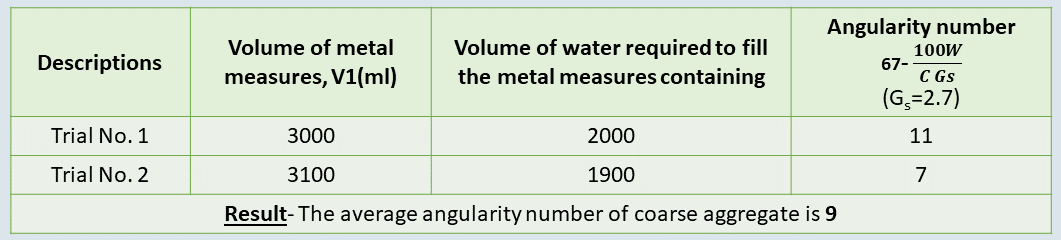
Make three separate descriptions and determine the average weight of aggregates in the cylinder.
Repeat the same procedure for the second set of observations. Conclusion- According to IS: 2386 (Part 1)-1963, the given sample of coarse aggregate can be considered suitable for construction purposes. The general range of angularity number for aggregate used in construction is 0-11. More is the angularity number, less workable is the concrete mix. 


|